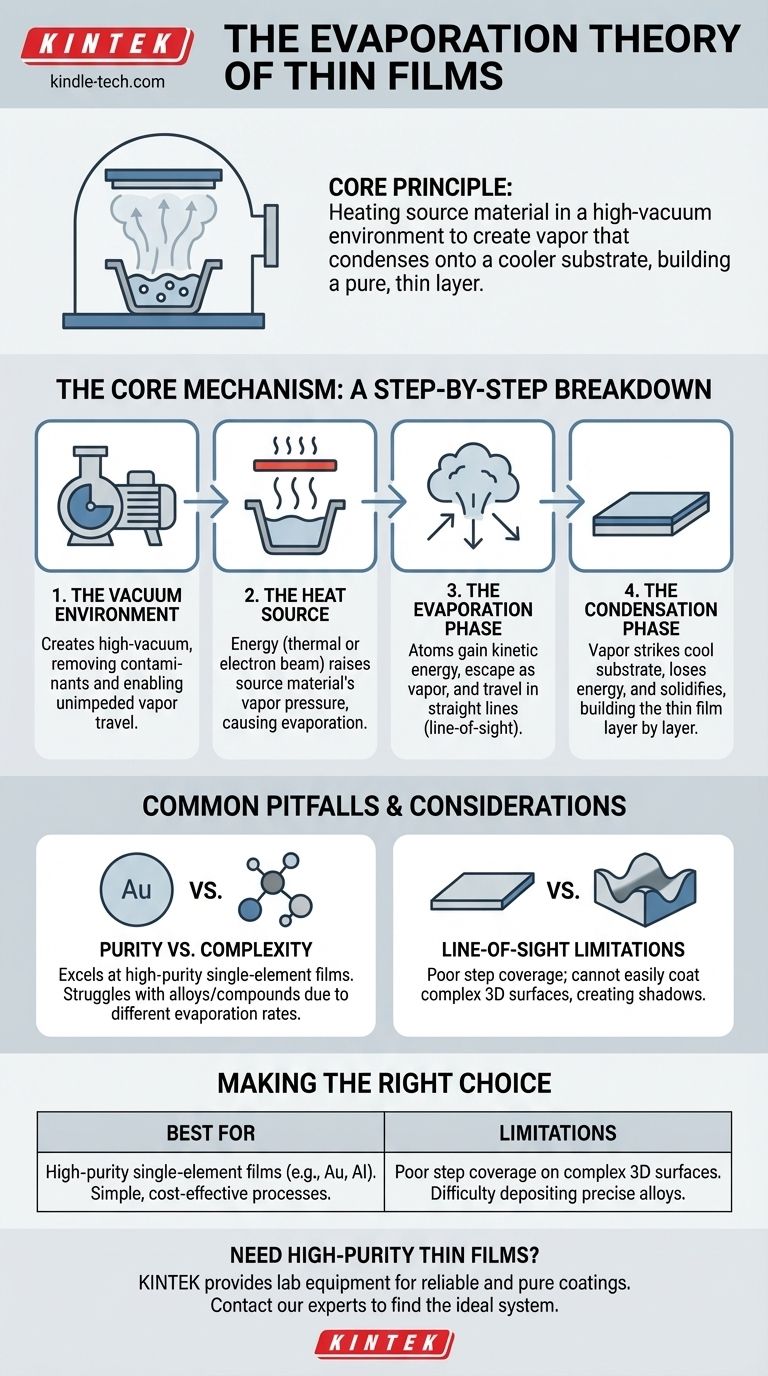
At its core, the evaporation theory of thin films describes a process where a source material is heated until it turns into a vapor within a high-vacuum chamber. This vapor then travels unimpeded and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, building up a highly pure, thin layer of the material atom by atom. It is a fundamental technique within the family of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods.
The central principle is straightforward: use heat to "boil" a material in a vacuum, allowing its vapor to travel in a straight line and solidify onto a target. This process is analogous to water vapor from a boiling pot condensing on a cool lid above it.
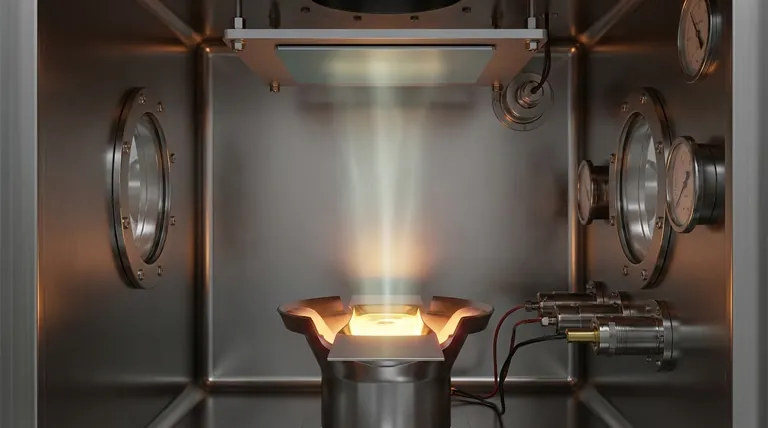

The Core Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly understand the theory, it's best to break the process down into its distinct, sequential stages. Each step is critical for achieving a high-quality film.
The Vacuum Environment
The entire process begins by creating a high-vacuum environment. This removes air and other unwanted gas molecules from the chamber.
This vacuum is essential for two reasons: it prevents the hot source material from reacting with contaminants, and it clears the path for evaporated atoms to travel to the substrate.
The Heat Source
Energy is applied to the source material, typically held in a container called a crucible. This energy is usually thermal, generated by resistance heating or an electron beam.
The heat must be sufficient to raise the material's vapor pressure significantly, providing the energy needed for its atoms to escape the solid or liquid state and enter a gaseous phase.
The Evaporation Phase
As the source material heats up, its atoms gain enough kinetic energy to evaporate. They are liberated from the source as a vapor.
Inside the vacuum, these vaporized atoms travel in straight lines, a characteristic known as line-of-sight travel.
The Condensation Phase
When the vaporized atoms strike the cooler substrate, they rapidly lose their energy and condense back into a solid state.
This process of condensation builds the thin film, layer by layer, on the substrate's surface. The final thickness of the film is controlled by the rate of evaporation and the duration of the process.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While effective, the simplicity of evaporation carries specific trade-offs that are critical to understand. This method is not universally applicable for all materials or film structures.
Purity vs. Complexity
Evaporation excels at creating very high-purity films from a single element, as the vacuum prevents contamination.
However, it struggles with alloys or compound materials. Different elements within a compound will evaporate at different rates based on their unique vapor pressures, making it difficult to maintain the correct stoichiometry in the final film.
Line-of-Sight Limitations
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, evaporation has poor step coverage. It cannot easily coat complex, three-dimensional surfaces with undercuts or deep trenches.
Areas not in the direct line of sight of the source will receive little to no deposition, creating "shadows" on the substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principles of evaporation allows you to determine when it is the most appropriate deposition method for your objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, single-element films: Evaporation is an excellent, cost-effective choice, particularly for materials like aluminum, gold, or chromium in applications like mirror coatings or electrical contacts.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object uniformly: You should consider alternative PVD methods, such as sputtering, which provide superior step coverage.
- If your primary focus is depositing a precise alloy or compound: Advanced evaporation techniques (co-evaporation) or sputtering are necessary to control the film's final composition accurately.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation is a foundational thin-film technique valued for its simplicity and ability to produce exceptionally pure films.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Removes contaminants, enables straight-line vapor travel. | Essential for purity and process efficiency. |
| Heat Source | Provides energy to vaporize the source material. | Must overcome the material's vapor pressure. |
| Evaporation | Atoms enter the gas phase and travel to the substrate. | Travel is line-of-sight, creating shadowing effects. |
| Condensation | Vapor atoms solidify on the substrate, building the film. | Determines film thickness, adhesion, and quality. |
| Best For | Limitations | |
| High-purity single-element films (e.g., Au, Al). | Poor step coverage on complex 3D surfaces. | |
| Simple, cost-effective deposition processes. | Difficulty depositing precise alloys or compounds. |
Need to deposit high-purity thin films for your research or production?
The evaporation theory is the foundation for reliable and pure coatings. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables, including evaporation systems and crucibles, to bring this theory to life in your laboratory. Whether you're working on mirror coatings, electrical contacts, or basic research, our solutions are designed for precision and performance.
Let's discuss your specific thin-film deposition needs. Contact our experts today to find the ideal system for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating


















