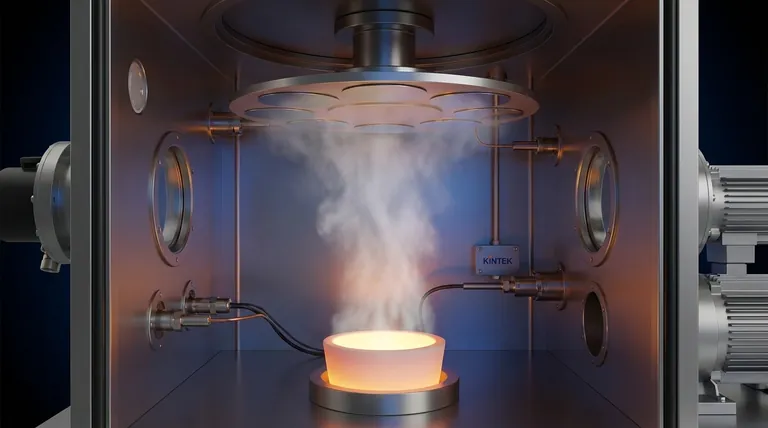
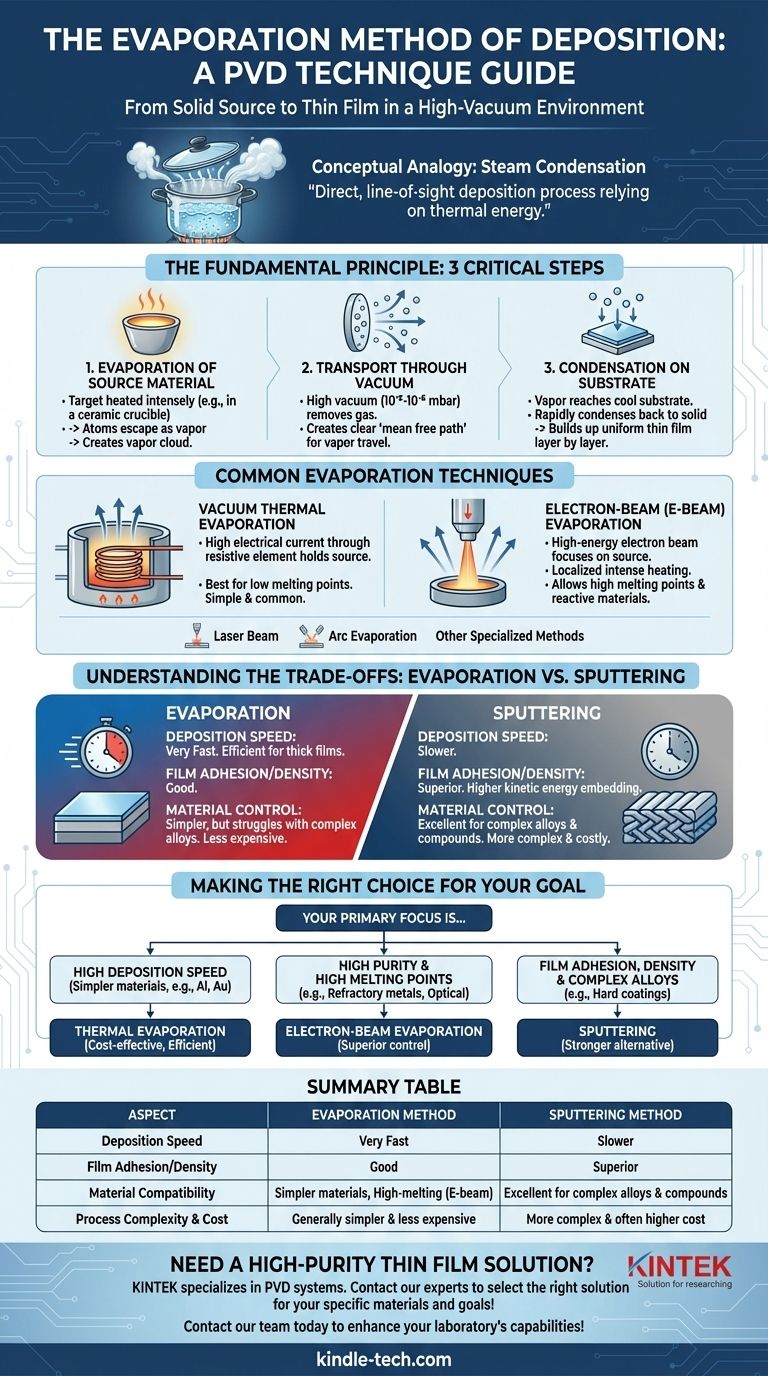
In essence, the evaporation method is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique where a source material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler surface, called a substrate, forming a thin, solid film. The entire process is conceptually similar to the way steam from a boiling pot of water condenses on a cold lid.
Evaporation is a direct, line-of-sight deposition process that relies on thermal energy to transform a solid source into a vapor. Its primary advantages are speed and simplicity, but its effectiveness is dictated by the ability to maintain a high vacuum and control the material's evaporation rate.

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Film
The evaporation process can be broken down into three critical steps, each occurring within a high-vacuum environment to ensure the purity and quality of the final film.
Step 1: Evaporation of the Source Material
The process begins with the source material, or "target," placed inside a holder, such as a ceramic crucible. This material is heated intensely.
As the material's temperature rises, its atoms gain enough thermal energy to break their bonds and escape the surface as a vapor. This generates a cloud of vapor particles, creating a specific vapor pressure within the chamber.
Step 2: Transport Through a Vacuum
The chamber is kept under a very high vacuum, typically at pressures of 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ millibars. This is arguably the most critical condition for the process.
This vacuum removes almost all air and other gas molecules. Its purpose is to create a clear, unobstructed "mean free path" for the vaporized atoms to travel from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles, which would cause them to scatter or react.
Step 3: Condensation on the Substrate
The vapor stream travels in a straight line until it reaches the substrate, which is strategically placed and kept at a lower temperature.
Upon contact with the cooler substrate, the vapor atoms lose their thermal energy and rapidly condense back into a solid state. They attach to the surface, gradually building up layer by layer to form a uniform thin film.
Common Evaporation Techniques
While the principle remains the same, the method of heating the source material defines the specific technique.
Vacuum Thermal Evaporation
This is the most common form, where a high electrical current is passed through a resistive element (the crucible or a "boat") holding the source material. The resistance generates intense heat, causing the material to evaporate. It is best suited for materials with relatively low melting points.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
In this more advanced method, a high-energy beam of electrons is focused onto the source material. This provides highly localized and intense heating, allowing for the deposition of materials with very high melting points or those that would react with a heating crucible.
Other Specialized Methods
Other techniques exist for specific applications, including laser beam evaporation, which uses a high-power laser as the heat source, and arc evaporation, which uses an electric arc to vaporize the material. These are used for depositing specific types of materials or achieving unique film properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Evaporation vs. Sputtering
Evaporation is often compared to sputtering, another major PVD technique. Understanding their differences is key to choosing the right method.
Deposition Rate
Evaporation is generally a much faster deposition process than sputtering. This makes it highly efficient for applications requiring thick films or high throughput.
Film Adhesion and Density
Sputtering typically produces films with superior adhesion and higher density. This is because sputtered atoms are ejected with much higher kinetic energy and embed themselves more effectively onto the substrate surface.
Material and Process Control
Evaporation can struggle with compound materials or alloys, as different elements may evaporate at different rates. Sputtering offers better stoichiometric control for complex materials. However, simple thermal evaporation is often a mechanically simpler and less expensive process to implement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between deposition methods requires aligning the technique's strengths with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high deposition speed for simpler materials: Thermal evaporation is often the most cost-effective and efficient choice for coatings like aluminum or gold.
- If your primary focus is high purity and depositing high-melting-point materials: Electron-beam evaporation offers the superior control and capability needed for refractory metals or optical coatings.
- If your primary focus is film adhesion, density, and complex alloy deposition: You should evaluate sputtering as a stronger alternative, especially for hard coatings or functional thin films.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can confidently select the deposition technique that aligns perfectly with your material and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Evaporation Method | Sputtering Method |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Film Adhesion/Density | Good | Superior |
| Material Compatibility | Simpler materials, high-melting-point (with E-beam) | Excellent for complex alloys & compounds |
| Process Complexity & Cost | Generally simpler & less expensive | More complex & often higher cost |
Need to deposit a high-purity thin film for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including evaporation and sputtering systems. Whether your priority is high-speed coating with thermal evaporation or superior film quality with e-beam evaporation, our experts can help you select the right PVD solution for your specific materials and performance goals.
Contact our team today to discuss your deposition requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Fast, Cost-Effective Thin Films
- What does an e-beam do? A Versatile Tool for Welding, Sterilization, and Microfabrication
- Is thermal evaporation better than magnetron sputtering? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the principle of electron beam deposition? A Guide to High-Speed, Versatile Thin Films
- What is the method of evaporation deposition? A Guide to Creating Ultra-Thin Films
- How does e-beam evaporation work? Achieve High-Purity Thin Films for Demanding Applications
- What is the industrial process of evaporation? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition Techniques
- What are the factors affecting sputtering? Control Your Thin Film Deposition Process



















