PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. A PVD machine is the equipment used to perform this advanced coating process, where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum and deposited onto a target surface as a pure, high-performance coating.
The term "PVD machine" refers to the entire vacuum chamber system that facilitates Physical Vapor Deposition. Understanding the process is more critical than just knowing the name, as it reveals how thin-film coatings are created to dramatically enhance the properties of a material.
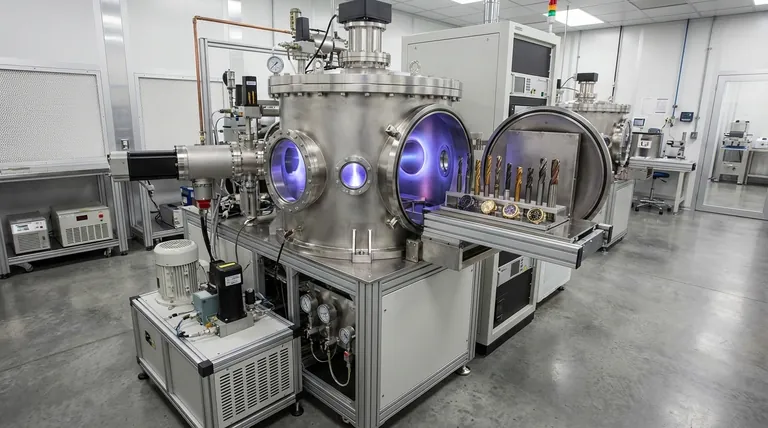

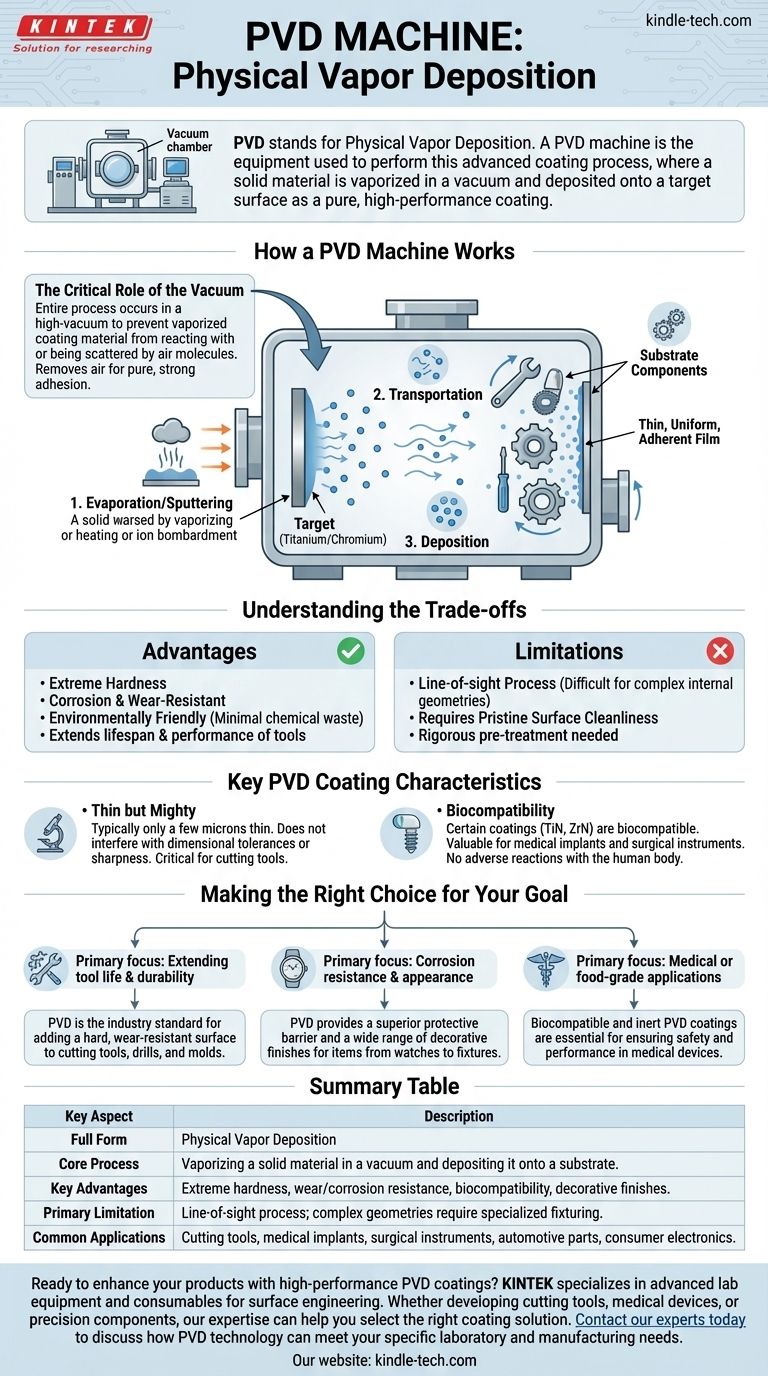
How a PVD Machine Works
A PVD machine is not a single device but a sophisticated system built around a vacuum chamber. The core function is to create an environment where a coating material can be turned into a vapor, transported, and then condensed onto a substrate.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a high-vacuum environment. This is essential to prevent the vaporized coating material from reacting with or being scattered by air molecules like oxygen and nitrogen.
Removing air ensures the final coating is pure and adheres strongly to the part's surface.
The Three Stages of Deposition
The process inside the machine, regardless of the specific technique, follows three fundamental steps:
-
Evaporation/Sputtering: A solid "target" material (like titanium or chromium) is vaporized. This can be done by heating it to its boiling point (evaporation) or by bombarding it with high-energy ions (sputtering).
-
Transportation: The vaporized atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum chamber from the source material to the components being coated.
-
Deposition: The vapor condenses on the target surfaces, forming a thin, uniform, and highly adherent film. The parts are often rotated on fixtures to ensure an even coating on all sides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD coatings offer remarkable benefits, the process involves specific considerations and is not suitable for every application.
The Advantages
PVD coatings are known for being extremely hard, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant. They can significantly increase the lifespan and performance of tools and components.
The process is also environmentally friendly compared to older electroplating methods, as it produces minimal chemical waste.
The Limitations
PVD is a line-of-sight process. This means the coating material travels in a straight line, making it difficult to coat complex internal geometries or deeply recessed areas without sophisticated part rotation.
Additionally, the process requires pristine surface cleanliness. Any contamination on the part will prevent proper coating adhesion, necessitating rigorous pre-treatment and cleaning steps.
Key PVD Coating Characteristics
The final film produced by a PVD machine is not just a simple layer; its properties are distinct and highly desirable for technical applications.
Thin but Mighty
PVD coatings are typically very thin, often only a few microns (thousandths of a millimeter). This ensures they don't interfere with the part's dimensional tolerances or sharpness, which is critical for cutting tools and precision components.
Biocompatibility
Certain PVD coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), are biocompatible. This makes them exceptionally valuable for medical implants and surgical instruments, as they won't cause adverse reactions with the human body.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is extending tool life and durability: PVD is the industry standard for adding a hard, wear-resistant surface to cutting tools, drills, and molds.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and appearance: PVD coatings provide a superior protective barrier and a wide range of decorative finishes for items from watches to fixtures.
- If your primary focus is medical or food-grade applications: The biocompatible and inert nature of specific PVD coatings makes them an essential technology for ensuring safety and performance.
Ultimately, a PVD machine enables the precise application of advanced coatings that fundamentally improve the surface characteristics of a product.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Form | Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Core Process | Vaporizing a solid material in a vacuum and depositing it onto a substrate. |
| Key Advantages | Extreme hardness, wear/corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, decorative finishes. |
| Primary Limitation | Line-of-sight process; complex geometries require specialized fixturing. |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, surgical instruments, automotive parts, consumer electronics. |
Ready to enhance your products with high-performance PVD coatings?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Whether you are developing cutting tools, medical devices, or precision components, our expertise can help you select the right coating solution to improve durability, performance, and biocompatibility.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD technology can meet your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















