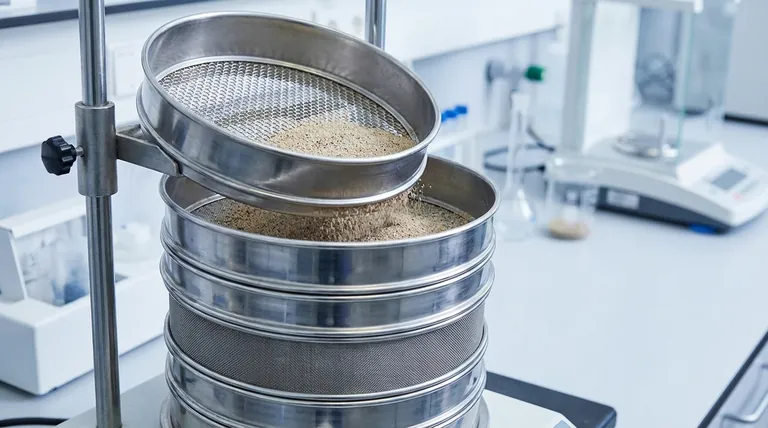
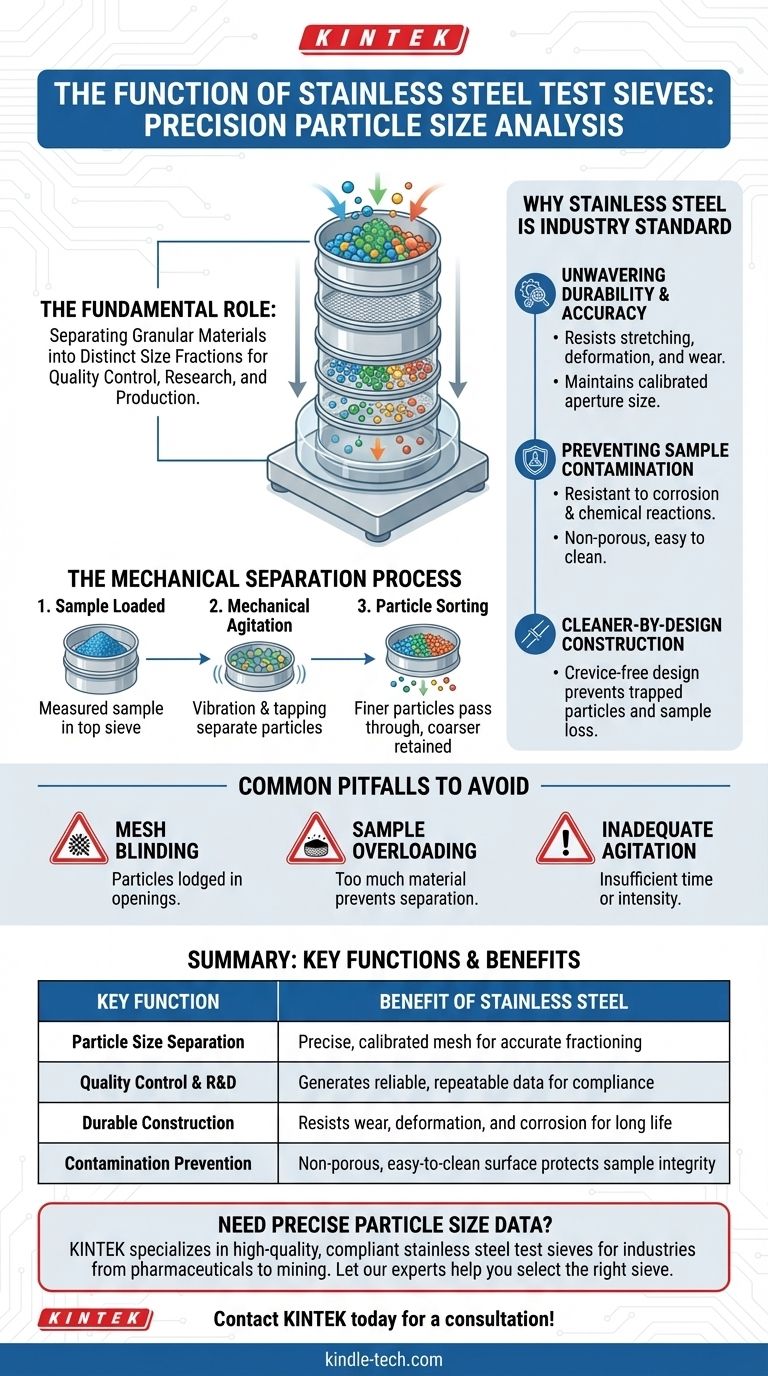
At its core, the primary function of a stainless steel test sieve is to perform particle size analysis. It acts as a precision instrument to accurately separate granular materials into distinct size fractions, providing critical data for quality control, research, and production processes.
A test sieve is not merely a filter; it is a calibrated measurement tool. The choice of stainless steel is fundamental to ensuring the accuracy, durability, and repeatability of the analysis by eliminating variables like corrosion, wear, and contamination.

The Fundamental Role in Particle Analysis
A test sieve provides a clear, quantitative snapshot of the particle size distribution within a given sample. This process, known as a sieve analysis, is a cornerstone of material characterization in countless industries.
The Mechanical Separation Process
The method involves a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings arranged from top to bottom. A measured sample of the material is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated by a mechanical shaker.
This action allows particles to pass through the mesh openings until they are retained by a sieve with a mesh too fine for them to pass.
Transforming Raw Material into Actionable Data
After shaking for a set duration, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. This data creates a particle size distribution profile, revealing the exact percentage of the sample that falls within each size range.
This insight is crucial for everything from ensuring the consistency of concrete aggregate to controlling the dissolution rate of a pharmaceutical tablet.
Why Stainless Steel is the Industry Standard
The material of the sieve is as important as the process itself. Stainless steel offers a unique combination of properties that directly protect the integrity of the measurement.
Unwavering Durability and Accuracy
Test sieves are subjected to significant mechanical stress from shakers and abrasive materials. Stainless steel’s hardness ensures the wire mesh resists stretching, deforming, or wearing down over time.
This durability is essential for maintaining the precise, calibrated aperture size of the mesh, which is the basis for the entire measurement.
Preventing Sample Contamination
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and chemical reactions. This prevents rust or other oxides from flaking off and contaminating the sample, which would skew the weight measurements and compromise the results.
Its non-porous surface also makes it easy to clean thoroughly, preventing cross-contamination between different sample tests.
Cleaner-by-Design Construction
High-quality sieves are designed to be crevice-free. In lesser designs, the point where the mesh meets the frame can have small gaps that trap fine particles.
This trapped material leads to sample loss and inaccurate readings. A smooth, seamless construction ensures that all of the sample material is accounted for in the analysis.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with the best equipment, procedural errors can invalidate results. Understanding these common issues is key to achieving reliable data.
Mesh Blinding
This occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh openings, effectively reducing the open area available for separation. This is common with materials that are flaky, elongated, or near the size of the mesh opening.
Sample Overloading
Placing too much material on a sieve is a frequent mistake. An overloaded sieve prevents particles from having a fair chance to pass through the mesh, leading to an inaccurate retention measurement.
Inadequate Agitation
Both the time and intensity of shaking are critical variables. Insufficient agitation will not provide a complete separation, while excessive agitation can cause unnecessary particle degradation (attrition), skewing the results toward finer sizes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sieve requires matching its features to your specific analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance (e.g., pharmaceuticals or food): Prioritize certified, crevice-free sieves to guarantee test integrity and eliminate any possibility of contamination.
- If your primary focus is heavy industrial use (e.g., aggregates or mining): Emphasize robust frame construction and the durability of the stainless steel mesh to ensure a long service life and consistent accuracy.
- If your primary focus is high-precision research and development: Focus on sieves with the tightest mesh aperture tolerances (e.g., ASTM E11 or ISO 3310-1 compliance) to ensure the highest degree of repeatability.
Ultimately, a quality test sieve transforms a simple mechanical process into a source of reliable, actionable data for your most critical applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Benefit of Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Separation | Precise, calibrated mesh for accurate fractioning |
| Quality Control & R&D | Generates reliable, repeatable data for compliance |
| Durable Construction | Resists wear, deformation, and corrosion for long life |
| Contamination Prevention | Non-porous, easy-to-clean surface protects sample integrity |
Need precise and reliable particle size data? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including durable, compliant stainless steel test sieves designed for accuracy and longevity in industries from pharmaceuticals to mining. Let our experts help you select the right sieve for your specific quality control or R&D needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and enhance your analytical capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- How do you use sieving method? A Step-by-Step Guide to Accurate Particle Separation
- What are standard test sieves used for? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Materials
- What is the application of sieving method in pharmacy? Ensure Drug Quality, Safety, and Efficacy
- How do you calculate the sieve test? Master Particle Size Distribution for Quality Control
- What is the use of sieving in laboratory? Ensure Material Quality & Accurate Particle Analysis
- What are the types of sieves used in pharmaceutical industry? Find the Right Sieving Solution for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory grinder with specific mesh sieves for oat straw? Optimize Pellet Quality
- Why would you use a sieve on your soil sample? To Determine Grain Size Distribution for Engineering



















