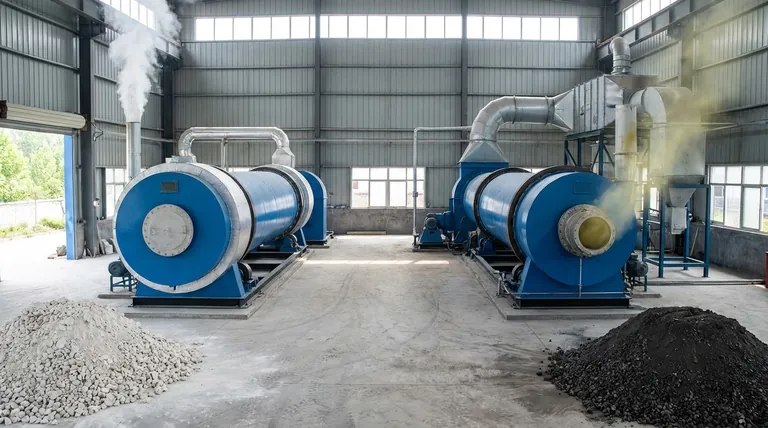
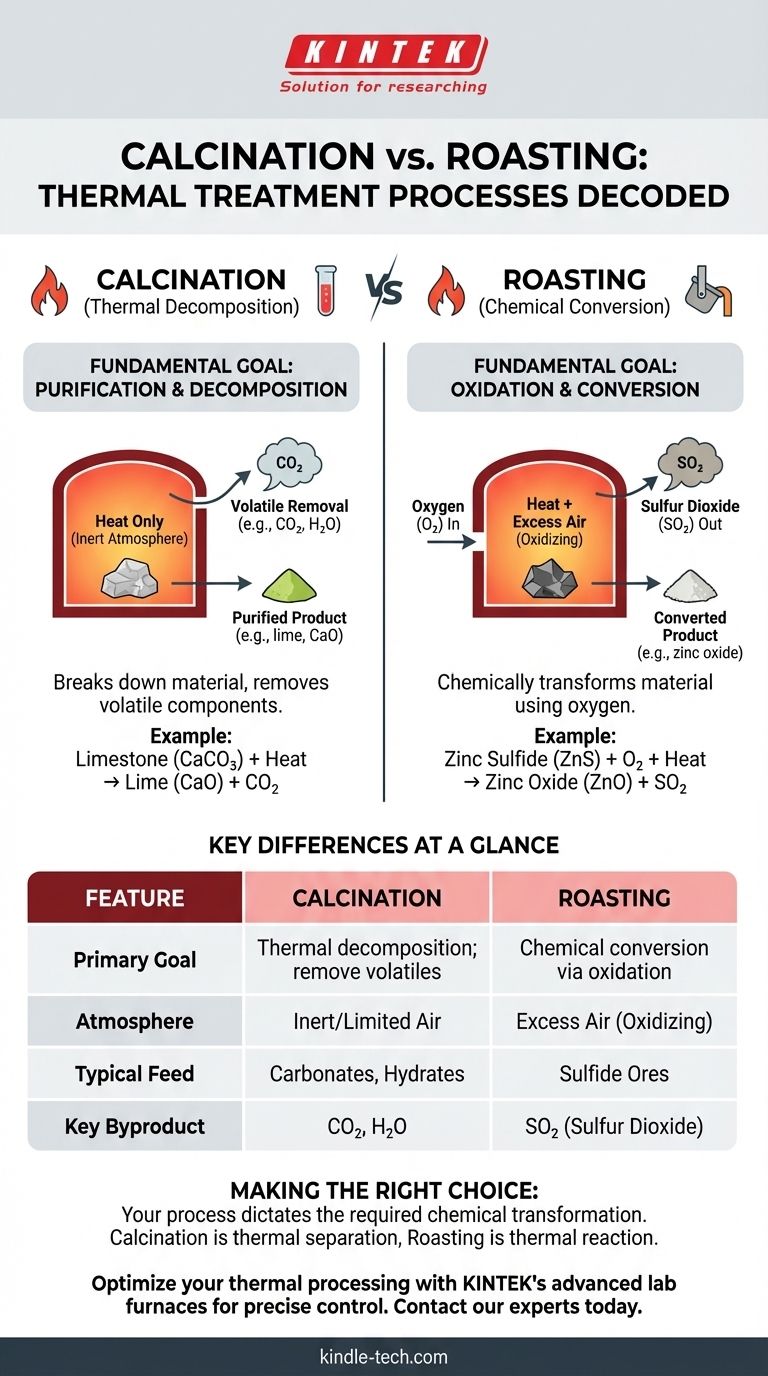
At its core, the difference between calcination and roasting is the chemical role of the furnace atmosphere. Calcination is a process of thermal decomposition performed in the absence or limited supply of air to drive off volatile substances. In contrast, roasting is a chemical conversion process carried out in an excess of air, specifically to oxidize a material, most often a metal sulfide ore.
Think of it this way: Calcination uses heat to break a substance down and remove a part of it, like driving water out of a wet solid. Roasting uses heat and air to chemically transform the entire substance into something new, like converting a sulfide into an oxide.

Deconstructing the Processes: Calcination
Calcination is a purification and decomposition step driven purely by heat. The goal is to break down the material into a more stable or desirable form by removing a volatile component.
The Fundamental Goal: Thermal Decomposition
The primary objective of calcination is to induce thermal decomposition. This means using high temperatures to break chemical bonds and release a specific part of the compound as a gas.
A classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). Heat breaks the carbonate down, releasing carbon dioxide.
CaCO₃ (solid) + Heat → CaO (solid) + CO₂ (gas)
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
Calcination is defined by its atmosphere, which is either inert or has a very limited supply of air (oxygen). This is crucial because the goal is to prevent oxidation or other unwanted reactions with the furnace environment.
The process is focused solely on what heat can do to the material itself.
Common Applications of Calcination
You will encounter calcination when preparing raw materials. Its uses include removing water from hydrates (like in bauxite processing), removing carbon dioxide from carbonates, or driving off volatile organic matter from various substances.
Deconstructing the Processes: Roasting
Roasting is a metallurgical process designed to chemically alter metal ores to make them easier for subsequent steps like smelting. It is fundamentally a reaction with oxygen.
The Fundamental Goal: Chemical Conversion via Oxidation
The objective of roasting is oxidation. The process intentionally reacts the feed material, typically a metal sulfide ore, with oxygen from the air.
This converts the metal sulfide into a metal oxide, which is more readily reduced to a pure metal in a later stage.
2ZnS (solid) + 3O₂ (gas) + Heat → 2ZnO (solid) + 2SO₂ (gas)
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
Roasting requires an oxidizing atmosphere, meaning an excess of air or oxygen is supplied to the furnace. Oxygen is not just the environment; it is a primary reactant in the process.
Without sufficient oxygen, the intended chemical conversion from sulfide to oxide cannot occur.
Common Applications of Roasting
Roasting is a cornerstone of extractive metallurgy. It is the principal method for preparing sulfide ores of metals like zinc, lead, copper, and nickel for smelting.
Key Differences at a Glance
The choice between calcination and roasting comes down to your starting material and your desired final product. They are distinct tools for different chemical objectives.
Purpose
Calcination aims to decompose a material and drive off a volatile component (e.g., H₂O, CO₂).
Roasting aims to chemically convert a material through oxidation (e.g., converting a metal sulfide to a metal oxide).
Atmospheric Conditions
Calcination occurs in an inert, reducing, or oxygen-poor atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Roasting occurs in an oxidizing atmosphere with an excess of air to promote oxidation.
Feed Materials
Calcination is typically used on hydrates, carbonates, and materials with volatile organic components.
Roasting is predominantly used on sulfide ores.
Gaseous Byproducts
Calcination primarily produces non-toxic gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O).
Roasting produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂), a significant pollutant that must be captured and often converted into sulfuric acid to prevent environmental damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process selection is dictated entirely by the chemical transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is to produce lime from limestone: You must use calcination to drive off CO₂ without any other reactions.
- If your primary focus is to prepare zinc sulfide ore for smelting: You must use roasting to convert the sulfide (ZnS) into zinc oxide (ZnO).
- If your primary focus is to remove the water of hydration from a mineral: You need calcination to gently drive off the H₂O without altering the base mineral.
- If your primary focus is to create an oxide feedstock from a sulfide ore: Roasting is the essential first step in your metallurgical flowsheet.
Ultimately, the distinction is simple: calcination is a thermal separation, while roasting is a thermal reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Calcination | Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition; remove volatile substances | Chemical conversion via oxidation |
| Atmosphere | Inert or limited air (oxygen-poor) | Excess air (oxidizing) |
| Typical Feed Material | Carbonates (e.g., limestone), hydrates | Sulfide ores (e.g., zinc sulfide) |
| Key Byproduct | CO₂, H₂O (water vapor) | SO₂ (sulfur dioxide) |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing?
Whether your goal is precise thermal decomposition or controlled oxidation, KINTEK's advanced lab furnaces provide the exact atmospheric control and temperature uniformity you need. Our equipment is designed for reliability and precision in demanding applications like materials purification and extractive metallurgy.
Let KINTEK be your partner in the lab. We specialize in the durable, high-performance equipment that research and quality control laboratories depend on.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thermal treatment requirements and find the perfect solution for your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















