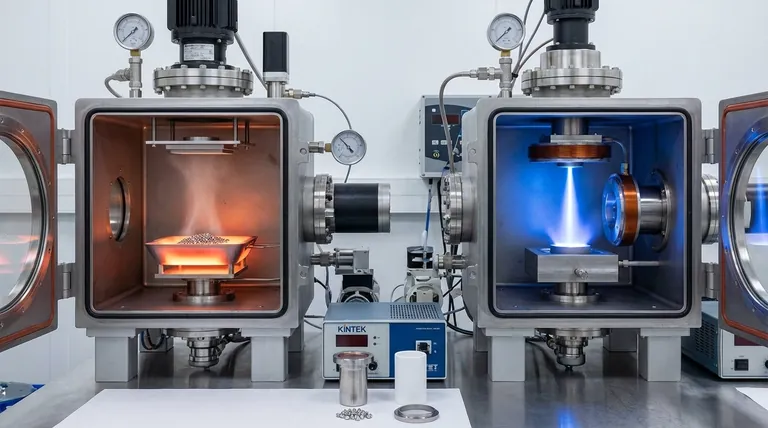
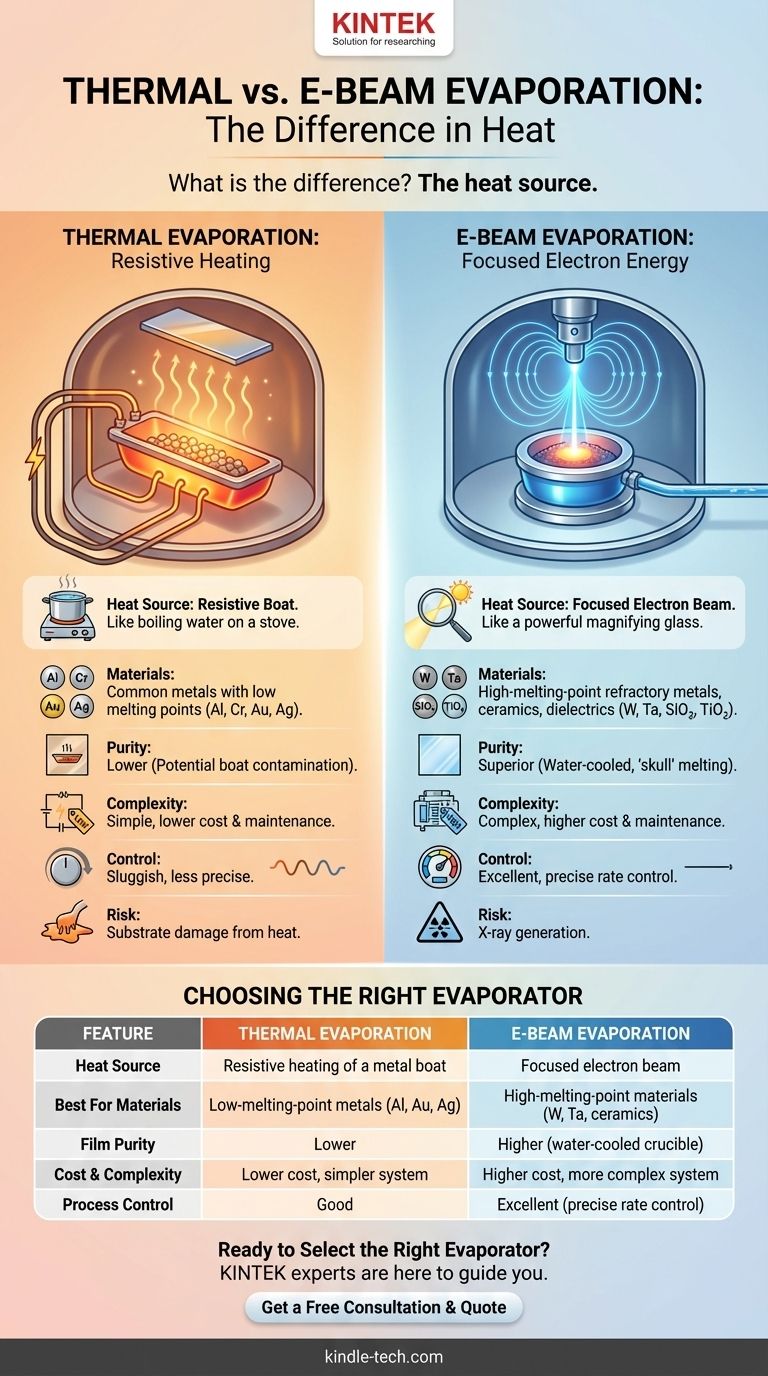
At its core, the difference is the heat source. Both thermal evaporation and electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation are physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques used to create thin films inside a vacuum. Thermal evaporation works by passing a large electrical current through a resistive boat or filament to heat it, which in turn heats the source material to its evaporation point. In contrast, e-beam evaporation uses a high-energy, magnetically-focused beam of electrons to directly strike and vaporize the source material.
While both methods deposit material onto a substrate, the choice between them is a critical engineering decision. Thermal evaporation is a simpler, less expensive method ideal for basic metals, while e-beam evaporation offers superior purity, control, and the ability to deposit virtually any material, including high-melting-point ceramics and refractory metals.

How the Heat is Delivered: The Fundamental Difference
To understand the practical implications, you must first grasp the distinct mechanisms for generating vapor. Both processes occur in a high vacuum to allow evaporated atoms to travel in a straight line ("line-of-sight") to the substrate.
Thermal Evaporation: Resistive Heating
In a thermal evaporator, the source material (e.g., pellets of aluminum) is placed in a small "boat" made of a refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum.
A very high electrical current is passed through this boat. Due to its electrical resistance, the boat heats up rapidly, often glowing white-hot. This heat is then conducted to the source material, raising its temperature until it begins to sublimate or evaporate.
This method is analogous to boiling water on an electric stove; the burner (the boat) gets hot and transfers its heat to the pot (the source material).
E-Beam Evaporation: Focused Electron Energy
E-beam evaporation uses a much more sophisticated approach. An electron gun, typically a hot tungsten filament, emits a stream of electrons.
These electrons are accelerated by a high voltage (e.g., 10 kV) and then guided by powerful magnetic fields to strike a small, specific spot on the source material. The material is held in a water-cooled copper hearth or crucible.
The immense kinetic energy of the electrons is converted to thermal energy upon impact, causing instantaneous, localized heating and evaporation only where the beam strikes. This is more like using a powerful magnifying glass to focus sunlight onto a single point.
Comparing Material Capability and Film Quality
The heating method directly dictates the types of materials you can deposit and the quality of the resulting film.
Material Selection: The E-Beam Advantage
Thermal evaporation is limited to materials with a lower melting point than the boat itself. You cannot evaporate tungsten from a tungsten boat. This restricts its use primarily to common metals like Aluminum (Al), Chromium (Cr), Gold (Au), and Silver (Ag).
E-beam evaporation has no such limitation. Because the heat is delivered directly to the source material and the crucible is actively water-cooled, you can deposit nearly anything. This includes refractory metals (Tungsten, Tantalum), dielectrics (Silicon Dioxide, Titanium Dioxide), and other ceramics.
Film Purity: Minimizing Contamination
In thermal evaporation, the hot boat material can also evaporate slightly, incorporating impurities into the growing film. This is a significant concern for high-purity applications like semiconductor interconnects or sensitive optical coatings.
E-beam provides a much cleaner process. The water-cooled hearth ensures that only the source material gets hot. In fact, a layer of the source material solidifies against the cold crucible wall, creating a "skull" or self-crucible that prevents any contamination from the hearth itself.
Alloy and Compound Deposition
Depositing a precise alloy with thermal evaporation is nearly impossible. Different elements have different vapor pressures, meaning they evaporate at different rates from a shared boat, leading to an unpredictable film composition.
E-beam systems, however, can be equipped with multiple electron guns and crucibles. By precisely controlling the power of each beam on its respective source, you can co-evaporate multiple materials simultaneously to create alloy films with highly controlled stoichiometry.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
The superior capabilities of e-beam evaporation come with clear trade-offs in complexity and operation.
System Complexity and Cost
Thermal evaporators are mechanically simple, consisting of a power supply and electrodes. This makes them significantly cheaper to purchase, operate, and maintain.
E-beam systems are far more complex. They require high-voltage power supplies, powerful electromagnets for beam steering, a sophisticated electron gun assembly, and extensive water cooling. This results in a much higher initial cost and more demanding maintenance.
Process Control and Repeatability
E-beam evaporation offers far superior process control. The deposition rate can be precisely and instantly adjusted by changing the electron beam's current. This rate is often monitored by a quartz crystal microbalance in a feedback loop, enabling highly repeatable and accurate film thicknesses.
Rate control in thermal evaporation is sluggish and less precise, as it relies on changing the current to the boat and waiting for its temperature to stabilize.
Potential for Substrate Damage
The large, hot boat in a thermal evaporator radiates a significant amount of heat, which can damage sensitive substrates like polymers or biological samples.
Conversely, the impact of high-energy electrons in an e-beam system generates X-rays. These X-rays can cause radiation damage to sensitive electronic devices or materials, requiring appropriate shielding and process consideration.
Choosing the Right Evaporator for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on your material requirements, budget, and desired film characteristics.
- If your primary focus is depositing simple metals (Al, Au, Cr) on a budget: Thermal evaporation is the efficient and cost-effective choice for these common applications.
- If your primary focus is high-purity films or refractory materials (W, Ta, Pt): E-beam evaporation is the only viable option due to its heating mechanism and purity.
- If your primary focus is creating optical coatings or complex dielectrics (SiO₂, TiO₂): E-beam evaporation provides the necessary material capability and rate control for multi-layer stacks.
- If your primary focus is depositing precise alloys or compounds: E-beam co-evaporation is the industry standard for achieving accurate compositional control.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental difference in heating empowers you to select the precise tool that aligns with your material, budget, and desired film quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Resistive heating of a metal boat | Focused electron beam |
| Best For Materials | Low-melting-point metals (Al, Au, Ag) | High-melting-point materials (W, Ta, ceramics) |
| Film Purity | Lower (potential boat contamination) | Higher (water-cooled crucible) |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler system | Higher cost, more complex system |
| Process Control | Good | Excellent (precise rate control) |
Ready to Select the Right Evaporator for Your Lab?
Choosing between thermal and e-beam evaporation is a critical decision that impacts your research quality, material capabilities, and budget. The experts at KINTEK are here to guide you. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment for your specific thin-film deposition needs.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements. Our team will help you determine the ideal PVD solution—whether it's a cost-effective thermal evaporator for standard metals or a high-precision e-beam system for advanced materials—ensuring you achieve the film purity and performance your work demands.
Get a Free Consultation & Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Is deposition the same as evaporation? Unraveling the Hierarchy of Thin-Film Technology
- Is electron beam assisted evaporation used for metals? The Key to High-Purity, High-Melting-Point Metal Films
- What is the difference between thermal and e-beam evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Lab
- What are the uses of evaporation in industry? From Food Concentration to High-Tech Thin Films
- What are the advantages of using Monel alloy reactors and nickel sample boats? Secure Purity in Carbon Fluorination
- What are the disadvantages of physical Vapour deposition? High Cost, Slow Speed, and Coating Limitations
- What precautions should be taken during evaporation process? Ensure High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are the factors affecting sputtering? Control Your Thin Film Deposition Process



















