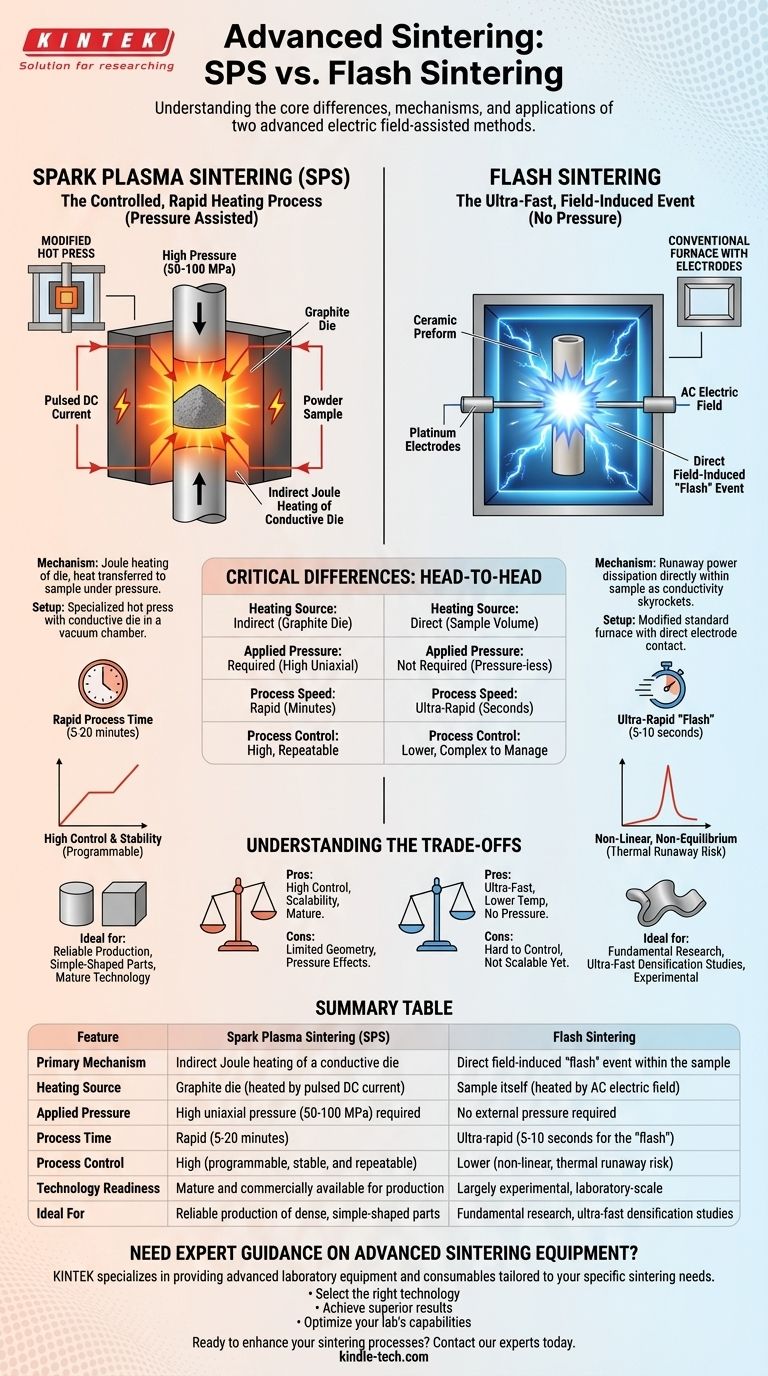
At its core, spark plasma sintering (SPS) and flash sintering are both advanced methods that use an electric field to rapidly densify materials. However, they operate on fundamentally different principles. SPS is a controlled, rapid heating process that uses a conductive die and pressure, while flash sintering is an ultra-fast, field-induced event that causes near-instantaneous densification directly within the material itself.
The crucial distinction is the role of the electric field and the physical setup. SPS uses the field to heat a graphite die, which then heats the sample under pressure. Flash sintering applies the field directly to the sample, triggering a sudden internal densification event in mere seconds.
Deconstructing Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Spark plasma sintering, also known as a field-assisted sintering technique (FAST), is a more established and commercially available process.
The Core Mechanism: Joule Heating and Pressure
SPS works by passing a pulsed direct current (DC) through a conductive graphite die that contains the powder sample. This current generates immense heat via the Joule effect.
This heat is transferred rapidly and uniformly to the sample. Simultaneously, a high uniaxial pressure (e.g., 50-100 MPa) is applied, which aids in particle rearrangement and densification.
The Setup: A Modified Hot Press
The SPS apparatus is essentially a specialized hot press. The powder is loaded into a graphite die, which is then placed between two punches within a vacuum chamber. The entire die/punch assembly acts as the heating element and pressure application tool.
Key Characteristics: Rapid and Uniform
The primary advantage of SPS is its speed and control. It achieves extremely high heating rates (up to 1000°C/min), allowing for full densification in minutes rather than the hours required for conventional sintering. This short duration preserves fine-grained microstructures.
Understanding Flash Sintering
Flash sintering is a newer, more experimental technique that produces results on an even faster timescale.
The Core Mechanism: The "Flash" Event
In flash sintering, two electrodes are attached directly to a ceramic preform, which is placed inside a conventional furnace. The furnace pre-heats the sample to a specific temperature.
An AC electric field is then applied. Once a critical combination of temperature and field strength is reached, the material's electrical conductivity suddenly and dramatically increases. This triggers a runaway power dissipation event within the sample, leading to full densification in as little as 5-10 seconds.
The Setup: A Conventional Furnace with Electrodes
Unlike the specialized SPS machine, flash sintering can be performed by modifying a standard laboratory furnace. The key components are a power supply and electrodes (often platinum) that make direct contact with the sample. Crucially, high external pressure is not required.
Key Characteristics: Ultra-Fast and Non-Linear
Flash sintering is defined by its extreme speed and non-linear behavior. The "flash" is a threshold phenomenon—nothing happens until the critical point is reached, at which point densification occurs almost instantly.
The Critical Differences: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Understanding where these techniques diverge is key to selecting the right one.
Heating Source and Method
SPS primarily uses indirect heating. The current heats the graphite die, which in turn heats the sample via conduction and radiation.
Flash Sintering uses direct heating. The energy is dissipated directly within the sample volume as its conductivity skyrockets, causing the densification.
Speed and Timescale
SPS is rapid, with total process times typically in the range of 5 to 20 minutes.
Flash Sintering is ultra-rapid. The actual densification event, the "flash," is completed in a matter of seconds.
Applied Pressure
SPS is fundamentally a pressure-assisted technique. High uniaxial pressure is a critical component of the process.
Flash Sintering generally requires no external pressure. Densification is driven entirely by the electro-thermal event within the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; each comes with significant trade-offs.
Process Control and Stability
SPS offers excellent process control. The temperature and pressure profiles are programmable and highly repeatable, making it a robust and reliable manufacturing technique.
Flash sintering is a non-equilibrium process that can be difficult to manage. The "flash" event is a form of thermal runaway that must be carefully controlled by limiting the current to prevent sample damage, melting, or arcing.
Sample Geometry and Scalability
SPS is limited to the simple shapes and sizes that can be accommodated by a rigid graphite die (typically cylinders or squares). However, the technology is mature, with large-scale machines available for industrial production.
Flash sintering is more flexible in principle regarding geometry but is currently much less mature. It remains a largely laboratory-scale technique, and scaling it up for industrial use is a significant ongoing challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your project goals, from industrial production to fundamental research.
- If your primary focus is reliable production of dense, simple-shaped parts: SPS is the more mature, robust, and predictable choice for achieving high-quality results.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research into ultra-fast densification: Flash sintering offers unique, unparalleled opportunities to study material behavior under extreme, non-equilibrium conditions.
- If your primary focus is sintering at the lowest possible furnace temperatures: Flash sintering can achieve densification at furnace temperatures hundreds of degrees lower than even SPS.
- If your primary focus is avoiding pressure-induced effects or tooling costs: The pressure-less nature and simpler apparatus of flash sintering make it an attractive option for specific research applications.
Ultimately, selecting the correct advanced sintering method requires understanding that you are choosing between a controlled, rapid heating process (SPS) and an ultra-fast, field-driven physical event (Flash).
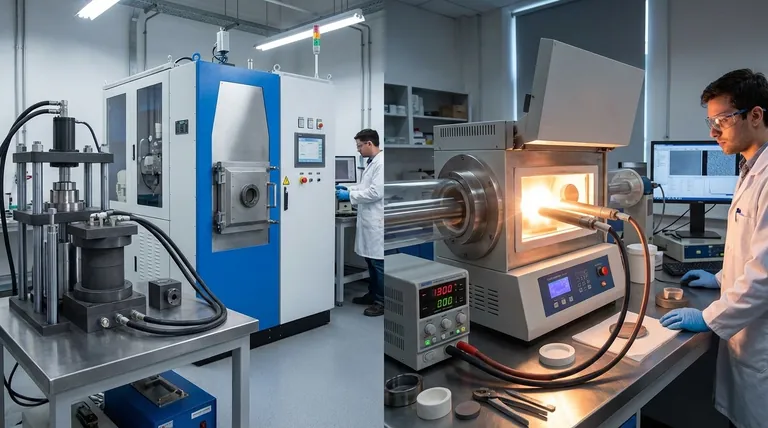

Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Flash Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Indirect Joule heating of a conductive die | Direct field-induced "flash" event within the sample |
| Heating Source | Graphite die (heated by pulsed DC current) | Sample itself (heated by AC electric field) |
| Applied Pressure | High uniaxial pressure (50-100 MPa) required | No external pressure required |
| Process Time | Rapid (5-20 minutes) | Ultra-rapid (5-10 seconds for the "flash") |
| Process Control | High (programmable, stable, and repeatable) | Lower (non-linear, thermal runaway risk) |
| Technology Readiness | Mature and commercially available for production | Largely experimental, laboratory-scale |
| Ideal For | Reliable production of dense, simple-shaped parts | Fundamental research, ultra-fast densification studies |
Need Expert Guidance on Advanced Sintering Equipment?
Choosing between Spark Plasma Sintering and Flash Sintering is a critical decision that impacts your research outcomes and production efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific sintering needs.
We help you:
- Select the right technology for your application, whether it's robust production with SPS or cutting-edge research with flash sintering.
- Achieve superior results with precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance.
- Optimize your lab's capabilities with equipment that enhances efficiency and accelerates your material development timeline.
Ready to enhance your sintering processes? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



















