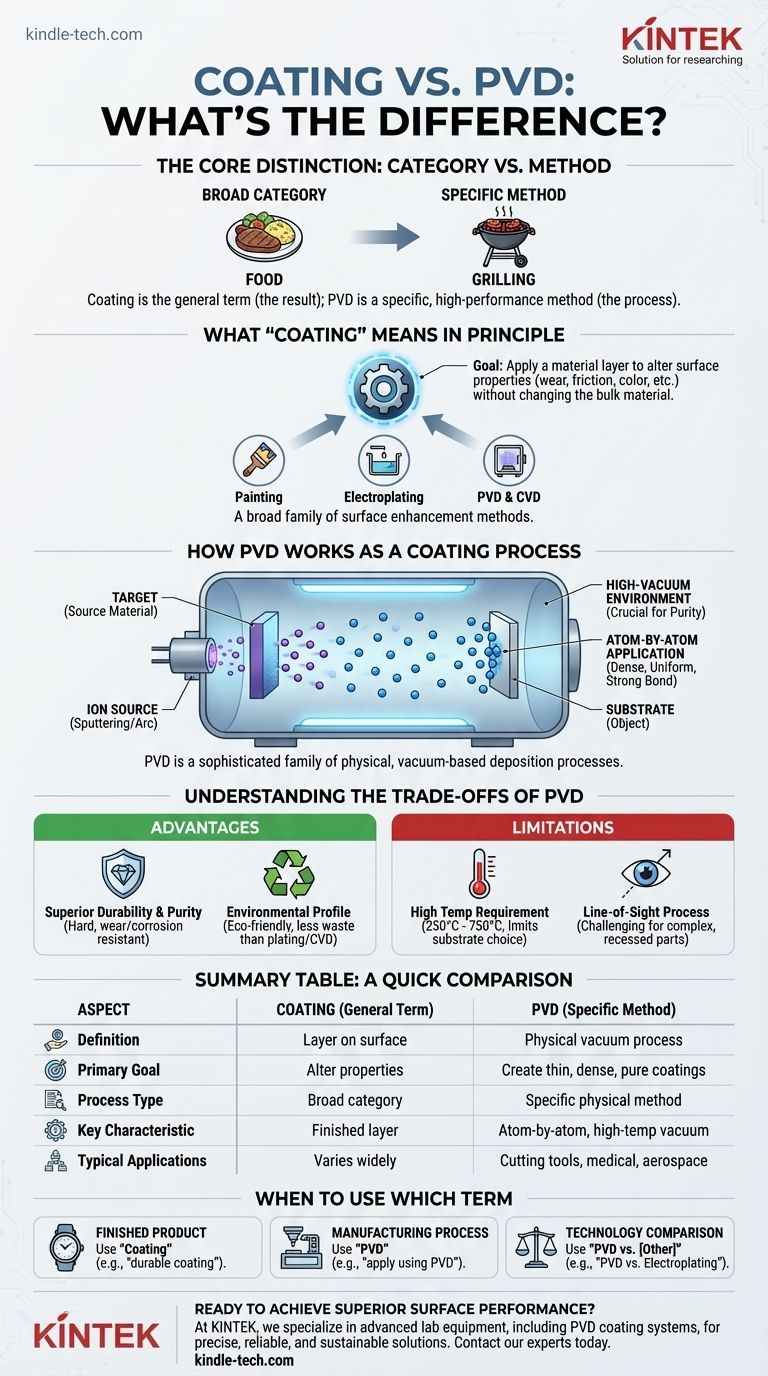
Simply put, coating is the general term for applying a new layer to a material's surface, while Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a specific, high-performance method used to apply that coating. "Coating" is the result; PVD is one of the premier processes for achieving it. Think of it as the difference between the broad category of "food" and the specific cooking technique of "grilling."
The core distinction is one of category versus method. "Coating" describes the goal of adding a functional surface layer to an object. PVD describes a specific vacuum-based process that physically transfers that coating material atom-by-atom from a solid source onto the object.
What "Coating" Means in Principle
A coating is any material layer, thick or thin, applied to the surface of an object, often called a substrate. The goal is to change the surface properties without altering the object's underlying bulk material.
A Broad Category of Surface Enhancement
Coating is a foundational concept in material science and manufacturing. It involves depositing a film or layer of a new material onto a substrate.
This is distinct from surface modification, like heat treatment, which changes the existing surface chemistry rather than adding a new layer.
The Primary Goal: Altering Properties
Coatings are applied for functional reasons. This can include improving wear resistance, reducing friction, preventing corrosion, changing the appearance or color, or altering optical and electrical properties.
Many Methods Exist
There are countless ways to apply a coating. These range from simple methods like painting to industrial processes like electroplating, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and, of course, PVD.
How PVD Works as a Coating Process
Physical Vapor Deposition is not a single action but a family of sophisticated coating processes that share a common principle. It is prized for creating exceptionally thin, durable, and pure coatings.
The Core Principle: Physical Deposition
The "Physical" in PVD is the key differentiator. The process starts with a solid source material (like titanium or chromium), known as a "target."
In a high-vacuum chamber, this target is vaporized into a cloud of atoms or molecules using a physical method like high-energy ion bombardment (sputtering) or a powerful electric arc.
The Vacuum Environment is Crucial
The entire process occurs inside a vacuum chamber. This pristine environment is critical because it removes air and other particles that could contaminate the coating and interfere with the process.
Atom-by-Atom Application
The vaporized material travels through the vacuum and condenses on the target object's surface. This deposition happens one atom at a time, creating an extremely dense, uniform, and strongly bonded layer.
Reactive gases like nitrogen can be introduced into the chamber to react with the metal vapor, forming ceramic compounds (like titanium nitride) directly on the surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PVD
While powerful, PVD is a specific tool with its own set of operational requirements and limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making informed engineering decisions.
Advantage: Superior Durability and Purity
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and highly resistant to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures. Because the bond is formed at an atomic level, the coating is nearly impossible to remove.
Advantage: Environmental Profile
Compared to traditional coating methods like electroplating or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), PVD is widely considered a more environmentally friendly "green" technology, as it produces less hazardous waste.
Limitation: High Temperature Requirement
The PVD process must be performed at high temperatures, often ranging from 250°C to 750°C (480°F to 1380°F). This makes it unsuitable for substrates that cannot withstand such heat, like many plastics or low-melting-point alloys.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Process
Generally, PVD is a "line-of-sight" process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This can make it challenging to achieve a uniform coating on complex parts with deep recesses or internal channels.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Using these terms correctly depends entirely on your context and what you need to communicate.
- If your primary focus is describing a finished product: You would refer to the outcome. For example, "This watch has a durable, scratch-resistant titanium nitride coating."
- If your primary focus is specifying a manufacturing process: You would name the method. For example, "To achieve the desired hardness, apply the coating using PVD."
- If your primary focus is comparing technologies: You would evaluate PVD against other coating methods. For example, "We are evaluating PVD versus electroplating for its durability and environmental impact."
Ultimately, recognizing that PVD is a specific method within the broader category of coating empowers you to speak with greater precision and clarity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Coating (General Term) | PVD (Specific Method) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A layer applied to a substrate's surface | A physical vapor deposition process in a vacuum |
| Primary Goal | Alter surface properties (wear, corrosion, appearance) | Create thin, dense, durable, and pure coatings |
| Process Type | Broad category (painting, plating, PVD, CVD) | Specific physical method (sputtering, arc evaporation) |
| Key Characteristic | The finished layer or film | Atom-by-atom deposition in a high-temperature vacuum |
| Typical Applications | Varies widely by method | Cutting tools, medical devices, watches, aerospace components |
Ready to achieve superior surface performance for your lab or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including PVD coating systems, to help you create durable, high-purity surface layers for your most demanding applications. Our solutions are designed for precision, reliability, and environmental sustainability.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you select the right coating technology for your specific goals.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















