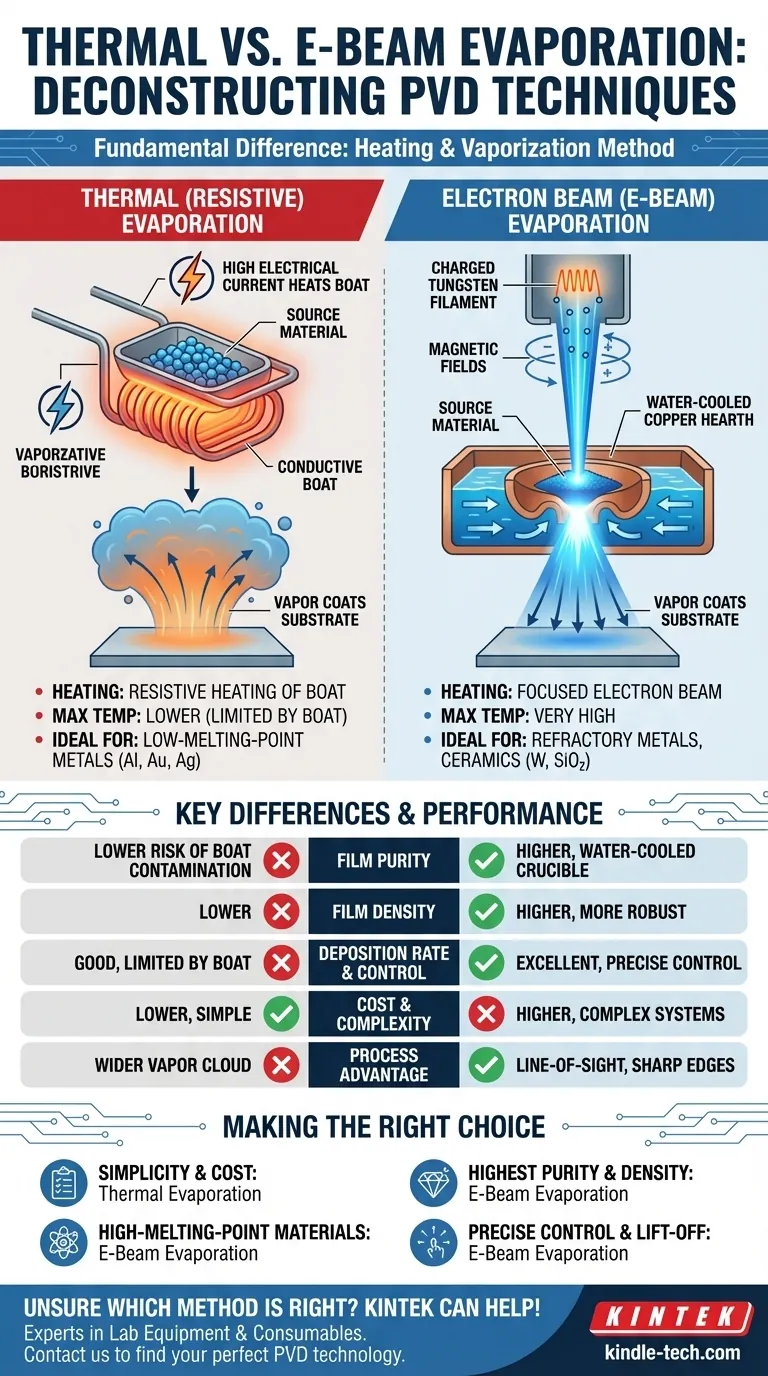
The fundamental difference between thermal and e-beam evaporation is the method used to heat and vaporize the source material. Thermal evaporation uses an electric current to heat a crucible or "boat" containing the material, similar to a filament in a light bulb. In contrast, e-beam evaporation uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to directly strike and heat the material itself, allowing for much higher temperatures and greater precision.
Your choice between these two methods is not merely about how you heat a material, but what materials you can deposit, the purity and density of the final film, and the level of control you have over the entire process.
Deconstructing the Heating Mechanisms
The heating method is the root cause of all other differences between these two physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques. Understanding how each works reveals its inherent strengths and weaknesses.
Thermal (Resistive) Evaporation
In thermal evaporation, the source material (often in pellet form) is placed in a small container, typically called a boat or coil. This boat is made of a conductive, high-melting-point metal.
A high electrical current is passed through the boat. Due to its electrical resistance, the boat heats up rapidly and intensely.
This heat is then transferred to the source material, causing it to first melt and then evaporate. The resulting vapor travels through the vacuum chamber and coats the target substrate.
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
E-beam evaporation is a more targeted and energetic process. It begins with a charged tungsten filament that emits a stream of electrons.
These electrons are accelerated by high voltage and then focused into a tight beam using magnetic fields.
This high-energy beam is directed onto the surface of the source material, which sits in a water-cooled copper hearth or crucible. The kinetic energy of the electrons is converted into intense thermal energy upon impact, heating a very small spot on the material to its evaporation point.
Key Differences in Performance and Outcome
The choice of heating mechanism directly impacts the deposition process and the quality of the resulting thin film.
Temperature Range and Material Compatibility
E-beam's direct energy transfer can achieve extremely high temperatures. This makes it capable of evaporating materials with very high melting points, such as refractory metals (platinum, tungsten) and dielectric ceramics (silicon dioxide, titanium oxide).
Thermal evaporation is limited by the melting point of the boat itself. It is therefore best suited for materials with lower evaporation temperatures, such as aluminum, silver, or gold.
Film Purity and Density
In thermal evaporation, the entire boat becomes white-hot. This creates a risk that the boat material itself will evaporate, introducing impurities into the final film.
With e-beam, only the source material is super-heated; the water-cooled crucible remains cool. This significantly reduces contamination, leading to much purer films. E-beam deposition also generally results in denser, more robust film structures.
Deposition Rate and Control
E-beam evaporation can deposit material at a much higher rate than thermal evaporation.
Furthermore, the intensity of the electron beam can be precisely controlled, allowing for fine-tuned adjustments to the deposition rate. This level of control is critical for creating complex, multi-layered films with specific properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While e-beam evaporation offers superior performance in several key areas, thermal evaporation remains a valuable and widely used technique due to its simplicity.
Complexity and Cost
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simpler and therefore generally less expensive to purchase and operate. Their power supplies and control systems are straightforward.
E-beam systems are more complex, requiring high-voltage power supplies, sophisticated magnetic focusing coils, and a robust cooling system. This increases their initial cost and maintenance requirements.
Process Advantages
The highly directional, line-of-sight nature of e-beam evaporation is a significant advantage for applications like lift-off patterning, where sharp, well-defined edges are required. Thermal evaporation produces a wider, less-focused vapor cloud.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method depends entirely on your material requirements, quality standards, and budget.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effective deposition of low-melting-point metals: Thermal evaporation is the most practical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials like ceramics or refractory metals: E-beam evaporation is your only viable option.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density: E-beam's direct heating and cooled crucible provide a clear advantage over thermal methods.
- If your primary focus is precise rate control for complex film structures or lift-off applications: The superior control and directionality of an e-beam system are essential.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences allows you to match the right deposition technology to the specific demands of your material and the desired quality of your thin film.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Resistive heating of a crucible/boat | Focused electron beam on material |
| Max Temperature | Lower (limited by boat) | Very High |
| Ideal Materials | Low-melting-point metals (Al, Au, Ag) | Refractory metals, ceramics (W, SiO₂) |
| Film Purity | Lower risk of boat contamination | Higher (water-cooled crucible) |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Deposition Control | Good | Excellent (precise rate control) |
Still unsure which evaporation method is right for your project? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific laboratory needs, whether you require a simple thermal evaporation system or a high-precision e-beam solution.
Contact us today to discuss your application, and let us help you achieve superior thin film results with the perfect PVD technology for your budget and performance requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What temperature is physical vapor deposition? A Guide to PVD's Flexible Heat Range
- What is the thermal evaporation of gold? A Simple Guide to Gold Thin Film Deposition
- Is electron beam assisted evaporation used for metals? The Key to High-Purity, High-Melting-Point Metal Films
- What is the electron beam evaporation process? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of thin film in electronics? Building the Foundation of Modern Devices
- What is the use of physical vapor deposition? Enhance Durability, Performance, and Purity
- What is the process of evaporation coating? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- How is the thickness of a deposited film measured? Master Optical Interference Techniques



















