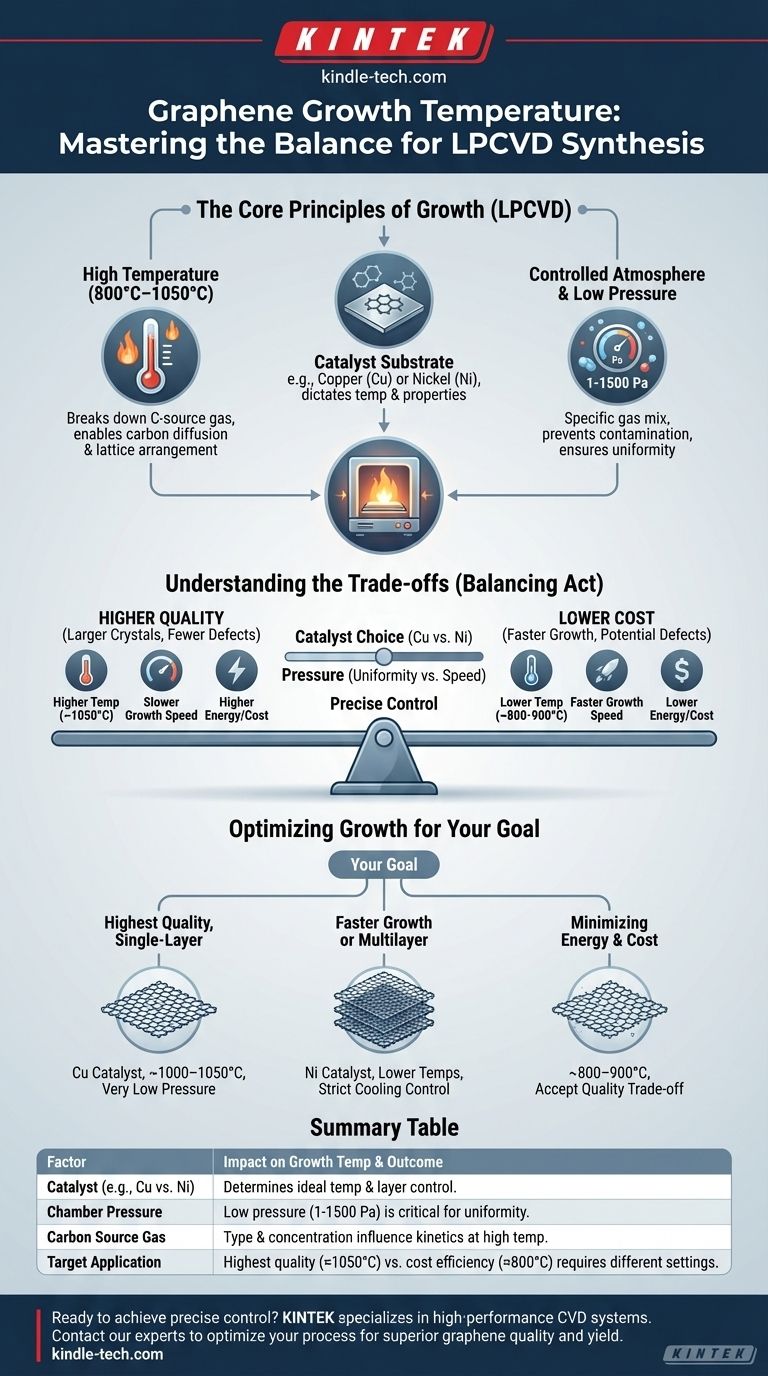
For the synthesis of graphene, there is no single fixed growth temperature. Using the most common method, Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD), graphene is typically grown in a temperature range of 800°C to 1050°C. This temperature is not an isolated value; it is critically dependent on the metallic catalyst used, the pressure within the chamber, and the type of carbon-source gas.
While a high temperature is the catalyst for forming graphene, successful synthesis is not about hitting a single number. The true goal is to achieve a precise balance between temperature, pressure, and the catalyst substrate to control the final quality and thickness of the graphene film.

The Core Principles of Graphene Growth
The specified temperature range is almost exclusively associated with Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the most scalable and widely used method for producing high-quality, large-area graphene sheets. Understanding this process reveals why temperature is just one piece of a larger puzzle.
The Role of High Temperature
The high temperatures (800°C+) serve two primary functions. First, they provide the necessary energy to break down the carbon-source gas (typically methane, CH₄) into reactive carbon atoms. Second, this heat enables these carbon atoms to dissolve into and diffuse across the surface of a metallic catalyst, where they arrange into the hexagonal lattice structure of graphene.
The Catalyst Substrate is Key
Graphene is not grown in a vacuum; it is grown on a substrate that also acts as a catalyst. Transition metals like copper (Cu) and nickel (Ni) are the industry standards for this purpose. The choice of metal directly influences the ideal temperature and the resulting graphene's properties.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
During CVD, the chamber is filled with a specific mixture of gases. This includes a carrier gas (like Argon or Hydrogen) and a very small amount of a carbon-containing gas. The entire system is kept at a very low pressure, typically between 1 and 1500 Pascals.
Why Low Pressure is Critical
Operating at low pressure is essential for high-quality growth. It prevents unwanted atmospheric molecules from contaminating the process and helps ensure the carbon atoms deposit uniformly across the catalyst surface, which is crucial for producing a consistent, single-layer sheet.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving the ideal growth temperature is a balancing act. The specific value chosen within the 800–1050°C range involves significant trade-offs between quality, cost, and complexity.
Temperature vs. Crystal Quality
Generally, higher temperatures within the range (approaching 1050°C) promote the growth of more pristine, larger-crystal graphene with fewer defects. However, these temperatures demand more robust and expensive equipment and consume significantly more energy.
Catalyst Choice Changes Everything
The ideal temperature is strongly linked to the catalyst. Copper has very low carbon solubility, meaning graphene forms directly on the surface in a self-limiting single layer, making it a popular choice. Nickel has higher carbon solubility, which allows for faster growth but risks the formation of undesirable, non-uniform multilayer graphene if the cooling process isn't controlled with extreme precision.
Pressure and Growth Rate
While low pressure is vital for uniformity, there is a trade-off with growth speed. Extremely low pressures can slow down the rate at which the carbon source gas interacts with the catalyst, reducing overall throughput. Engineers must find a pressure low enough for quality but high enough for efficient production.
Optimizing Growth for Your Goal
The "best" temperature is defined by your objective. Whether you are conducting academic research or developing a commercial product, your goal dictates the ideal process parameters.
- If your primary focus is the highest-quality, single-layer graphene: You will likely use a copper (Cu) foil catalyst near the top of the temperature range (~1000–1050°C) under very low pressure.
- If your primary focus is exploring multilayer graphene or faster growth: A nickel (Ni) catalyst is a viable option, often at slightly lower temperatures, but requires strict control over the cooling phase to manage carbon precipitation.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy cost and equipment strain: Operating at the lower end of the temperature range (~800–900°C) is possible, but you must accept a probable trade-off in film quality and an increase in structural defects.
Ultimately, mastering graphene growth is about understanding and precisely controlling these interconnected variables to achieve your specific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Growth Temperature & Outcome |
|---|---|
| Catalyst (e.g., Cu vs. Ni) | Determines ideal temperature and layer control (single vs. multilayer). |
| Chamber Pressure | Low pressure (1-1500 Pa) is critical for uniformity and high-quality films. |
| Carbon Source Gas | Gas type and concentration influence the reaction kinetics at high temperatures. |
| Target Application | Highest quality (≈1050°C) vs. cost efficiency (≈800°C) requires different settings. |
Ready to achieve precise control over your graphene synthesis? The right lab equipment is fundamental to mastering the balance of temperature, pressure, and catalyst. KINTEK specializes in high-performance CVD systems and lab consumables designed for advanced materials research. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you optimize your process for superior graphene quality and yield.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















