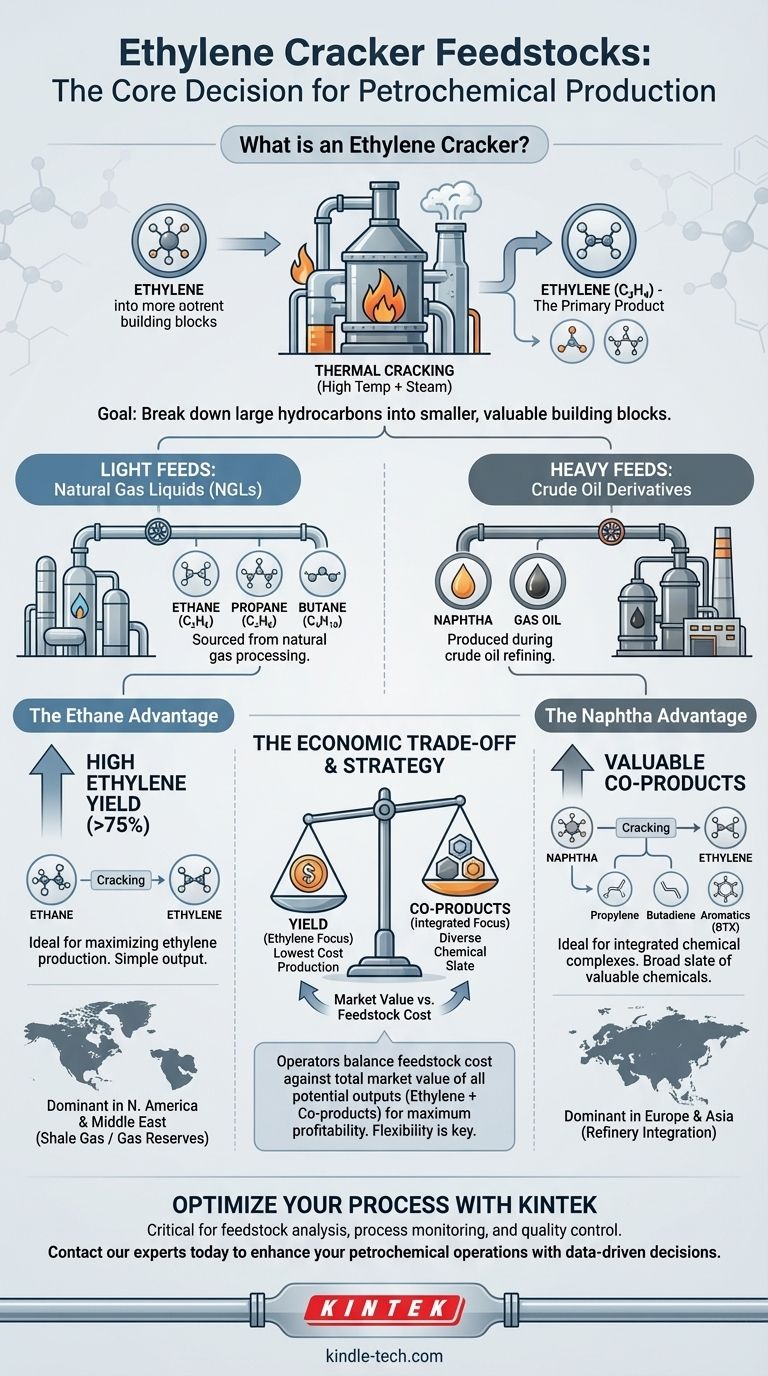
The primary feedstocks for an ethylene cracker are hydrocarbons derived from either natural gas or crude oil. The most common feedstocks include light hydrocarbons like ethane, propane, and butane, as well as heavier liquids from oil refining such as naphtha and gas oil. The specific choice depends heavily on regional availability, cost, and the desired output of other valuable chemicals.
The core decision in operating an ethylene cracker is not just what feedstock to use, but why. This choice is a strategic trade-off between maximizing the yield of ethylene (from lighter feeds like ethane) and producing a broader, more valuable slate of chemical co-products (from heavier feeds like naphtha).

What is an Ethylene Cracker? A Quick Primer
The Goal: Thermal Cracking
An ethylene cracker, more formally known as a steam cracker, is the heart of a modern petrochemical plant. Its function is to break down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more valuable ones.
This is achieved through thermal cracking, a process that uses extremely high temperatures (around 850°C or 1560°F) and steam to "crack" the feedstock molecules.
The Primary Product: Ethylene
The main target of this process is ethylene (C₂H₄), one of the most important building blocks in the chemical industry. Ethylene is the starting point for producing polyethylene—the world's most common plastic—as well as countless other chemicals.
The Spectrum of Feedstocks: From Light to Heavy
Ethylene crackers can be fed a range of hydrocarbons, which are typically categorized as "light" or "heavy."
Light Feeds: Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs)
These feedstocks are sourced from natural gas processing.
- Ethane (C₂H₆): The simplest and most preferred feedstock when the sole goal is maximizing ethylene production.
- Propane (C₃H₈): Another common NGL feed that produces ethylene along with a significant amount of propylene.
- Butane (C₄H₁₀): Less common than ethane or propane but still a viable light feedstock.
Heavy Feeds: Crude Oil Derivatives
These liquid feedstocks are produced during the refining of crude oil.
- Naphtha: A primary feedstock, especially in Europe and Asia. It's a complex mixture of hydrocarbons heavier than propane but lighter than gasoline.
- Gas Oil: A heavier feedstock than naphtha, similar to diesel fuel. It is used when it is economically advantageous but produces an even more complex mix of outputs.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Yield vs. Co-products
The choice of feedstock is the most critical economic decision for a cracker operator. It directly determines the plant's entire output and profitability.
The Ethane Advantage: High Ethylene Yield
When a cracker uses ethane, the process is relatively simple. The ethane molecule is cracked almost exclusively into ethylene. This results in a very high "yield" of ethylene, often over 75% by weight.
This is ideal when ethylene prices are high and the cost of ethane is low, a situation common in regions with abundant shale gas, like the United States.
The Naphtha Advantage: A Slate of Co-products
Cracking a heavier and more complex feedstock like naphtha produces a much wider array of products. The ethylene yield is lower (around 30%), but the plant also produces significant quantities of other valuable chemicals.
These co-products include:
- Propylene: The building block for polypropylene.
- Butadiene: Used to make synthetic rubber.
- Aromatics (BTX): Benzene, toluene, and xylene, which are foundational for many other chemical processes.
This strategy is beneficial for large, integrated chemical complexes that can use or sell this entire slate of products.
The Economic Calculation
Ultimately, the decision is purely economic. Operators constantly compare the cost of a feedstock against the total market value of all its potential outputs (ethylene plus all co-products). The most profitable option wins.
Why Feedstock Choice Varies Globally
The dominant feedstock in a region is a direct reflection of its natural resources.
North America & the Middle East: The Ethane Leaders
Thanks to the shale gas revolution in the U.S. and massive natural gas reserves in the Middle East, these regions have access to abundant, low-cost ethane. Consequently, most crackers in these areas are designed to run on ethane.
Europe & Asia: The Naphtha Norm
These regions have less access to cheap NGLs and have historically relied on imported crude oil. Their large, established refineries make naphtha a readily available and economically logical feedstock for their crackers.
How Feedstock Determines a Plant's Strategy
- If your primary focus is maximizing ethylene production at the lowest cost: Ethane is the ideal feedstock, assuming you have access to an inexpensive supply.
- If your primary focus is operating an integrated chemical complex: Heavier feedstocks like naphtha are more strategic, as they supply a diverse range of valuable chemical building blocks beyond just ethylene.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and market opportunism: A cracker designed to handle multiple feedstock types (a "flexible cracker") offers the greatest advantage, allowing operators to switch based on market prices.
Understanding the feedstock is the key to understanding the economic engine of the entire petrochemical industry.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Type | Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Light Feeds (NGLs) | Ethane, Propane | High ethylene yield (>75% for ethane); simpler output; ideal for maximizing ethylene production. |
| Heavy Feeds (Oil Derivatives) | Naphtha, Gas Oil | Lower ethylene yield (~30%); produces valuable co-products (propylene, butadiene, aromatics); ideal for integrated chemical complexes. |
Optimize Your Petrochemical Processes with KINTEK
Choosing the right feedstock is critical for the efficiency and profitability of your ethylene production. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables essential for analyzing feedstock properties, monitoring cracking processes, and ensuring product quality.
Whether you are focused on maximizing ethylene yield from light feeds or managing the complex output from heavier feeds, our solutions support your R&D and quality control needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your petrochemical operations and help you make data-driven feedstock decisions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
People Also Ask
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab













