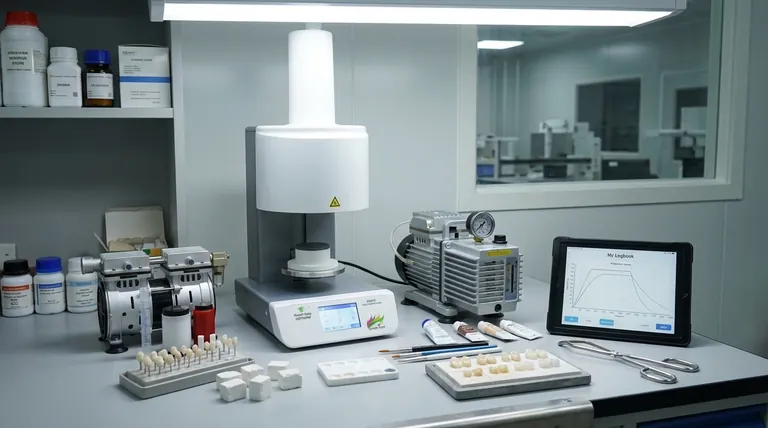
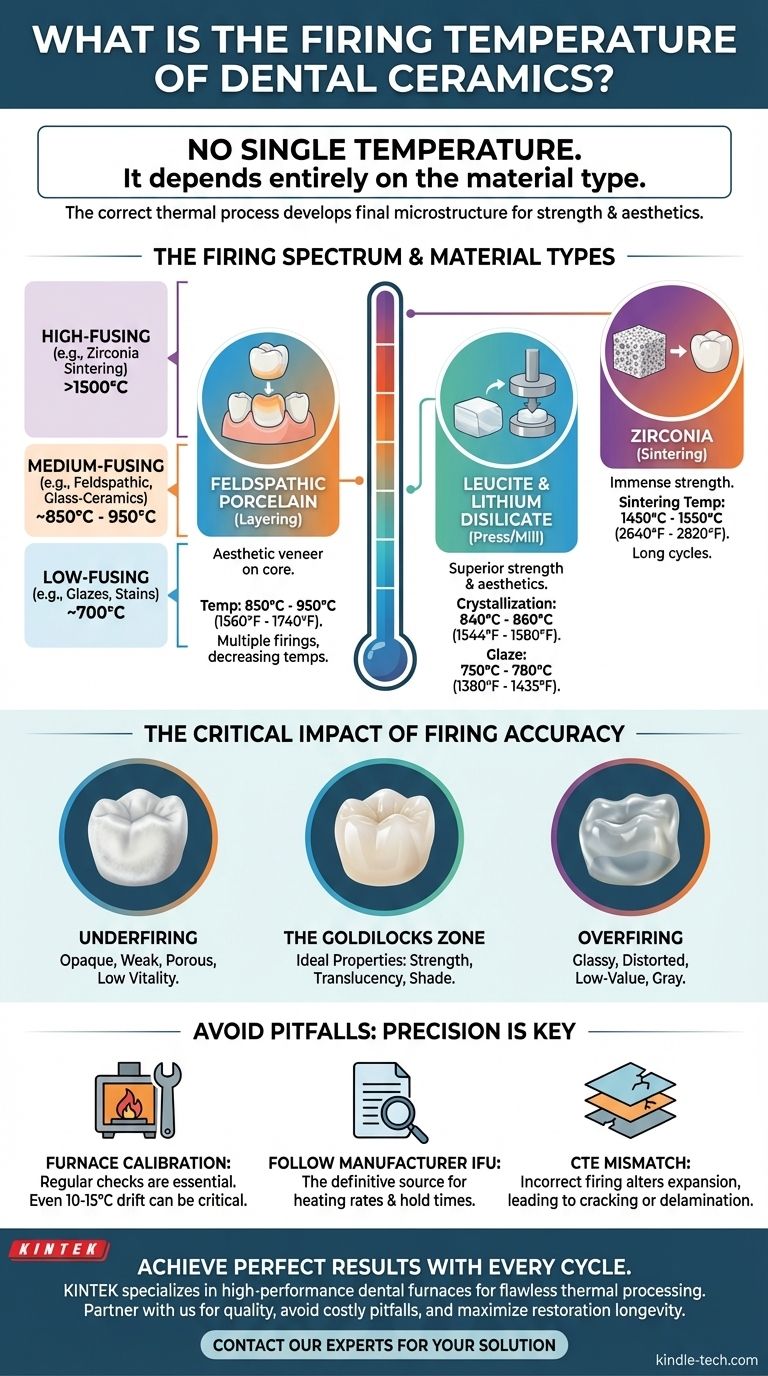
There is no single firing temperature for all dental ceramics. The correct temperature is dictated entirely by the specific type of ceramic material being used, with a vast range spanning from approximately 700°C for low-fusing glazes to over 1500°C for sintering high-strength zirconia. Using the wrong temperature, even by a small margin, can ruin the restoration's strength and aesthetic properties.
The core principle to understand is that firing is not just about heating; it's a precise thermal process that develops the ceramic's final microstructure. The specific temperature target unlocks the intended balance of strength, translucency, and color for that unique material system.

The Firing Spectrum: Why Material Type Dictates Temperature
Dental ceramics are not a monolithic group. They are a family of materials, each with a unique composition and a corresponding thermal cycle required to achieve its desired clinical properties.
Feldspathic Porcelain (Layering Ceramics)
These are traditional, glass-based materials primarily used to build up the aesthetic veneer layer over a stronger core (like metal or zirconia).
Their firing temperatures are relatively low, typically falling between 850°C and 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F). Multiple firings are often needed, with each subsequent firing (e.g., for stain or glaze) done at a slightly lower temperature to avoid distorting the previous layers.
Leucite & Lithium Disilicate (Pressable/Millable Glass-Ceramics)
These materials, such as IPS Empress and IPS e.max, offer a superior combination of strength and aesthetics compared to feldspathic porcelain. They are processed differently.
They are first pressed or milled, then undergo a crystallization firing cycle around 840°C - 860°C (1544°F - 1580°F) to develop their final high-strength crystal structure. A separate, lower-temperature glaze firing around 750°C - 780°C (1380°F - 1435°F) is then applied to create the final surface luster.
Zirconia (High-Strength Polycrystalline Ceramics)
Zirconia is in a class of its own. It does not "fire" in the glassy sense; it sinters. The material starts as a porous, chalk-like block ("green state") and is heated to extremely high temperatures.
This sintering process fuses the individual zirconia particles together, causing the restoration to shrink significantly and gain its immense strength. Sintering temperatures are the highest in dental ceramics, typically ranging from 1450°C to 1550°C (2640°F - 2820°F) and lasting for several hours.
The Critical Impact of Firing Accuracy
As the references highlight, minor deviations from the ideal firing cycle can lead to major clinical failures. The temperature directly controls the final balance of the ceramic's glass and crystalline phases.
Underfiring: The Opaque, Weak Result
If the temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the ceramic particles do not fuse completely. This results in a porous, under-sintered material that appears opaque, chalky, and reflective, completely lacking the vitality of a natural tooth. It is also significantly weaker and more prone to fracture.
Overfiring: The Glassy, Distorted Outcome
When the temperature is too high, the material's glassy phase flows excessively. This can cause the restoration to slump and distort, ruining the marginal fit. Aesthetically, it becomes overly translucent, often taking on a low-value, gray appearance as too much light passes through it.
The "Goldilocks Zone": Achieving Ideal Properties
Hitting the manufacturer's recommended temperature and cycle is the only way to achieve the intended properties. This "Goldilocks Zone" ensures the correct level of particle fusion and crystal growth, producing a restoration with the desired strength, translucency, and shade.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving a perfect firing cycle involves more than just setting the right temperature on the furnace display.
Furnace Calibration is Non-Negotiable
The temperature displayed on your furnace screen can easily drift from the actual temperature inside the muffle. A deviation of just 10-15 degrees can be enough to push a ceramic from an ideal to an over- or under-fired state. Regular calibration using silver or other calibration kits is essential for predictable results.
Following Manufacturer Instructions (IFU)
The temperature ranges provided here are general guidelines. The Instructions for Use (IFU) provided by the material manufacturer are the definitive source of truth. Always adhere to their specific recommendations for heating rates, target temperatures, and hold times.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) Mismatch
Incorrect firing doesn't just affect aesthetics; it alters a material's physical properties, including its Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). If you are layering one ceramic over another (e.g., porcelain over a zirconia core), an altered CTE can create internal stress, leading to delayed cracking, chipping, or delamination of the veneer layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your firing protocol must be tailored to your material and your clinical objective.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics with layering porcelain: Your key is executing multiple, precise, low-temperature firings to build color and form without distorting underlying layers.
- If your primary focus is strength with monolithic zirconia: Your key is a fully calibrated, high-temperature sintering cycle to ensure complete densification and maximum fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is efficiency with pressable ceramics: Your key is strictly following the two-stage process of pressing and then glaze firing to guarantee optimal fit, strength, and surface finish.
Mastering the science of thermal processing is fundamental to producing durable and lifelike dental restorations.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Typical Firing Temperature Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic Porcelain | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) | Aesthetic veneer layering |
| Leucite & Lithium Disilicate | 840°C - 860°C (Crystallization) | Strength & aesthetics for pressable/millable ceramics |
| Zirconia | 1450°C - 1550°C (2640°F - 2820°F) | Sintering for maximum strength |
Achieve Perfect Results with Every Firing Cycle
Precision is non-negotiable in dental ceramics. KINTEK specializes in high-performance dental furnaces and consumables designed for flawless thermal processing. Whether you are working with layered porcelain, pressable ceramics, or high-strength zirconia, our equipment delivers the accuracy and reliability your laboratory demands.
Let KINTEK be your partner in quality:
- Ensure precise temperature control for optimal strength and aesthetics.
- Avoid the costly pitfalls of underfiring and overfiring.
- Maximize the longevity and performance of your restorations.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your specific ceramic materials and clinical goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can ceramic teeth stain? Why High-Quality Dental Ceramics Resist Discoloration
- What is the effect of high speed sintering on zirconia? Dramatically Faster Cycles with Critical Trade-offs
- Which is better ceramic or metal crown? Weighing Aesthetics vs. Durability for Your Smile
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconia? Achieve Optimal Strength and Aesthetics
- What is ceramic dental restoration? A Guide to Modern, Aesthetic, and Durable Tooth Repair
- How long does ceramic teeth last? Maximize Your Smile's Lifevity with Expert Care
- What is the most common dental ceramics? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- What types of materials can a Dental Press Furnace process? Versatile Solutions for High-Performance Ceramics



















