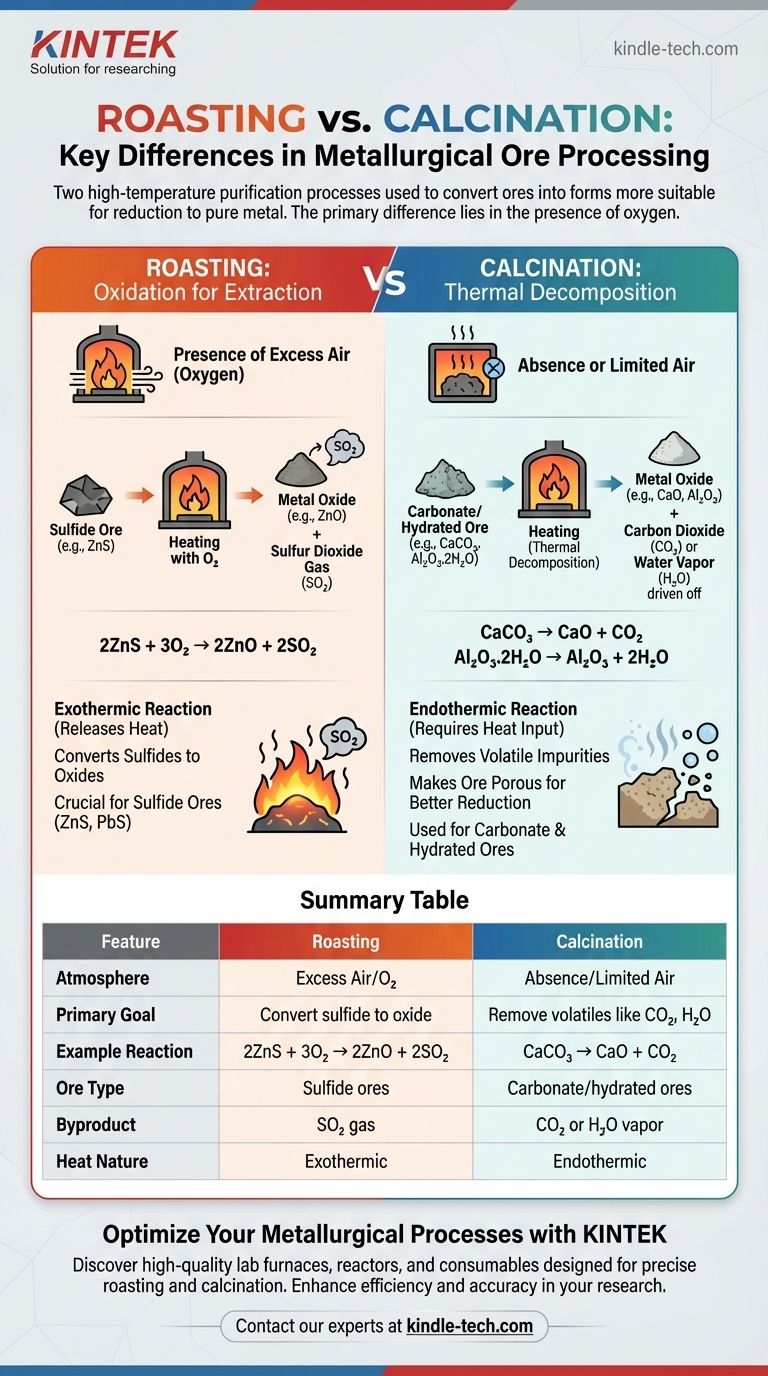
At its core, the primary difference between roasting and calcination lies in the presence of oxygen. Roasting is the process of heating a concentrated ore to a high temperature in the presence of excess air. In contrast, calcination involves heating an ore to a high temperature either in the absence of air or with a very limited supply. Both are crucial preliminary steps in metallurgy designed to convert ores into a form more suitable for reduction to the pure metal.
While both are high-temperature purification processes, roasting uses oxygen to chemically convert sulfide ores into oxides. Calcination, on the other hand, uses heat alone to thermally decompose carbonate or hydrated ores, driving off volatile substances like carbon dioxide and water.
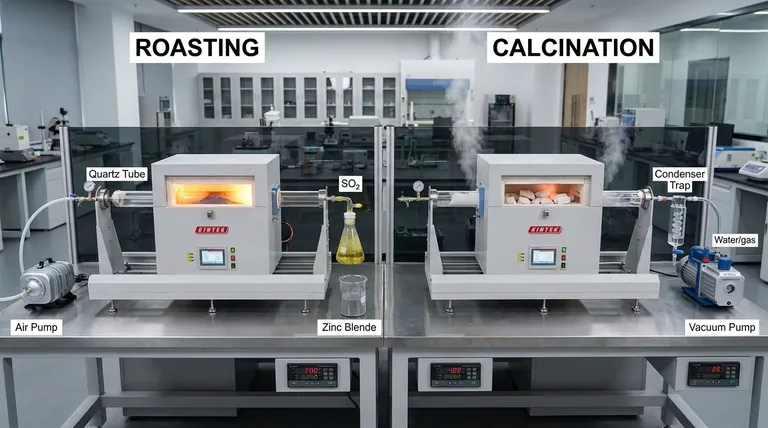
Understanding Roasting: Oxidation for Extraction
Roasting is a key pyrometallurgical process, meaning it uses heat to bring about chemical changes in an ore. Its main application is for sulfide ores.
The Fundamental Goal
The primary purpose of roasting is to convert a metal sulfide into a metal oxide. Metal oxides are significantly easier and more economically viable to reduce to a pure metal than their sulfide counterparts.
The Chemical Reaction and Example
During roasting, the ore reacts with oxygen from the air. This converts the metal sulfide to a metal oxide and produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂) gas as a byproduct.
A classic example is the roasting of zinc blende (ZnS) to produce zinc oxide (ZnO), a crucial step in extracting zinc:
2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂
Key Characteristics of Roasting
This process is performed in a specialized furnace, like a reverberatory or flash furnace, at a temperature below the ore's melting point. For many sulfide ores, the reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat and can sustain itself once started.
Understanding Calcination: Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is another thermal treatment process, but its chemical mechanism is entirely different. It is primarily used for carbonate and hydrated ores.
The Fundamental Goal
The goal of calcination is to remove volatile impurities by heating the ore. This drives off substances like carbon dioxide (from carbonates) or water (from hydrated oxides), leaving a more concentrated metal oxide behind.
The Chemical Reaction and Example
Calcination is a thermal decomposition reaction that occurs in the absence of air. A primary example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO):
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Another common use is for hydrated ores, such as bauxite (hydrated aluminum oxide), to remove water before the aluminum extraction process:
Al₂O₃.2H₂O → Al₂O₃ + 2H₂O
Key Characteristics of Calcination
This process is endothermic, requiring a continuous input of heat. It makes the ore porous, which increases the surface area available for the subsequent reduction step, thereby increasing its efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
Choosing between these processes is not a matter of preference; it is dictated by the ore's chemistry. Understanding why is key to understanding metallurgy.
Why Not Reduce Sulfides Directly?
Reducing metal sulfides directly to metal is thermodynamically difficult and expensive. Converting them to oxides first provides a much more efficient and cost-effective pathway for reduction, typically using carbon (coke) as a reducing agent.
Handling the Byproducts
Roasting produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂), a gas that can cause acid rain if released into the atmosphere. Modern metallurgical plants capture this gas and use it to manufacture sulfuric acid, turning a potential environmental liability into a valuable commercial product.
The Importance of a Porous Ore
Calcination's ability to create a porous, crumbly ore is a significant advantage. This increased surface area allows the reducing agent (like carbon monoxide in a blast furnace) to interact more effectively with the metal oxide, speeding up the final extraction of the metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Ore
The choice between roasting and calcination is dictated entirely by the chemical composition of the ore you need to process.
- If your ore is a sulfide (like zinc blende, ZnS, or galena, PbS): You must use roasting to convert the sulfide into an oxide before it can be reduced to the pure metal.
- If your ore is a carbonate (like calamine, ZnCO₃, or limestone, CaCO₃): You must use calcination to thermally decompose it and drive off carbon dioxide, yielding the metal oxide.
- If your ore is a hydrated oxide (like bauxite, Al₂O₃.2H₂O): You must use calcination to remove the chemically bound water and produce a pure, anhydrous oxide.
Understanding this fundamental distinction is the first step in designing an effective and efficient metallurgical extraction process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Roasting | Calcination |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Excess air (presence of O₂) | Absence or limited air |
| Primary Goal | Convert sulfide ores to oxides | Remove volatile impurities (CO₂, H₂O) |
| Example Reaction | 2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂ | CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ |
| Ore Type | Sulfide ores (e.g., ZnS, PbS) | Carbonate/hydrated ores (e.g., CaCO₃, bauxite) |
| Byproduct | SO₂ gas | CO₂ or H₂O vapor |
| Heat Nature | Exothermic (releases heat) | Endothermic (requires heat input) |
Optimize Your Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Whether you are processing sulfide ores through roasting or decomposing carbonates via calcination, having the right laboratory equipment is crucial for efficiency and accuracy. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab furnaces, reactors, and consumables designed to meet the rigorous demands of metallurgical testing and research.
Our products ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and durability—key factors for successful roasting and calcination operations. By partnering with KINTEK, you gain access to:
- Reliable equipment that enhances process reproducibility
- Expert support to help you select the right tools for your specific ore type
- Solutions that improve safety and environmental compliance
Ready to refine your extraction process? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK’s lab equipment can support your metallurgical innovations and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry



















