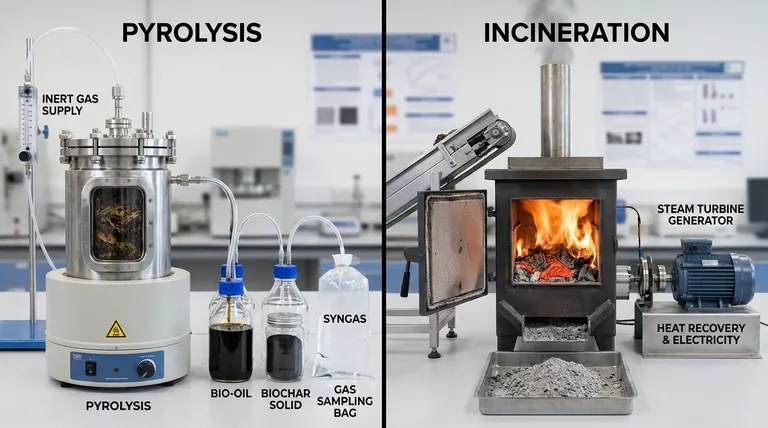
At its core, the difference between pyrolysis and incineration lies in the presence of oxygen. Incineration is the rapid burning of waste with oxygen at high temperatures to destroy it, while pyrolysis is the slower thermal decomposition of waste without oxygen at lower temperatures to convert it into valuable new products. This fundamental difference in chemistry dictates their temperatures, outputs, and ultimate purpose.
Incineration is a disposal technology focused on waste destruction and heat recovery. Pyrolysis is a recovery technology focused on chemically converting waste into valuable resources like fuel, gas, and char.
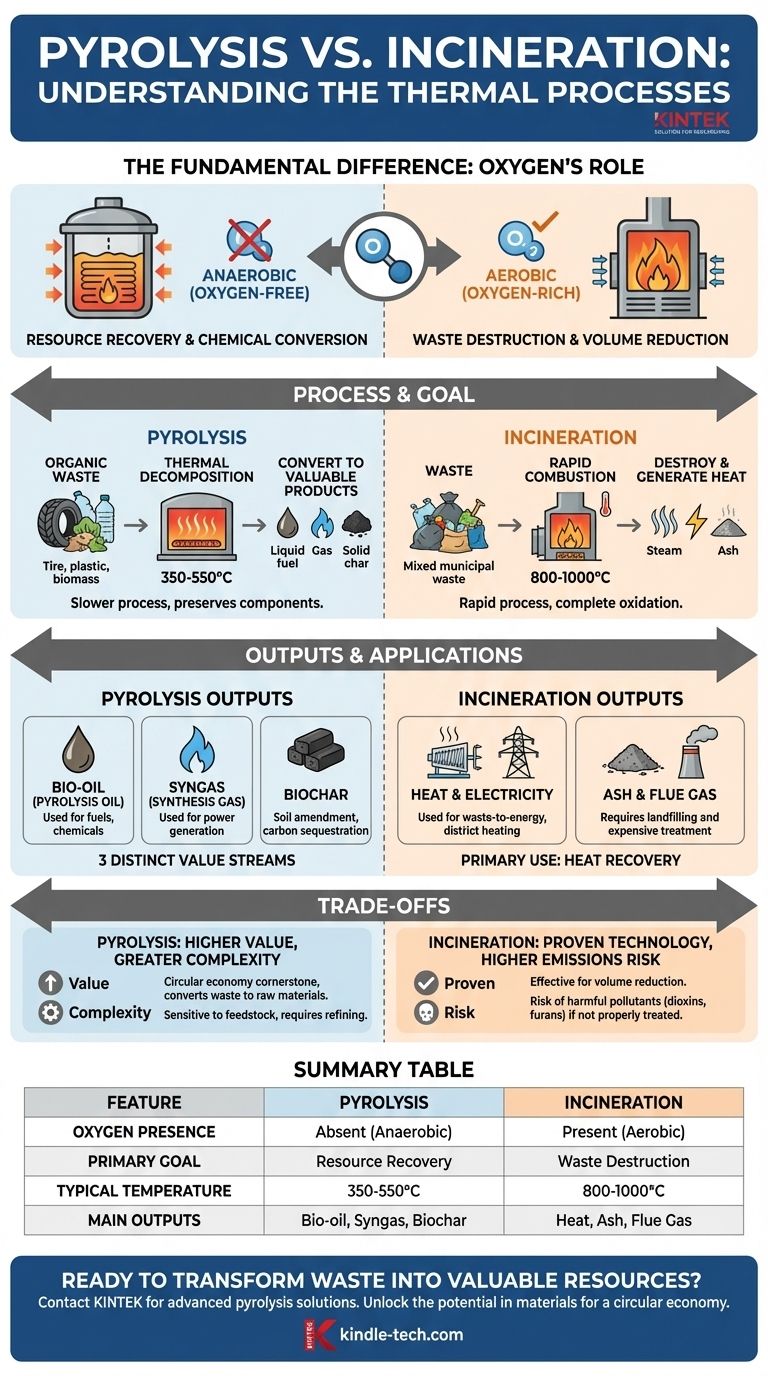
The Fundamental Difference: Oxygen's Role
The choice between these two thermal processes comes down to one critical element: oxygen. Its presence or absence completely changes the chemical reactions, the resulting products, and the overall goal of the system.
Incineration: Combustion in an Oxygen-Rich Environment
Incineration is simply high-temperature burning. By introducing oxygen and heat (typically 800-1000°C), the process drives a rapid and complete oxidation of the waste material.
The primary goal is destruction and volume reduction. The organic materials in the waste are converted into carbon dioxide and water, releasing a significant amount of heat in the process.
Pyrolysis: Decomposition in an Oxygen-Free Environment
Pyrolysis is a form of thermochemical decomposition, not burning. By heating organic material in an inert, oxygen-free atmosphere (typically at 350-550°C), the long-chain polymer molecules are broken down.
Instead of being destroyed, the chemical components are preserved and re-formed into simpler, valuable substances. The goal is resource recovery and chemical conversion.
Comparing the Outputs and Applications
The different chemical environments of incineration and pyrolysis result in drastically different end products. This is the most important factor when deciding which technology is appropriate for a given goal.
Incineration Outputs: Heat, Ash, and Flue Gas
The main useful product of incineration is heat. This heat is captured in a boiler to create steam, which can then be used to generate electricity (a "waste-to-energy" plant) or provide district heating.
The other outputs are bottom ash, a solid residue that must often be landfilled, and flue gas, which requires extensive and costly cleaning to remove pollutants before being released into the atmosphere.
Pyrolysis Outputs: Bio-oil, Syngas, and Biochar
Pyrolysis creates three distinct, valuable product streams from a single feedstock.
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A liquid fuel that can be refined into transportation fuels or used as a feedstock for producing new plastics and chemicals.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be burned to power the pyrolysis process itself or used to generate electricity.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid material. It is an excellent soil amendment that improves water retention and can sequester carbon for hundreds of years. This stands in stark contrast to incinerator ash.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a perfect solution. Choosing between them requires a clear understanding of their respective advantages and limitations.
Incineration: Proven Technology, Higher Emissions Risk
Incineration is a mature, well-understood technology that has been used for decades. It is highly effective at reducing the volume of municipal solid waste, which is its primary application.
However, its main drawback is the risk of creating and releasing harmful pollutants like dioxins, furans, and heavy metals if combustion is incomplete or flue gas treatment fails. It is a disposal method that destroys the material value of waste.
Pyrolysis: Higher Value, Greater Complexity
Pyrolysis excels at resource recovery and is a cornerstone of a true circular economy, turning waste like plastics, tires, and biomass back into valuable raw materials.
The trade-off is its technical complexity. The process is more sensitive to the composition and purity of the feedstock, and the resulting bio-oil often requires further refining before it can be used. It is less of a "brute force" solution and requires more precise operational control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use pyrolysis or incineration should be driven entirely by your primary objective for managing a waste stream.
- If your primary focus is maximum waste volume reduction and energy generation from mixed municipal waste: Incineration is a direct and established method for converting general waste into heat and electricity.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery and creating value-added products: Pyrolysis is the superior choice for transforming specific, homogenous feedstocks (like plastics or tires) into marketable fuels, chemicals, and char.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil improvement: Pyrolysis is the only technology of the two that produces biochar, a stable form of carbon that can lock away carbon and regenerate soil.
Ultimately, the choice depends on whether you view waste as a problem to be eliminated or a resource to be unlocked.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Presence | Absent (Anaerobic) | Present (Aerobic) |
| Primary Goal | Resource Recovery | Waste Destruction |
| Typical Temperature | 350-550°C | 800-1000°C |
| Main Outputs | Bio-oil, Syngas, Biochar | Heat, Ash, Flue Gas |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? The right technology is critical for achieving your goals in waste management, resource recovery, and sustainability. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis systems, to help you unlock the potential in materials like plastics, biomass, and tires. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to convert waste into fuel, chemicals, and biochar for a circular economy. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can empower your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer



















