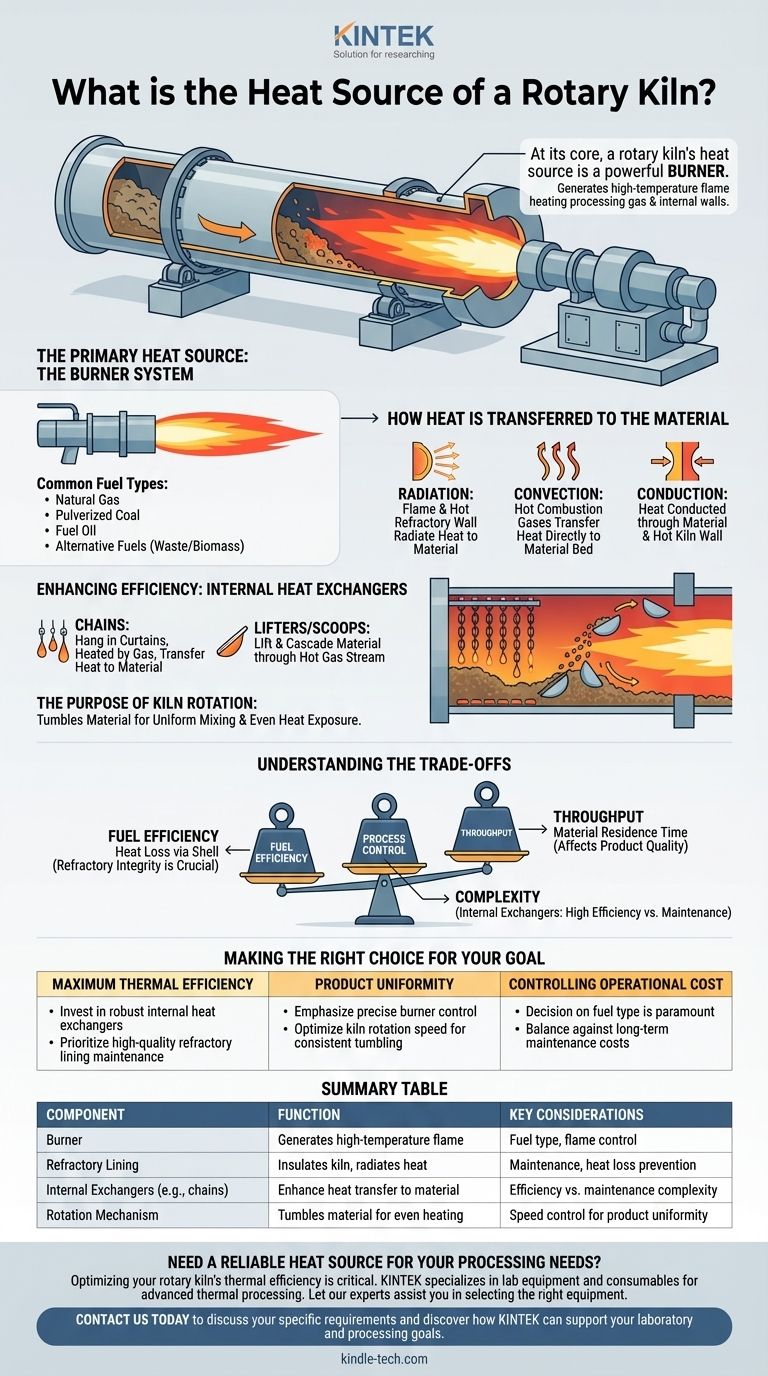
At its core, a rotary kiln's heat source is a powerful burner. This burner, typically positioned at the discharge end of the kiln, generates a high-temperature flame that heats both the processing gas and the internal refractory walls. The specific fuel can vary widely, but the principle remains the same: create an intensely hot environment to drive the desired chemical reactions or physical changes in the material being processed.
The heat source is a burner system, but the true effectiveness of a rotary kiln lies not just in generating heat, but in its sophisticated design for transferring that heat into the material through rotation, gas flow, and internal exchangers.

The Primary Heat Source: The Burner System
The process begins with the generation of immense thermal energy. This isn't a passive heat, but a directed and controlled flame that acts as the engine of the entire system.
The Role of the Burner
A large, high-intensity burner is mounted at one end of the kiln. It projects a long flame down the central axis of the rotating cylinder, creating the primary source of radiant heat. The temperature, shape, and length of this flame are critical control parameters.
Common Fuel Types
The choice of fuel is driven by cost, availability, and process requirements. Common fuels include natural gas, pulverized coal, fuel oil, and increasingly, alternative fuels like industrial waste or biomass. Each fuel has different combustion characteristics that affect the heat profile inside the kiln.
How Heat is Transferred to the Material
Generating heat is only the first step. The kiln's design is optimized to ensure this heat is efficiently transferred to the material through multiple mechanisms working in concert.
The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
Heat exchange in a rotary kiln occurs through radiation, convection, and conduction.
- Radiation: This is often the dominant mode. The material absorbs heat radiated directly from the flame and from the hot refractory lining of the kiln shell.
- Convection: The hot combustion gases flowing through the kiln transfer heat directly to the material bed.
- Conduction: Heat is conducted through the material bed itself and from the hot kiln wall as the material tumbles and makes contact with it.
The Critical Role of Internal Heat Exchangers
To enhance heat transfer, especially convective heat transfer, kilns are often fitted with internal heat exchangers. The most common type is chains, which hang in curtains and are heated by the hot gas. As the kiln rotates, the hot chains pass through the material bed, transferring heat directly.
Other designs use lifters or scoops along the kiln shell. These continuously lift material and cascade it through the hot gas stream, dramatically increasing the surface area available for heat exchange.
The Purpose of Kiln Rotation
The slow, constant rotation of the kiln is fundamental. It tumbles the material, ensuring that it is mixed thoroughly and exposed evenly to all three modes of heat transfer. This prevents localized overheating and ensures a uniform final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The efficiency of a rotary kiln is a balance of interacting factors. Optimizing one area can negatively impact another if not managed carefully.
Fuel Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
While a powerful burner provides the necessary heat, any energy that escapes through the kiln shell is wasted. The refractory lining is the primary insulator, and its integrity is crucial. A degraded lining not only wastes fuel but can also damage the steel shell of the kiln.
Throughput vs. Heat Transfer
Increasing the feed rate (throughput) can boost production, but it also reduces the material's residence time in the kiln. If the material moves through too quickly, it may not be heated sufficiently or uniformly, leading to poor product quality. The system's heat transfer capabilities create a natural limit on its throughput.
Process Control vs. Complexity
Adding complex internal exchangers like chain systems significantly improves thermal efficiency. However, they also add mechanical complexity and are subject to wear, corrosion, and potential clogging, requiring more sophisticated maintenance and operational oversight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and operation of a kiln's heating system must align with the specific goal of the process.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency: Invest in a robust system of internal heat exchangers and prioritize the maintenance of a high-quality refractory lining.
- If your primary focus is product uniformity: Emphasize precise burner control and optimize the kiln's rotation speed to ensure consistent material tumbling and heat exposure.
- If your primary focus is controlling operational cost: Your decision on fuel type will be paramount, balanced against the long-term cost of maintaining the refractory and burner systems.
Ultimately, the heating system is an integrated part of the entire kiln, where the burner provides the energy and the kiln's mechanical design delivers it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Burner | Generates high-temperature flame | Fuel type (gas, coal, oil), flame control |
| Refractory Lining | Insulates kiln, radiates heat | Maintenance, heat loss prevention |
| Internal Exchangers (e.g., chains) | Enhance heat transfer to material | Efficiency vs. maintenance complexity |
| Rotation Mechanism | Tumbles material for even heating | Speed control for product uniformity |
Need a Reliable Heat Source for Your Processing Needs?
Optimizing your rotary kiln's thermal efficiency is critical for product quality and cost control. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables that support advanced thermal processing. Whether you're scaling up R&D or maintaining production lines, our solutions help you achieve precise temperature management and uniform heat transfer.
Let our experts assist you in selecting the right equipment to enhance your process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and processing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















