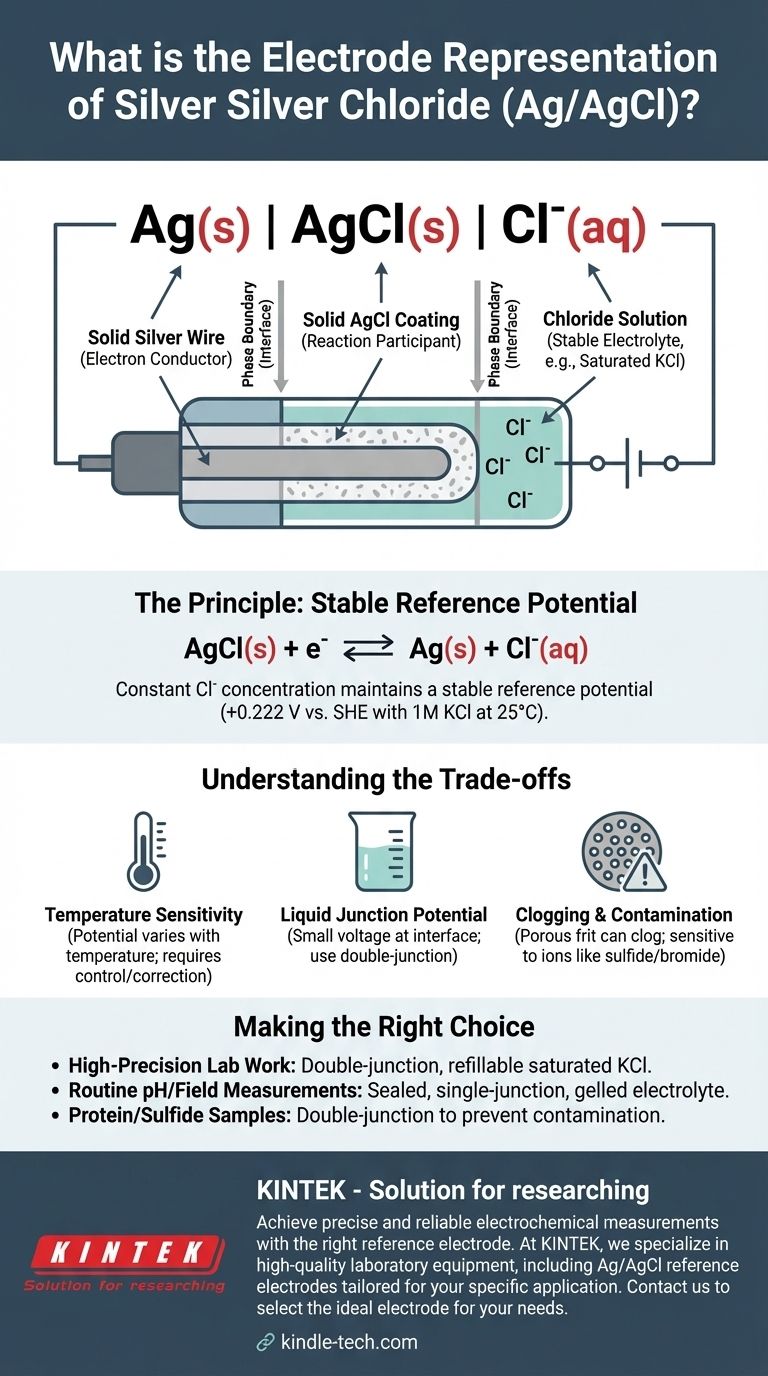
The standard shorthand representation for a silver-silver chloride electrode is Ag(s) | AgCl(s) | Cl⁻(aq). This electrochemical notation describes the physical and chemical phases of the electrode, from the solid silver metal wire to the aqueous solution containing chloride ions. The specific potential of the electrode is critically dependent on the concentration of these chloride ions.
This notation is more than a technical label; it's a schematic for one of the most reliable and common reference electrodes in electrochemistry. It describes a system designed to maintain a constant, stable potential, providing a fixed baseline against which the potentials of other electrodes can be accurately measured.

Deconstructing the Electrode Notation
The representation Ag(s) | AgCl(s) | Cl⁻(aq) details the structure of the electrode from the inside out. Each component and symbol has a precise meaning.
The Solid Phase: Ag(s)
This represents a solid silver wire. This wire serves as the electron conductor, connecting the electrode to the external measuring circuit (a voltmeter or potentiostat).
The Phase Boundary: |
The single vertical bar | signifies a phase boundary. It indicates the interface where two different physical states meet, in this case, the solid silver metal and the solid silver chloride layer.
The Insoluble Salt Layer: AgCl(s)
This denotes a layer of solid, sparingly soluble silver chloride that is coated directly onto the surface of the silver wire. This layer is the heart of the electrode's function, participating directly in the electrochemical reaction.
The Second Phase Boundary: |
A second vertical bar marks the boundary between the solid silver chloride coating and the surrounding aqueous electrolyte solution.
The Electrolyte Solution: Cl⁻(aq)
This represents the aqueous solution that the coated wire is immersed in. This solution must contain a known and constant concentration of chloride ions (Cl⁻). Typically, a potassium chloride (KCl) solution is used, often at a specific concentration like 1 M or, most commonly, a saturated solution.
The Principle of a Reference Electrode
The Ag/AgCl electrode is valued not for its own reaction, but for its stability. It provides a constant voltage that acts as a reliable zero point for other measurements.
The Governing Reaction
The stable potential is established by a reversible equilibrium between the solid components and the chloride ions in the solution. The half-reaction is:
AgCl(s) + e⁻ ⇌ Ag(s) + Cl⁻(aq)
As long as the concentration (more accurately, the activity) of the chloride ions in the solution remains constant, the potential of this half-cell will not change.
The Importance of Constant Chloride Concentration
Using a saturated KCl solution ensures the Cl⁻ concentration is constant and reproducible. If some water evaporates, more KCl salt simply dissolves to maintain saturation. This is why the reference potential is so stable. For a 1M KCl solution at 25°C (298 K), this potential is +0.222 V relative to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly reliable, the Ag/AgCl electrode is not without limitations that require consideration for precise work.
Temperature Sensitivity
The electrode's potential is a function of temperature. For highly accurate measurements, the temperature of the cell must be controlled or the measured potentials must be corrected for temperature variations.
Liquid Junction Potential
When the electrode's KCl solution comes into contact with a different sample solution, a small voltage known as a liquid junction potential can develop at the interface. This introduces a small but systematic error into the measurement, which can be minimized using a double-junction electrode.
Clogging and Contamination
The porous frit that allows electrical contact between the internal solution and the sample can become clogged. It can also be contaminated by ions in the sample (like sulfide, bromide, or iodide) that can react with the silver, causing the electrode potential to drift over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Measurement
Your application dictates which electrode configuration is best.
- If your primary focus is high-precision lab work: Use a double-junction Ag/AgCl electrode with a refillable, saturated KCl solution to minimize junction potential and allow for easy maintenance.
- If your primary focus is routine pH or field measurements: A sealed, single-junction electrode with a gelled electrolyte is durable, low-maintenance, and perfectly adequate.
- If your primary focus is analyzing samples containing proteins or sulfides: You must use a double-junction electrode to prevent clogging and contamination of the primary reference junction.
Understanding this notation transforms it from a cryptic label into a functional schematic for reliable electrochemical measurement.
Summary Table:
| Component | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Silver Wire | Ag(s) | Conductor connecting to the external circuit. |
| Silver Chloride Coating | AgCl(s) | Insoluble salt layer enabling the reversible reaction. |
| Chloride Ion Solution | Cl⁻(aq) | Aqueous electrolyte (e.g., KCl) with constant Cl⁻ concentration. |
| Phase Boundary |
Achieve precise and reliable electrochemical measurements with the right reference electrode.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality laboratory equipment, including a range of Ag/AgCl reference electrodes tailored for your specific application—whether you require high-precision double-junction models for sensitive lab work or durable, low-maintenance options for routine analysis.
Our experts can help you select the ideal electrode to ensure stable potential, minimize errors, and enhance the accuracy of your research.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our reliable consumables and equipment can support your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercurous sulfate? A Guide to Chloride-Free Electrochemistry
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?



















