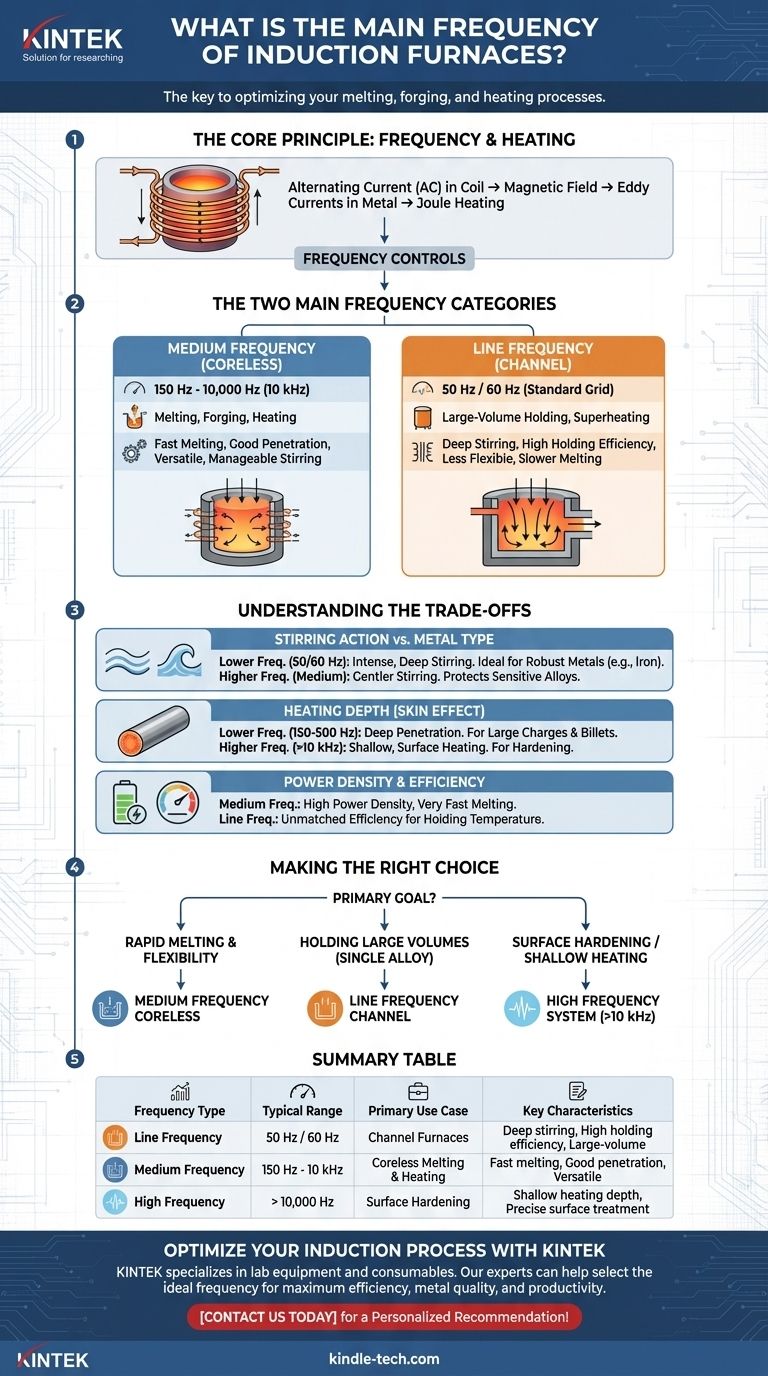
The primary frequency for modern induction furnaces used in melting, forging, and heating applications is medium frequency, which typically ranges from 150 Hz to 10,000 Hz (10 kHz). However, a different class of furnace, known as a channel furnace, operates at the standard electrical line frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The choice between these frequencies is not arbitrary; it is determined entirely by the furnace's intended application.
The operating frequency of an induction furnace is its most critical design parameter. It dictates the heating depth, the intensity of the molten metal's stirring action, and the overall efficiency for a specific task, directly separating rapid-melting furnaces from large-volume holding furnaces.
How Frequency Defines Furnace Behavior
To understand why frequency is so important, we must first look at the core principle of induction heating.
The Principle: Creating Heat with Magnetism
An induction furnace works by passing a powerful alternating current through a copper coil. This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the metal charge placed inside the coil.
This magnetic field induces powerful secondary currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and melt, a process known as the Joule effect.
The Control: Frequency's Role in Heating
The frequency of the alternating current in the coil is the primary control variable. It directly influences two key factors: the stirring action and the heating depth (skin effect).
Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the metal and create a more vigorous, turbulent stirring of the molten bath.
Higher frequencies concentrate their heating effect near the surface of the metal and produce a much gentler stirring action.
The Two Main Frequency Categories
Based on this principle, induction furnaces are built in two main categories, each suited for different industrial jobs.
Medium-Frequency Coreless Furnaces (150 Hz – 10 kHz)
This is the modern standard for most foundries, forges, and heat-treatment facilities. The references point to these as "medium frequency melting furnaces" or "medium frequency heating furnaces."
Their key characteristic is flexibility. By operating in this frequency range, they achieve a balance of good heating penetration and manageable stirring, making them excellent for quickly melting scrap metal, purifying materials, and heating billets for forging.
Line-Frequency Channel Furnaces (50/60 Hz)
This older, highly specialized design operates at the low frequency supplied directly by the power grid. As described in the references, it functions like a transformer where the primary coil induces current in a closed loop or "channel" of molten metal.
The extremely low frequency creates a very strong, deep stirring action and is exceptionally efficient at maintaining the temperature of an already-molten bath of metal. These furnaces are not fast at melting from cold but excel as large-capacity holding and superheating units in high-volume operations, such as for cast iron.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a frequency involves critical trade-offs between speed, efficiency, and the desired metallurgical outcome.
Stirring Action vs. Metal Type
The intense stirring of a line-frequency (50/60 Hz) furnace is ideal for ensuring a uniform temperature and composition in large baths of robust metals like iron. However, this same turbulence can damage sensitive alloys or increase gas pickup and oxidation.
A medium-frequency furnace provides a much gentler stir, offering greater control and protecting the quality of more reactive or specialized metals.
Heating Depth (Skin Effect)
For melting a large charge or heating a thick metal billet for forging, you need heat to penetrate deep into the material. A lower frequency (e.g., 150 Hz to 500 Hz) is required to accomplish this effectively.
For applications like surface hardening, you only want to heat the outer layer of the steel. This requires a very high frequency (often 10 kHz and above) to concentrate the energy right at the surface.
Power Density and Efficiency
Medium-frequency power supplies allow for very high power to be concentrated in a relatively small furnace, resulting in high power density and very fast melting times.
Line-frequency channel furnaces are unmatched in their electrical efficiency for holding metal at temperature but are much slower to melt from a solid state and less flexible for frequent alloy changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the required frequency.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting and alloy flexibility: A coreless medium-frequency furnace is the definitive choice for its speed and versatility.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single alloy: A line-frequency channel furnace provides the highest efficiency for continuous, high-throughput operations.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or shallow heating: A dedicated high-frequency induction system (typically above 10 kHz) is necessary to control the heating depth precisely.
Ultimately, understanding the direct link between operating frequency and the metallurgical outcome is the key to selecting the right induction technology.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Type | Typical Range | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Frequency | 50 Hz / 60 Hz | Channel Furnaces | Deep stirring, high holding efficiency, ideal for large-volume cast iron |
| Medium Frequency | 150 Hz - 10,000 Hz | Coreless Melting & Heating | Fast melting, good penetration, versatile for various metals and alloys |
| High Frequency | >10,000 Hz | Surface Hardening | Shallow heating depth, precise surface treatment |
Optimize your melting or heating process with the right induction furnace technology. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for laboratory and industrial heating needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal frequency and furnace type to maximize efficiency, metal quality, and productivity for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















