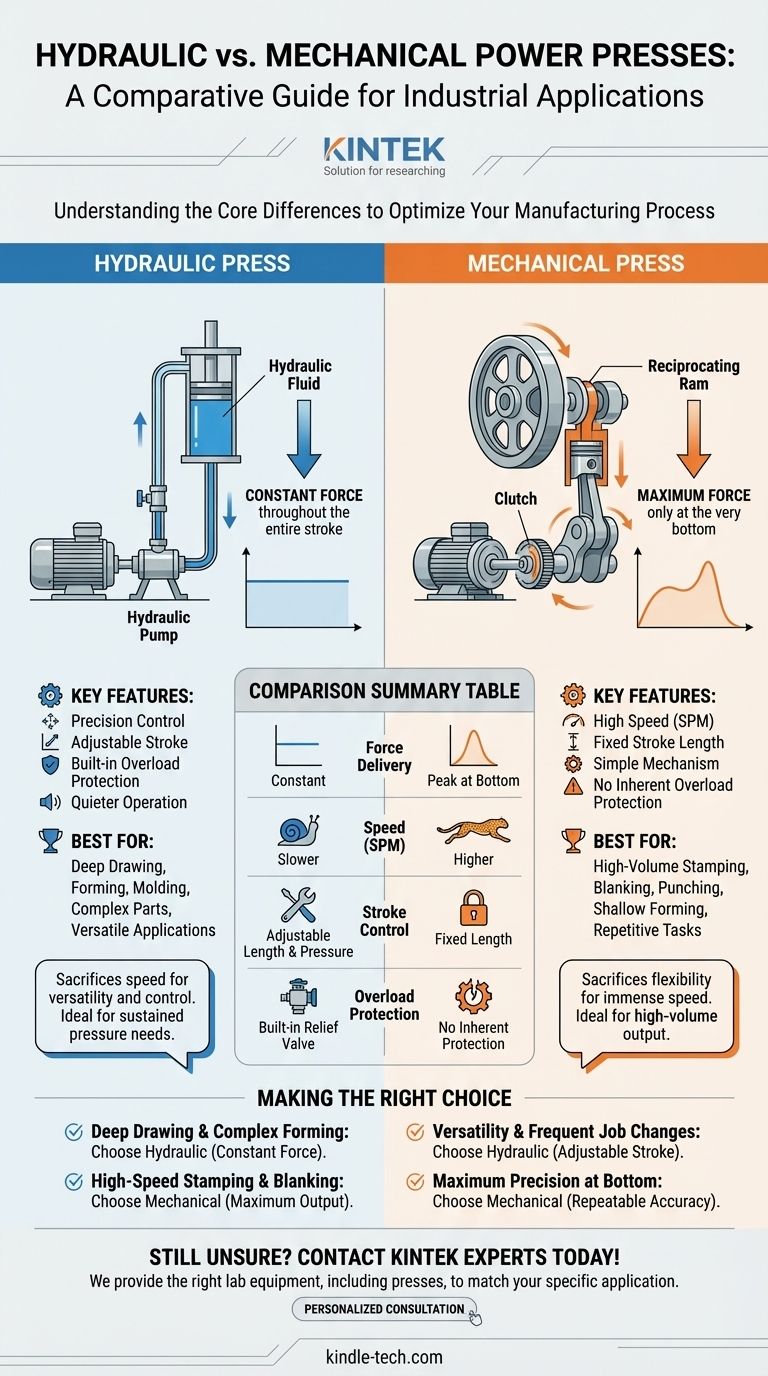
At their core, the difference between a hydraulic and a mechanical power press lies in how they generate and deliver force. A hydraulic press uses pressurized fluid to move a piston, delivering constant force throughout its entire stroke. In contrast, a mechanical press uses a motor-driven flywheel and crankshaft to move a ram, delivering its maximum force only at the very bottom of its fixed stroke.
The choice is not about which press is universally better, but which tool's method of applying force aligns with your specific industrial application. Hydraulic presses offer control and constant force, while mechanical presses offer speed and precision for high-volume, repetitive tasks.

The Fundamental Difference: How Force is Generated
To choose the right machine, you must first understand the core principle that separates them. Their names reveal their mechanisms.
Hydraulic Presses: Constant Force Through Fluid Pressure
A hydraulic press operates on the principle of Pascal's law. An electric motor powers a pump that pressurizes hydraulic fluid (typically oil).
This pressurized fluid is then forced into a cylinder, pushing a piston down with tremendous force. The key characteristic is that full tonnage is available at any point in the stroke, from the top to the bottom.
This system provides exceptional control over pressure and stroke length, and because it has fewer moving parts, it tends to be significantly quieter.
Mechanical Presses: Variable Force Through Motion
A mechanical press stores energy from a motor in a massive, spinning flywheel. When activated, a clutch connects the flywheel to a crankshaft.
This crankshaft converts the flywheel's rotational motion into the vertical, reciprocating motion of the ram, much like the pistons in a car engine.
Because of this mechanism, the press only achieves its maximum rated force at the very bottom of the stroke. The force is variable throughout the rest of the ram's travel.
Key Operational Distinctions
The fundamental difference in force generation leads to distinct operational advantages and disadvantages for each type of press.
Force and Stroke Control
Hydraulic presses offer variable stroke length and precise pressure control. You can adjust the ram to return as soon as a specific pressure is met or a certain position is reached, making them highly versatile.
Mechanical presses have a fixed stroke length determined by the eccentricity of the crankshaft. Adjustments are more limited, making them less flexible for jobs with varying requirements.
Speed and Production Rate
Mechanical presses are built for speed. Their simple, cyclical motion allows for significantly higher strokes per minute (SPM), making them the standard for high-volume stamping, blanking, and coining operations.
Hydraulic presses are generally slower. While modern hydraulics are improving in speed, they typically cannot match the raw output rate of a mechanical press for simple, repetitive tasks.
Versatility and Applications
The full, constant force of a hydraulic press makes it the backbone of industries requiring deep drawing, forming, and molding. Applications like forging, bending, and sheet drawing benefit from the sustained pressure.
The high speed and repeatable bottom-of-stroke precision of a mechanical press make it ideal for blanking, punching, and shallow forming in high-volume environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither press is a perfect solution for every problem. The choice involves accepting a set of compromises that best fit your operational needs.
The Hydraulic Press Compromise: Speed for Versatility
While incredibly versatile and controllable, hydraulic presses sacrifice speed. They are also slightly less energy-efficient on shorter strokes, as the pump runs continuously to maintain pressure.
The Mechanical Press Compromise: Flexibility for Speed
You gain immense speed with a mechanical press, but you lose flexibility. The fixed stroke and variable force curve make it unsuitable for jobs that require sustained pressure or have varying depth requirements.
Overload Protection
This is a critical distinction. A hydraulic press has a built-in safety mechanism in its pressure relief valve. If the force exceeds the set tonnage, the valve opens, preventing damage to the press or the tooling.
A mechanical press has no inherent overload protection. If it is overloaded, something will break—often resulting in a catastrophic and expensive failure of the frame or crankshaft.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the primary demands of your manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is deep drawing or forming complex parts: A hydraulic press is the correct choice due to its constant force delivery throughout the entire stroke.
- If your primary focus is high-speed stamping, blanking, or coining: A mechanical press provides the speed and repeatability needed for maximum output.
- If your primary focus is versatility and frequent job changes: The adjustable stroke and pressure of a hydraulic press offer unmatched flexibility.
- If your primary focus is maximum precision at the bottom of the stroke: A mechanical press offers superior repeatability for tasks like coining where bottom-dead-center accuracy is critical.
By matching the machine's fundamental operating principle to your production goals, you ensure you are selecting the most effective and efficient tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hydraulic Press | Mechanical Press |
|---|---|---|
| Force Delivery | Constant force throughout the stroke | Maximum force only at bottom of stroke |
| Speed (SPM) | Slower | Higher strokes per minute |
| Stroke Control | Adjustable stroke length and pressure | Fixed stroke length |
| Best For | Deep drawing, forming, molding | High-volume stamping, blanking, punching |
| Overload Protection | Built-in pressure relief valve | No inherent protection |
Still unsure which press is right for your lab or production line? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment, including presses, to match your specific application—whether you need the versatility of a hydraulic press or the high-speed precision of a mechanical press.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your manufacturing process with the perfect equipment solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a laboratory hydraulic press for LATP electrolyte pellets? Achieve Optimal Density & Conductivity
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used to compress powders into pellets? Enhance Solid-State Reaction Kinetics
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required during the preparation of Ti3AlC2 precursor pellets?
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis



















