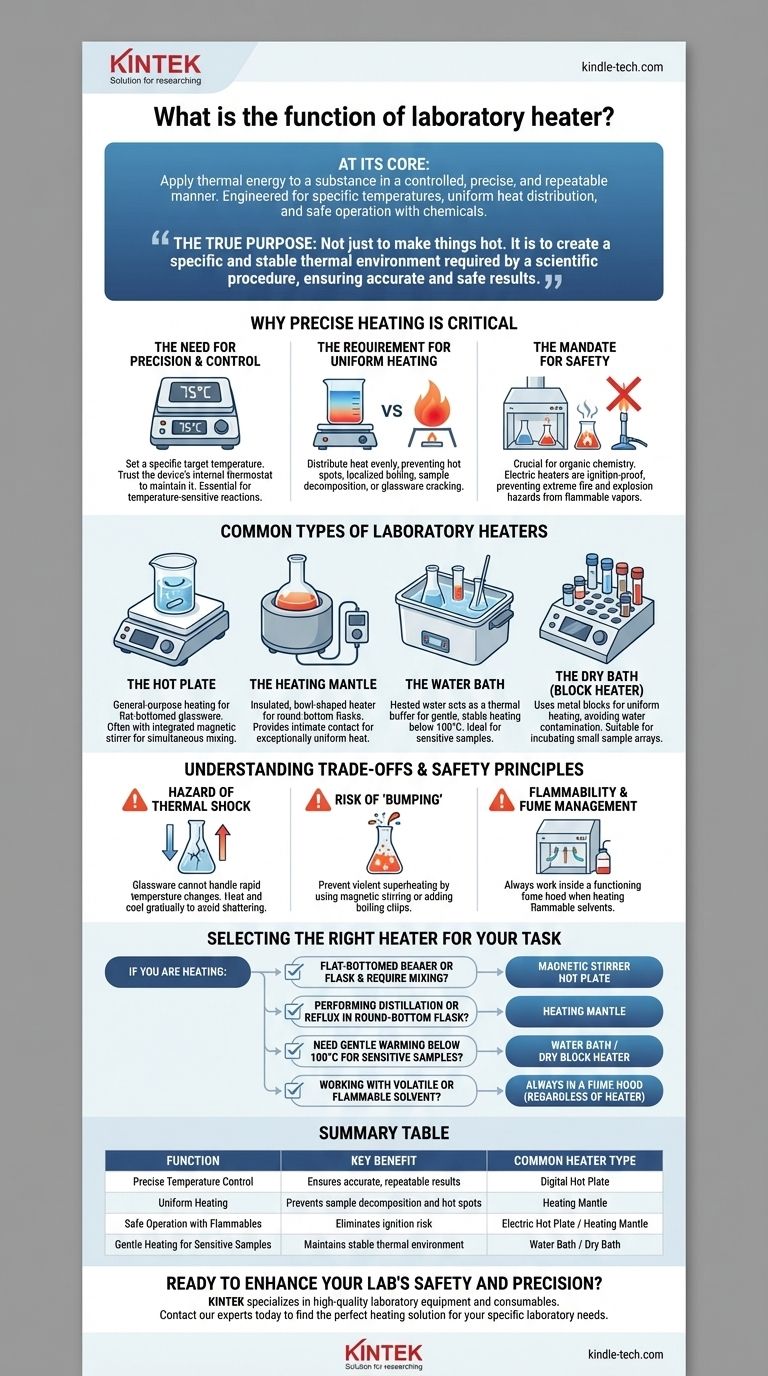
At its core, the function of a laboratory heater is to apply thermal energy to a substance in a controlled, precise, and repeatable manner. Unlike a simple kitchen stove or an open flame, these devices are engineered to maintain specific temperatures, ensure uniform heat distribution, and operate safely with potentially volatile chemicals, making them fundamental tools for scientific experiments.
The true purpose of a laboratory heater isn't merely to make things hot. It is to create a specific and stable thermal environment required by a scientific procedure, ensuring that results are both accurate and safely obtained.

Why Precise Heating is Critical
Before the advent of modern electric heaters, the Bunsen burner was the primary heat source in a lab. While iconic, its limitations highlight the function and necessity of today's specialized equipment.
The Need for Precision and Control
A Bunsen burner offers crude "low" or "high" heat settings. A laboratory heater, such as a digital hot plate, allows a user to set a specific target temperature (e.g., 75°C) and trust the device's internal thermostat to maintain it.
This level of control is non-negotiable for reactions that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
The Requirement for Uniform Heating
An open flame creates a single, intense hot spot on glassware. This can cause localized boiling, decomposition of the sample, or even cracking of the vessel.
Laboratory heaters are designed to distribute heat evenly over a surface, preventing these issues and ensuring the entire sample is at the desired temperature.
The Mandate for Safety
The single most important reason for using a modern lab heater is safety. Many chemical procedures, especially in organic chemistry, involve flammable solvents.
Using an open flame in the presence of these vapors is an extreme fire and explosion hazard. Electric heaters are designed to be ignition-proof, making them the only acceptable choice in these environments.
Common Types of Laboratory Heaters
The term "laboratory heater" encompasses several distinct devices, each designed for a specific application, vessel, and level of precision.
The Hot Plate
A hot plate is the most common laboratory heater, featuring a flat ceramic or metal top surface. It is the workhorse for general-purpose heating of solutions in flat-bottomed glassware like beakers and Erlenmeyer flasks.
Many models are stirrer hot plates, which contain a rotating magnet under the surface. When a magnetic stir bar is placed in the liquid, it spins, providing simultaneous mixing and heating for maximum uniformity.
The Heating Mantle
Heating mantles are insulated, fabric-like bowls designed to fit snugly around round-bottom flasks. This shape is critical for procedures like distillation or reflux.
The mantle's design provides intimate contact with the flask's surface, delivering exceptionally uniform heat and preventing the dangerous hot spots that a flat hot plate would create on rounded glass.
The Water Bath
A water bath is a container of heated water used to provide gentle and extremely stable heating for sensitive samples, often held in test tubes or small flasks.
Because the samples are never in direct contact with the heating element, the water acts as a thermal buffer, ensuring a very uniform temperature, typically below the boiling point of water (100°C). This is common in biological and biochemical applications.
The Dry Bath (Block Heater)
A dry bath functions like a water bath but uses drilled aluminum blocks instead of water. Vials or test tubes are placed into the holes in the block.
This method avoids any potential water contamination and can often reach higher temperatures than a water bath, making it ideal for incubating arrays of small samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Principles
Choosing and using a heater correctly is a matter of both experimental success and personal safety. Misuse can lead to failed experiments or serious accidents.
Hazard of Thermal Shock
Glassware does not tolerate rapid, extreme temperature changes. Placing a cold flask onto a pre-heated 200°C hot plate can cause it to shatter. Always heat and cool glassware gradually.
Risk of "Bumping"
When a liquid is heated without agitation, it can become superheated and then boil violently all at once in a dangerous eruption known as bumping.
This is prevented by using a magnetic stirrer or adding boiling chips to the liquid before heating.
Flammability and Fume Management
Even with a safe electric heater, heating flammable solvents produces flammable vapors. All procedures involving such chemicals must be performed inside a properly functioning fume hood to vent these vapors safely away from the lab.
Selecting the Right Heater for Your Task
The correct tool depends entirely on your substance, vessel, and required precision.
- If you are heating a flat-bottomed beaker or flask and require mixing: A magnetic stirrer hot plate is your standard, versatile choice.
- If you are performing a distillation or reflux in a round-bottom flask: A heating mantle is essential for safe and uniform heating.
- If you need to gently warm sensitive biological samples below 100°C: A water bath or dry block heater provides the most stable thermal environment.
- If you are working with any volatile or flammable solvent: Always work inside a properly ventilated fume hood, regardless of the electric heater used.
Mastering controlled heating is fundamental to achieving reliable and safe experimental results.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Heater Type |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures accurate, repeatable results | Digital Hot Plate |
| Uniform Heating | Prevents sample decomposition and hot spots | Heating Mantle |
| Safe Operation with Flammables | Eliminates ignition risk | Electric Hot Plate / Heating Mantle |
| Gentle Heating for Sensitive Samples | Maintains stable thermal environment | Water Bath / Dry Bath |
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and precision?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you need a reliable hot plate, a specialized heating mantle, or safety accessories for your workflows, we provide the precise tools to ensure your experiments are accurate, efficient, and safe.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- Can pyrolysis oil be refined? Unlocking High-Value Fuels from Bio-Crude
- What is the basic theory of XRF? Unlock Atomic-Level Material Analysis
- What units are used for heat capacity? A Guide to J/K, J/(kg·K), and J/(mol·K)
- How does a thermostatic shaker improve sugar yield? Maximize Biomass Conversion Efficiency
- What is the vacuum level of a thermal evaporator? Achieve Purity with High Vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ Torr)
- Is graphite a conductive metal? Discover Why This Non-Metal Powers Modern Technology
- What is coating film thickness? The Key to Coating Performance, Durability, and Cost Control
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in biomass pretreatment? Ensure Precise Analysis for Cassava & Maize



















