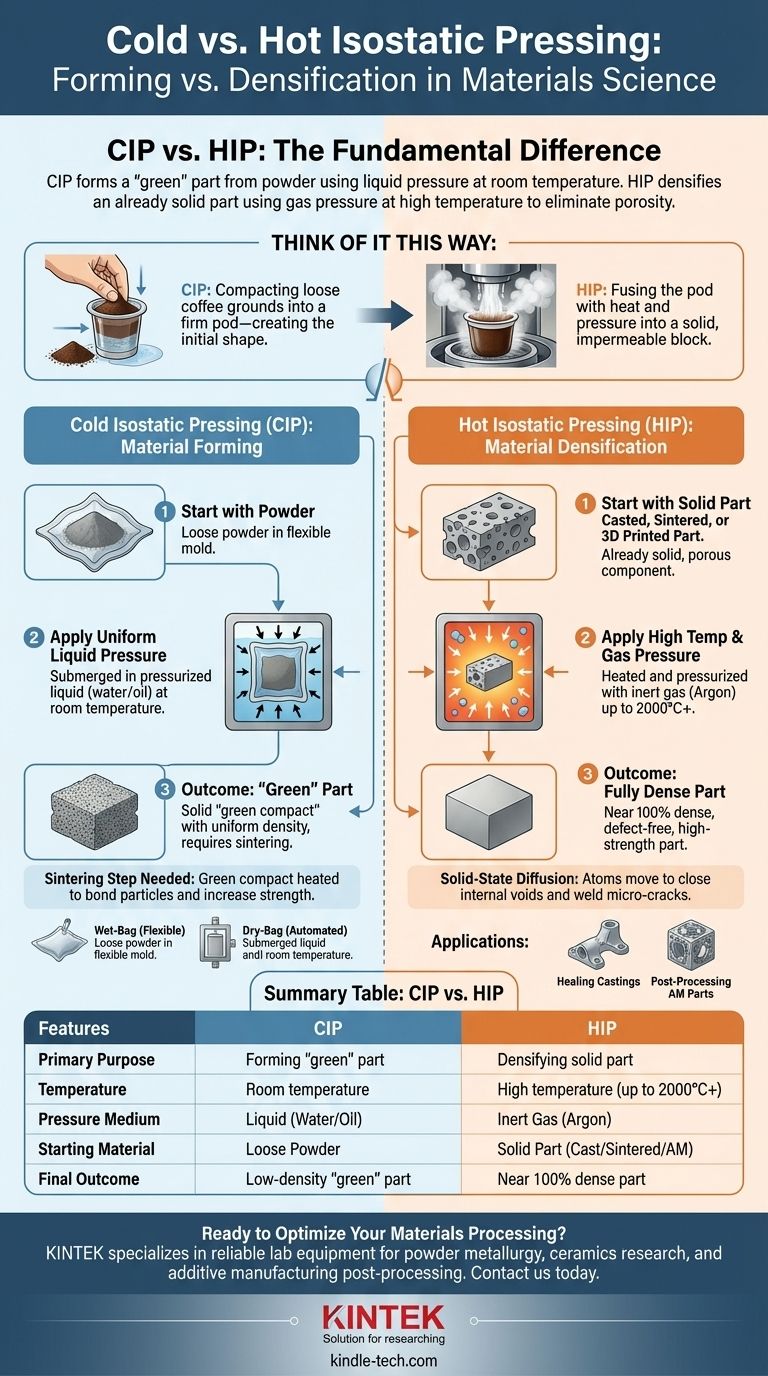
The fundamental difference between cold and hot isostatic pressing lies in their purpose and timing within the manufacturing process. Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) uses liquid pressure at room temperature to form a solid "green" part from powder. In contrast, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) uses gas pressure at high temperatures to eliminate internal porosity and fully densify a part that is already solid.
Think of it this way: CIP is like compacting loose coffee grounds into a firm pod—it creates the initial shape. HIP is like taking that pod and using heat and pressure to fuse the grounds together into a single, solid, impermeable block.
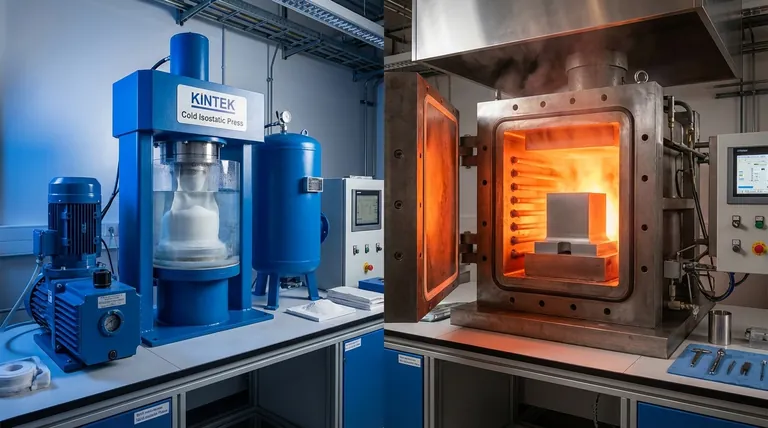

What is Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)?
Cold Isostatic Pressing is a material forming process. Its primary goal is to take a loose powder and compact it into a solid shape with uniform density.
The Core Principle: Forming Under Uniform Pressure
In CIP, a powder is placed inside a flexible, sealed mold (often made of rubber or urethane). This mold is then submerged in a liquid-filled high-pressure chamber.
The liquid, typically water or oil, is pressurized, exerting equal force on all surfaces of the mold. This uniform pressure compacts the powder into a coherent mass.
The "Green" Part Outcome
The result of CIP is a "green compact." This part is solid enough to be handled and machined, but it has not yet reached its final strength or density. It still contains significant porosity between the powder particles.
The Necessary Next Step: Sintering
To achieve final strength, a green compact from CIP must undergo a subsequent heating process called sintering. During sintering, the part is heated to a high temperature (below its melting point), causing the powder particles to bond and fuse together, which increases density and strength.
Wet-Bag vs. Dry-Bag CIP
CIP itself has two main variations based on how the mold is handled:
- Wet-Bag: The mold is manually filled, sealed, and submerged in the pressure fluid for each cycle. This method is flexible and ideal for complex shapes and small production runs.
- Dry-Bag: The mold is integrated into the pressure vessel itself. The powder is poured in, pressed, and ejected in a more automated process, making it suitable for simpler shapes and high-volume production.
What is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)?
Hot Isostatic Pressing is a material densification and defect-healing process. It is not used to form a shape from loose powder, but rather to perfect an already solid component.
The Core Principle: Densification at Temperature
HIP places a pre-formed solid part inside a vessel that is then filled with a high-pressure inert gas, typically Argon. The vessel is simultaneously heated to extremely high temperatures.
The Starting Material: Already Solid
Critically, HIP is applied to parts that are already solid. This includes components made by casting, additive manufacturing, or parts previously formed by CIP and then sintered.
The Outcome: Eliminating Porosity
The combination of intense heat and uniform gas pressure causes the material's atoms to move and diffuse, a process called solid-state diffusion. This closes and welds shut any internal voids, pores, or micro-cracks within the component.
The result is a part that approaches 100% of its theoretical maximum density, dramatically improving its mechanical properties like fatigue life, ductility, and fracture toughness. This is why it is essential for high-performance applications like jet engine turbines and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Process Comparison
The choice between CIP and HIP is not a choice between alternatives, but a decision about which manufacturing step is needed for your goal.
Purpose: Forming vs. Finishing
CIP is a forming process used at the beginning of a part's life to create its basic shape from powder. HIP is a finishing process used at the end to perfect a solid part's internal structure.
Temperature and Pressure Medium
CIP operates at or near room temperature using a liquid to transmit pressure. HIP operates at very high temperatures using an inert gas to transmit pressure.
Material State: Powder vs. Solid
CIP starts with powder in a flexible mold. HIP starts with a solid part.
Final Density and Strength
CIP alone produces a low-strength "green" part that requires sintering. HIP produces a fully dense, high-strength part by eliminating residual porosity from an already solid component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex part from a powder: Your process will involve Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) to form the shape, followed by sintering to strengthen it.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the reliability of a critical casting: Use Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) as a post-processing step to heal internal casting defects and achieve full density.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible performance from a powder metallurgy component: Use a multi-step process: CIP to form the green part, followed by sintering, and then HIP as a final step to eliminate any remaining porosity.
Ultimately, your choice depends entirely on whether you are creating a new shape from powder or perfecting the internal quality of an existing solid part.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Forming a "green" part from powder | Densifying an existing solid part |
| Temperature | Room temperature | High temperature (up to 2000°C+) |
| Pressure Medium | Liquid (water/oil) | Inert gas (Argon) |
| Starting Material | Loose powder | Solid part (cast, sintered, or 3D printed) |
| Final Outcome | Low-density "green" part requiring sintering | Near 100% dense, high-strength part |
| Typical Applications | Creating complex shapes from powder | Healing defects in castings, improving AM parts |
Ready to Optimize Your Materials Processing?
Whether you need to form complex parts from powder with Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) or achieve maximum density and performance with Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's needs.
We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for:
- Powder metallurgy and ceramics research
- Additive manufacturing post-processing
- High-performance materials development
Contact us today to discuss how our isostatic pressing solutions can enhance your material properties and streamline your manufacturing process.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What's the difference between cold press and regular press? Choosing Between Quality and Efficiency
- Purpose of CIP in c-LLZO ceramic pellets? Achieve >90% Density & Superior Uniformity with Cold Isostatic Pressing
- What are the considerations of powder metallurgy? Key Factors for Manufacturing Success
- What is isostatic pressing in powder metallurgy? Unlock Superior Part Density and Complexity
- What is the process of CIP and HIP? Forming vs. Densifying for Superior Materials



















