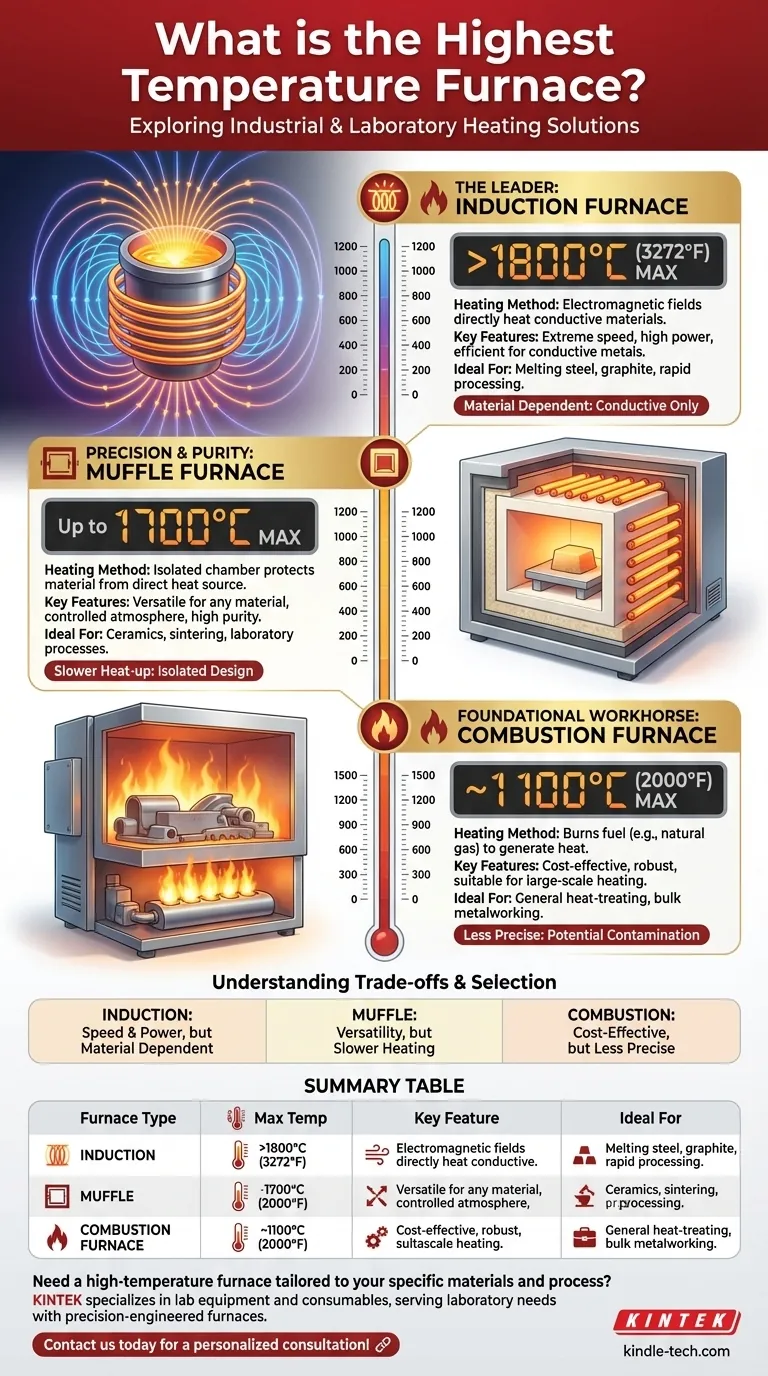
Of the common industrial and laboratory options, the induction furnace is capable of reaching the highest temperatures. While many furnaces operate in the 1100-1200°C range, specialized induction furnaces can exceed 1800°C (3272°F) by using electromagnetic fields to directly heat conductive materials.
The maximum temperature a furnace can achieve is fundamentally determined by its heating technology. While induction furnaces lead in raw temperature for specific materials, the best choice always depends on the material being heated and the desired process outcome.

A Comparison of High-Temperature Furnaces
Different furnace designs use fundamentally different methods to generate heat, which directly impacts their maximum temperature and ideal applications. Understanding these methods is key to grasping their capabilities.
Induction Furnaces: The Temperature Leader
An induction furnace does not use conventional heating elements. Instead, it uses a powerful alternating current passed through a coil to create a strong electromagnetic field.
When a conductive material (like steel or graphite) is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents within the material itself, generating immense heat rapidly. This direct heating method allows some models to reach 1800°C or higher.
Muffle Furnaces: Precision and Purity
A muffle furnace heats materials within an isolated chamber, or "muffle." The heat source (burners or electric elements) is outside this chamber, protecting the material inside from direct contact with flames or contaminants.
This design is crucial for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere or high purity. While many models operate up to 1200°C, advanced versions with specialized heating elements can reach maximum temperatures of 1700°C. Dental furnaces, used for sintering materials like zirconia, are a specialized type of high-temperature muffle furnace.
Combustion Furnaces: The Foundational Workhorse
The most traditional furnace type, a combustion furnace, generates heat by burning a fuel like natural gas. The flame directly or indirectly heats the furnace chamber.
While robust and cost-effective, their maximum temperatures are generally lower. A typical natural gas furnace reaches temperatures around 1100°C (2000°F), making it suitable for general heat-treating and metalworking but not for advanced ceramics or refractory metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace isn't just about finding the highest temperature; it's about matching the technology to the task. Each design comes with distinct advantages and limitations.
Induction: Speed and Power, but Material Dependent
The primary advantage of induction heating is its incredible speed and efficiency. However, it only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It cannot directly heat ceramics, glass, or other insulators unless a conductive crucible is used.
Muffle: Versatility, but Slower Heating
Muffle furnaces are highly versatile because they can heat any material placed inside the chamber, regardless of its properties. This makes them ideal for labs and diverse processes. The trade-off is often a slower heat-up time compared to induction.
Combustion: Cost-Effective, but Less Precise
Combustion furnaces are often the most economical solution for large-scale heating. Their primary drawbacks are less precise temperature control and the potential for the material to be contaminated by the byproducts of combustion.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Process
Your specific application dictates which furnace technology is the most appropriate.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting conductive metals: An induction furnace is the unparalleled choice for speed and high-temperature capability.
- If your primary focus is processing ceramics or materials in a controlled, pure atmosphere: A high-temperature muffle furnace provides the necessary precision and protection.
- If your primary focus is general heat-treating or bulk heating where cost is a major factor: A combustion furnace is often the most practical and sufficient solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace requires aligning the tool's core strengths with your specific high-temperature goal.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Max Temperature | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | > 1800°C (3272°F) | Direct, rapid heating via electromagnetic fields | Melting conductive metals (steel, graphite) |
| Muffle Furnace | Up to 1700°C | Isolated chamber for purity & control | Ceramics, lab processes, controlled atmospheres |
| Combustion Furnace | ~1100°C (2000°F) | Cost-effective, fuel-powered | General heat-treating, bulk metalworking |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your specific materials and process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision-engineered furnaces. Whether you require the extreme heat of an induction furnace, the controlled environment of a muffle furnace, or a cost-effective combustion solution, our experts will help you select the ideal equipment to enhance efficiency, purity, and performance.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















