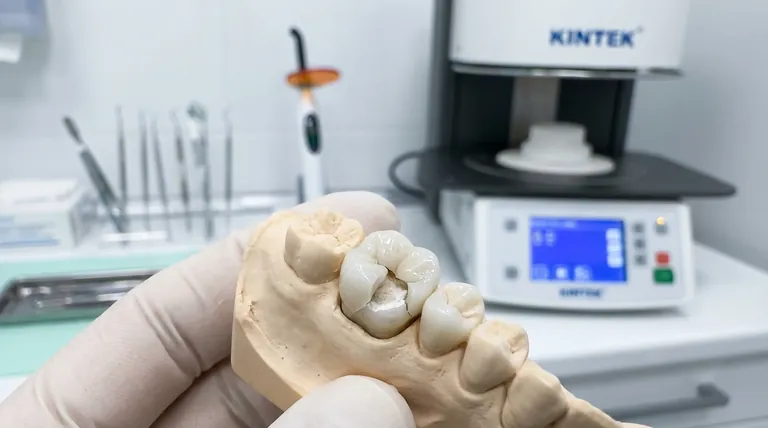
The primary disadvantage of dental ceramics is their inherent brittleness. While they possess high compressive strength, meaning they can withstand significant biting forces, they have low tensile strength, making them susceptible to fracture or chipping when subjected to flexing or sharp, focused impacts. This risk is the central consideration when choosing a ceramic restoration.
While dental ceramics offer unparalleled aesthetics that mimic natural teeth, their brittle nature presents the primary clinical trade-off. The risk of fracture is the core challenge that both material science and clinical technique aim to overcome.
Why Brittleness is the Core Challenge
The defining characteristic of ceramic is its glass-like structure. This provides its signature translucency and beauty but also dictates its physical limitations.
The Nature of Ceramic Materials
Ceramics are exceptionally strong under compression (pushing forces), which is the primary force in chewing. However, they are weak under tension (pulling or bending forces).
Any tiny surface crack or internal flaw can concentrate stress. When the material flexes, even slightly, these stress points can quickly propagate into a full fracture.
Clinical Implications of Fracture Risk
This brittleness is most relevant for restorations on posterior teeth (molars and premolars), which bear the brunt of chewing forces.
Patients with bruxism (teeth grinding or clenching) place extreme and prolonged stress on their teeth, significantly increasing the risk of fracturing a ceramic crown or veneer.
The Critical Role of Preparation and Bonding
The success of a ceramic restoration is highly technique-sensitive. The dentist must prepare the tooth precisely to ensure the ceramic is adequately supported and not placed under tension.
Furthermore, the quality of the adhesive bond between the ceramic and the tooth is paramount. A strong bond distributes forces evenly into the underlying tooth structure, protecting the brittle ceramic from flexing and fracturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ceramics vs. Other Materials
No dental material is perfect. The choice always involves balancing aesthetics, durability, and the specific clinical situation.
Aesthetics: The Unmatched Advantage
The primary reason for choosing ceramics is their appearance. Their ability to mimic the translucency, color, and texture of natural enamel is unmatched by any other material.
This makes them the gold standard for restorations on front teeth, where cosmetic appearance is the highest priority.
Durability: Metal and PFM Restorations
Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns have long been a reliable workhorse. They have a strong metal substructure covered by a layer of porcelain, offering good strength but sometimes compromising aesthetics if the metal margin becomes visible at the gumline.
Full-metal crowns (like gold) are the most durable and long-lasting option. They are extremely strong, fracture-resistant, and gentle on opposing teeth, but their metallic appearance limits their use to non-visible areas like back molars.
Biocompatibility and Wear
Ceramics are highly biocompatible, meaning they are very well tolerated by the gums and surrounding tissues.
However, some older or harder ceramic materials can be abrasive and cause wear on the opposing natural teeth over time. This is a key consideration that dentists factor into material selection.
The Evolution of Stronger Ceramics
The field of dental ceramics has advanced significantly to address the problem of brittleness. Not all ceramics are created equal.
From Feldspathic to Zirconia
Early ceramics, known as feldspathic porcelain, were beautiful but relatively weak, limiting their use to veneers or low-stress areas.
Modern materials like lithium disilicate (e.g., E.max) and zirconia have revolutionized restorative dentistry. These materials incorporate crystalline structures that interrupt crack propagation, making them dramatically stronger and more fracture-resistant than their predecessors.
Monolithic vs. Layered Restorations
Monolithic zirconia is milled from a single, solid block of high-strength ceramic. This provides maximum durability and is an excellent choice for molars, though it can sometimes appear less translucent than other ceramics.
Layered zirconia uses a strong zirconia core covered with a more aesthetically pleasing porcelain. This offers a beautiful, life-like appearance but reintroduces the risk of the weaker outer layer chipping.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Discussing these factors with your dental professional is the best way to determine the ideal material for your unique situation.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics for front teeth: A modern ceramic like lithium disilicate or layered zirconia often provides the best balance of beauty and sufficient strength.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for back teeth: A monolithic zirconia or a traditional full-gold crown is often the most reliable and fracture-proof solution.
- If you grind your teeth heavily: Your dentist will likely recommend the strongest possible material, such as monolithic zirconia or gold, to withstand the extreme forces.
Understanding this core trade-off between aesthetics and brittleness empowers you to have a more informed discussion with your dentist about the best material for your long-term dental health.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Ceramics | Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) | Full-Metal (e.g., Gold) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | High compressive strength, low tensile strength (brittle) | Strong metal substructure with porcelain aesthetic layer | Extremely strong and fracture-resistant |
| Aesthetics | Excellent, mimics natural tooth translucency | Good, but metal margin may show | Poor, metallic appearance |
| Best For | Front teeth, high aesthetic priority | Balance of strength and aesthetics | Posterior teeth, maximum durability |
| Fracture Risk | Higher risk of chipping/fracture | Lower risk than all-ceramic, but porcelain can chip | Very low risk |
Choose the right ceramic solution for your lab's needs with KINTEK!
As a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides the tools and materials needed for precise dental ceramic processing. Whether you're working with modern lithium disilicate, high-strength zirconia, or traditional feldspathic porcelain, our products support the creation of durable, aesthetically-pleasing dental restorations.
Let us help you optimize your workflow and achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your dental laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What function does a high-temperature sintering furnace serve in biomass carbonization? Unlock Superior MFC Performance
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What are some positive and negative environmental effects of using biomass? A Balanced Look at a Renewable Energy Source



















