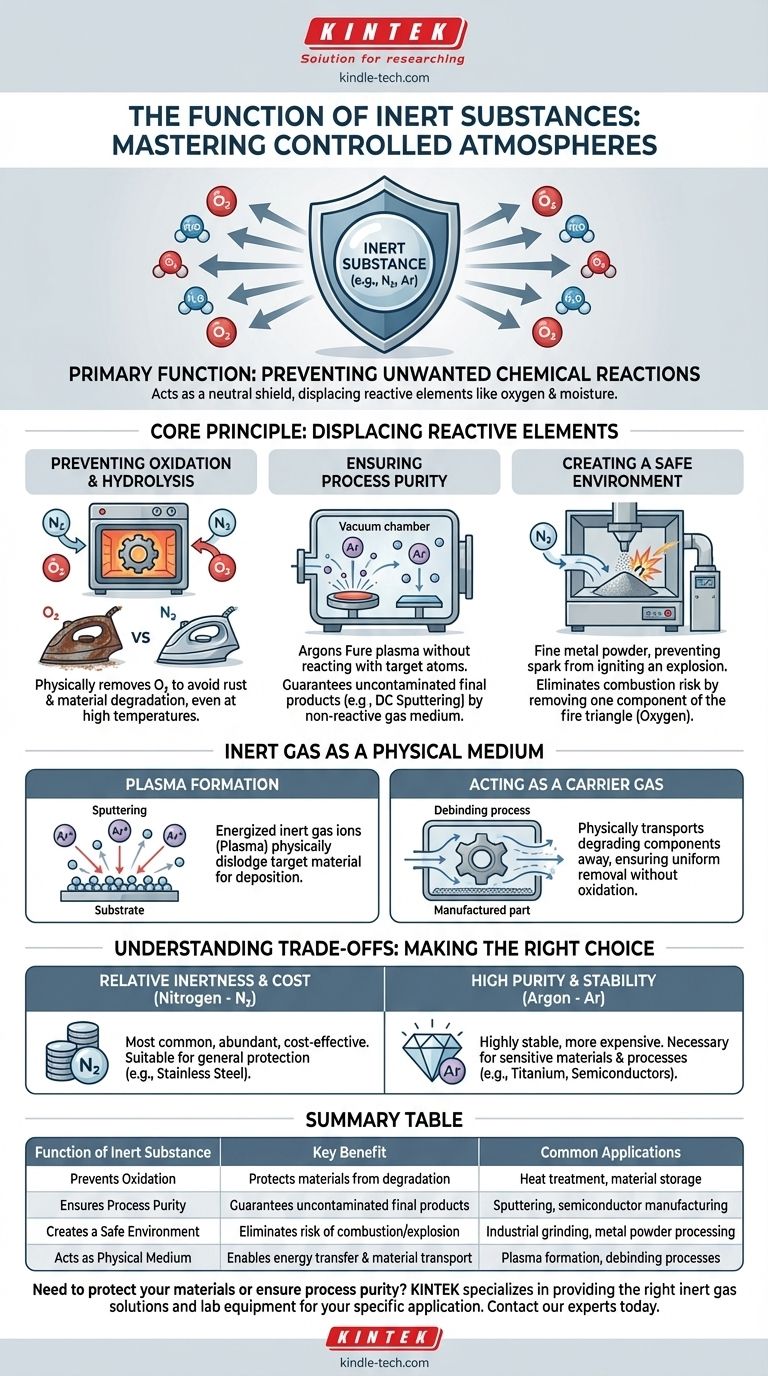
The primary function of an inert substance is to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. In most industrial and scientific applications, this means using a non-reactive gas to create a controlled atmosphere that displaces reactive elements, primarily the oxygen and moisture found in ambient air.
The core purpose of using an inert substance is not about what it does, but what it prevents. It acts as a neutral shield, creating a safe and pure environment where processes can occur without the degrading effects of oxidation or other unintended chemical changes.

The Core Principle: Displacing Reactive Elements
The air we live in is a highly reactive environment. It contains approximately 21% oxygen and variable amounts of water vapor, both of which are eager to react with other materials. An inert substance, typically a gas, is used to push this air out of a closed environment.
Preventing Oxidation and Hydrolysis
Oxidation is the most common undesirable reaction. It's the process responsible for rust on iron and the degradation of many sensitive materials when exposed to oxygen.
By filling a chamber, such as an oven or grinding enclosure, with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, you physically remove the oxygen. This protective blanket prevents oxidation from occurring, even at high temperatures.
Ensuring Process Purity
In high-tech manufacturing like DC sputtering, the goal is to deposit a pure film of one material onto another. If reactive gases were present, they could chemically combine with the target material.
An inert gas is used because it will not react with the target or the substrate. It serves its physical purpose in the process without becoming an unwanted chemical ingredient in the final product.
Creating a Safe Environment
Certain materials, especially fine metal powders, can create an explosive reaction when mixed with the oxygen in the air and an ignition source.
Using an inert shield gas in processes like industrial grinding displaces the oxygen, effectively removing one of the key components of the fire triangle. This makes the entire operation significantly safer.
Inert Gas as a Physical Medium
Beyond simply preventing reactions, inert gases often play a direct, non-chemical role in a process. They can be a medium to transfer energy or a vehicle to transport other substances.
The Role in Plasma Formation
In processes like sputtering, a high voltage is applied to the inert gas (usually argon) held at a low pressure. This energizes the gas atoms, stripping away their electrons and forming a plasma.
These energized ions are then accelerated into a target material, physically knocking atoms loose, which then deposit onto a substrate. The inert gas is the essential medium that enables this physical transfer of material.
Acting as a Carrier Gas
During processes like debinding, where binding agents are removed from a manufactured part, an inert gas serves another physical role.
The gas flows through the chamber and acts as a carrier, physically transporting the degrading polymer components away from the part. This ensures they are removed uniformly without causing oxidation or other reactions on the metal surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use an inert atmosphere is not without its considerations. The effectiveness and cost depend entirely on the specific application and materials involved.
"Inert" is Relative
While noble gases like argon are extremely non-reactive, other common "inert" gases like nitrogen can react under certain conditions of high heat and pressure, especially with reactive metals.
The term "inert" is therefore context-dependent. The gas only needs to be non-reactive with the specific materials used in a given process.
Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is the most widely used inert gas because it is abundant and relatively inexpensive to produce. However, for highly sensitive materials like titanium alloys, the more stable—and more expensive—argon is required.
The choice often comes down to a balance: is the added cost of a more truly inert gas justified by the required purity and integrity of the final product?
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The inert substance you choose and how you apply it depends on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is general material protection: Nitrogen is often the most cost-effective choice for preventing oxidation in ovens, storage, or processing common materials like stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing: A more stable noble gas like argon is necessary for sensitive processes like semiconductor fabrication, sputtering, or welding reactive alloys.
- If your primary focus is process safety: The key is simply to displace oxygen effectively to prevent combustion, making nitrogen a common and effective choice.
Ultimately, using an inert substance is about taking deliberate control of the chemical environment to guarantee the desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Function of Inert Substance | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Protects materials from degradation | Heat treatment, material storage |
| Ensures Process Purity | Guarantees uncontaminated final products | Sputtering, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Creates a Safe Environment | Eliminates risk of combustion/explosion | Industrial grinding, metal powder processing |
| Acts as Physical Medium | Enables energy transfer and material transport | Plasma formation, debinding processes |
Need to protect your materials or ensure process purity? KINTEK specializes in providing the right inert gas solutions and lab equipment for your specific application. Whether you're working with sensitive alloys, high-purity manufacturing, or safety-critical processes, our expertise ensures you achieve optimal results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you create the perfect controlled environment for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2








