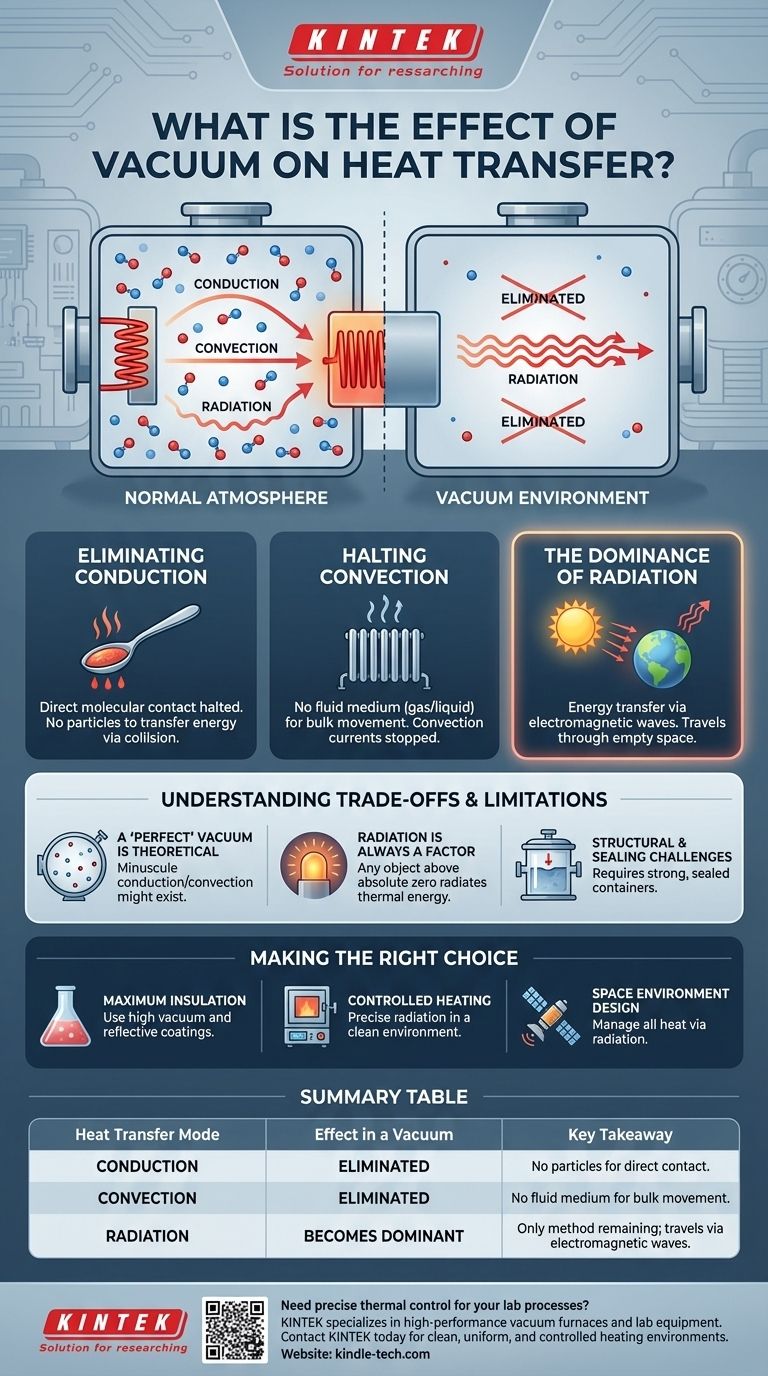
In short, a vacuum fundamentally alters heat transfer by virtually eliminating two of the three methods of thermal exchange. Because a vacuum is a space devoid of matter, it removes the medium required for both conduction and convection, leaving only thermal radiation as a viable path for heat to travel. This makes a vacuum one of the most effective thermal insulators known.
A vacuum does not stop heat transfer entirely, but it forces it into a single mode: radiation. By eliminating the transfer of heat through physical particle interaction (conduction and convection), it becomes a powerful tool for either insulating a system or applying heat with extreme precision.
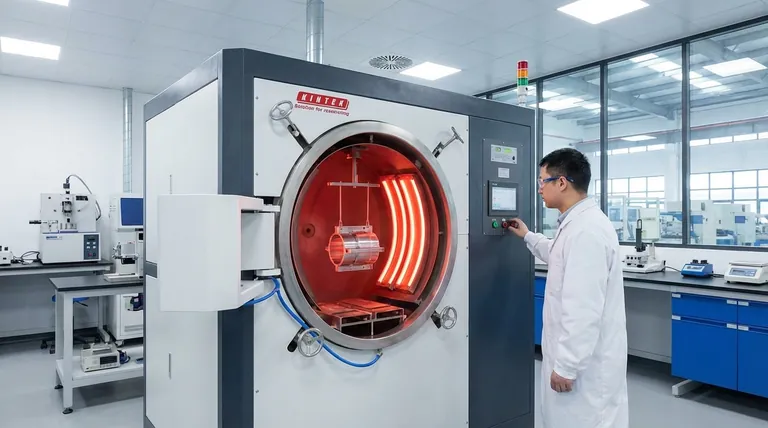

Why a Vacuum Disrupts Conventional Heat Transfer
To understand the effect of a vacuum, we must first recognize the three ways heat moves. A vacuum systematically neutralizes the two methods that rely on physical particles.
Eliminating Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct molecular contact. Think of a metal spoon heating up in a hot cup of coffee; the energy travels from one molecule to the next up the handle.
A vacuum, by definition, has an extremely low density of particles. With no molecules to vibrate against each other, the pathway for conduction is effectively removed.
Halting Convection
Convection is heat transfer through the bulk movement of fluids (gases or liquids). A radiator heats the air around it, which then rises, creating a current that circulates warmth throughout a room.
Since a vacuum removes the air or other gases, there is no fluid medium available to create convection currents. Heat cannot be carried from one place to another by flowing matter.
The Dominance of Thermal Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. Unlike conduction and convection, it requires no medium to propagate.
This is how the Sun heats the Earth across the vacuum of space. In an engineered vacuum, like a vacuum furnace, radiation becomes the sole method for transferring heat from a heating element to the product inside.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While a powerful tool, a vacuum is not a magical barrier to all heat. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
A "Perfect" Vacuum is Theoretical
Achieving a perfect vacuum with zero particles is practically impossible. Industrial and commercial vacuums still contain some stray molecules, meaning a minuscule amount of conduction and convection can still occur, though it is almost always negligible.
Radiation is Always a Factor
A vacuum only stops particle-based heat transfer. Any object with a temperature above absolute zero will radiate thermal energy.
Therefore, two objects facing each other across a vacuum will still exchange heat. The effectiveness of this transfer depends on their temperature difference and surface properties, such as color and texture (known as emissivity). This is why vacuum flasks have reflective silver coatings to minimize radiative heat loss.
Structural and Sealing Challenges
Creating and maintaining a vacuum requires a strong, perfectly sealed container capable of withstanding the crushing pressure of the outside atmosphere. This presents a significant engineering and cost challenge for any application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Leveraging a vacuum for thermal management requires aligning your approach with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum insulation: Your goal is to create a high-quality vacuum between two surfaces and use highly reflective coatings to minimize the inevitable heat transfer from radiation.
- If your primary focus is controlled heating in a clean environment: Use a vacuum to eliminate unpredictable convection and remove sources of contamination, relying on precisely controlled heating elements that transfer energy via radiation.
- If your primary focus is designing for a space environment: You must manage all thermal energy through radiation, using specialized surfaces and radiators to either reject waste heat or absorb solar energy as needed.
Ultimately, understanding that a vacuum leaves only radiation in play is the key to mastering thermal control in any engineered system.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | Effect in a Vacuum | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Eliminated | No particles for direct molecular contact. |
| Convection | Eliminated | No fluid medium for bulk movement of heat. |
| Radiation | Becomes Dominant | Only method remaining; travels via electromagnetic waves. |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces and lab equipment that leverage the principles of vacuum heat transfer. Our solutions provide clean, uniform, and precisely controlled heating environments, free from convection inconsistencies and contamination.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our vacuum technology can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process



















