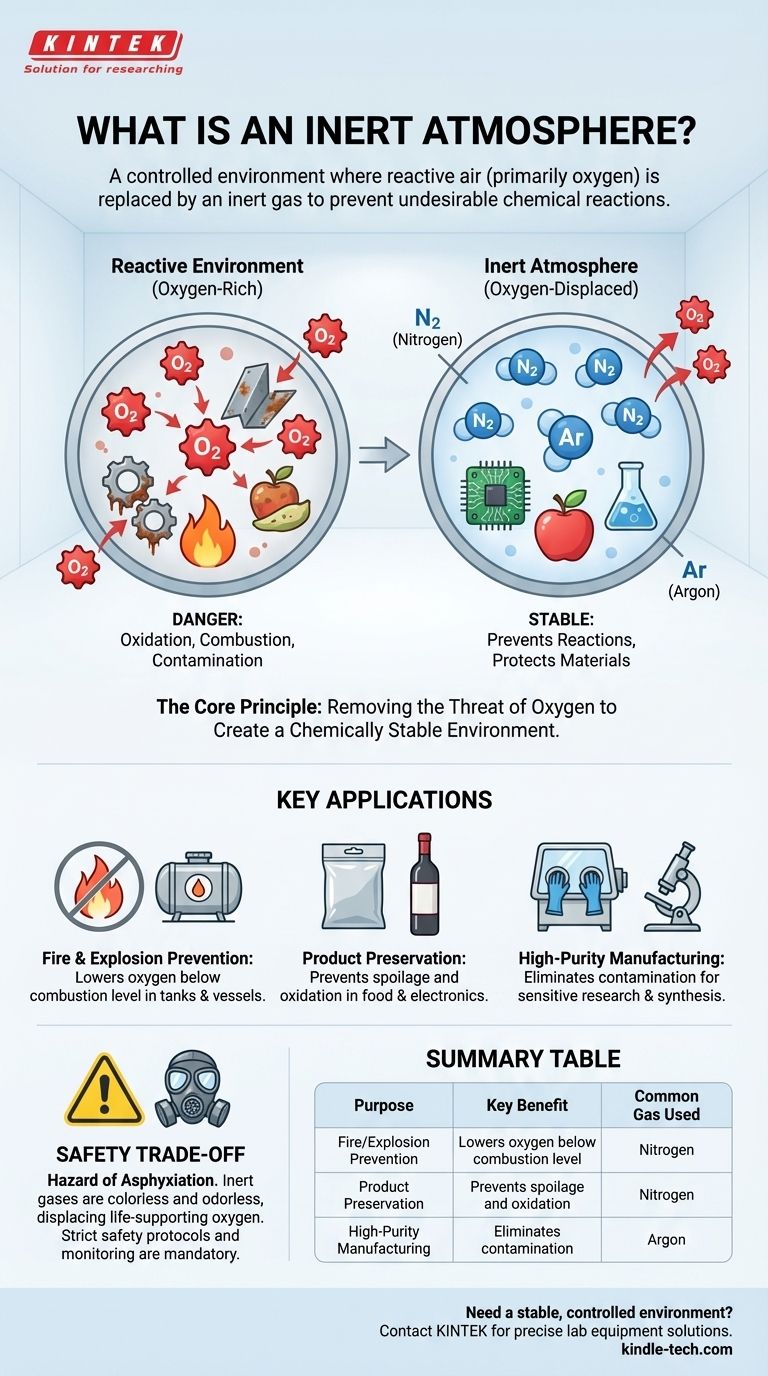
An inert atmosphere is a controlled environment where the normal, reactive air—primarily oxygen—has been replaced by a gas that does not readily participate in chemical reactions. This process, known as "inerting," is used to deliberately prevent or slow down undesirable outcomes like fires, explosions, oxidation, and product contamination. The most common gas used for this purpose is nitrogen.
The fundamental purpose of an inert atmosphere is not to add a special ingredient, but to remove a problematic one: reactive oxygen. By displacing oxygen with a stable gas, you create a chemically stable environment that protects materials and prevents dangerous reactions.

The Core Principle: Removing the Threat of Oxygen
The science behind an inert atmosphere is based on managing chemical reactivity. By understanding why ambient air is often a problem, we can see why replacing it is a powerful solution.
Why Oxygen is the Problem
Oxygen is essential for life, but it is also a highly reactive element. It aggressively combines with other substances in a process called oxidation.
This reactivity is the root cause of many common problems. It enables combustion (fire), causes metals to corrode (rust), and makes foods and beverages spoil.
How Inert Gases Solve the Problem
Inert gases, by their chemical nature, have a very low tendency to react with other substances. When you flood a confined space with an inert gas like nitrogen, it pushes out, or displaces, the oxygen.
By removing oxygen from the equation, you eliminate the key ingredient required for these unwanted reactions.
The Impact on Reaction Rates
Without oxygen present, the rate of oxidation reactions drops dramatically, often to a near-complete stop. This creates a stable system that protects sensitive contents from degradation, even when other conditions like temperature change.
Key Applications of Inert Atmospheres
Inerting is a critical process used across many industries to ensure safety, quality, and purity. The specific goal dictates how the inert atmosphere is applied.
Preventing Fire and Explosions
In chemical plants or fuel storage facilities, flammable vapors can mix with air, creating an explosive risk. By filling the empty space in a storage tank (the "ullage") with an inert gas, the oxygen level is lowered below the point where combustion can occur.
This proactive measure makes the confined space safe by removing one of the three components of the fire triangle: oxygen.
Preserving Products and Materials
Oxidation is a primary enemy of quality for many consumer and industrial goods. An inert atmosphere is the solution.
This is why wine bottles are often purged with nitrogen before corking and why bags of potato chips are filled with it—it displaces the oxygen that would cause the product to spoil or go stale. The same principle is used in electronics manufacturing to protect sensitive components from corroding during soldering.
Ensuring Purity in Research and Manufacturing
In a scientific laboratory or during the manufacturing of specialty chemicals, even tiny amounts of atmospheric oxygen or moisture can contaminate a reaction and ruin the result.
Working inside a sealed container like a "glovebox" filled with a high-purity inert gas ensures that the chemical process remains completely pure and uncontaminated by outside air.
Understanding the Critical Safety Trade-off
While incredibly useful, creating an inert atmosphere introduces a significant and non-negotiable risk that must be managed.
The Hazard of Asphyxiation
An atmosphere that cannot support a fire also cannot support human life. Inert gases are colorless and odorless, providing no sensory warning of their presence.
Entering a confined space that has been made inert will cause immediate unconsciousness and death from asphyxiation. For this reason, strict safety protocols, ventilation, and continuous oxygen monitoring are absolutely mandatory wherever inert gases are used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying an inert atmosphere effectively depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety and fire prevention: Your goal is to displace oxygen below the combustion threshold, making nitrogen a cost-effective and reliable choice for inerting tanks and vessels.
- If your primary focus is product preservation: You need to eliminate oxygen to halt spoilage, which is why inert gas flushing is a standard and essential step in modern food packaging.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing or research: You must prevent any atmospheric contamination, often requiring a highly controlled environment like a glovebox filled with a very pure inert gas like argon.
Ultimately, an inert atmosphere is a powerful tool for taking control of a chemical environment by strategically removing its most reactive element.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Common Gas Used |
|---|---|---|
| Fire/Explosion Prevention | Lowers oxygen below combustion level | Nitrogen |
| Product Preservation | Prevents spoilage and oxidation | Nitrogen |
| High-Purity Manufacturing | Eliminates contamination | Argon |
Need to create a stable, controlled environment for your lab processes?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to safely implement inert atmospheres for applications like materials research, chemical synthesis, and product preservation. Our solutions help you prevent contamination, ensure purity, and enhance safety.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how we can support your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments



















