At its core, the main function of a rotary kiln is to process solid materials at extremely high temperatures. It is a massive, rotating industrial furnace designed to continuously heat materials to the point where they undergo a fundamental chemical reaction or physical change, such as calcination.
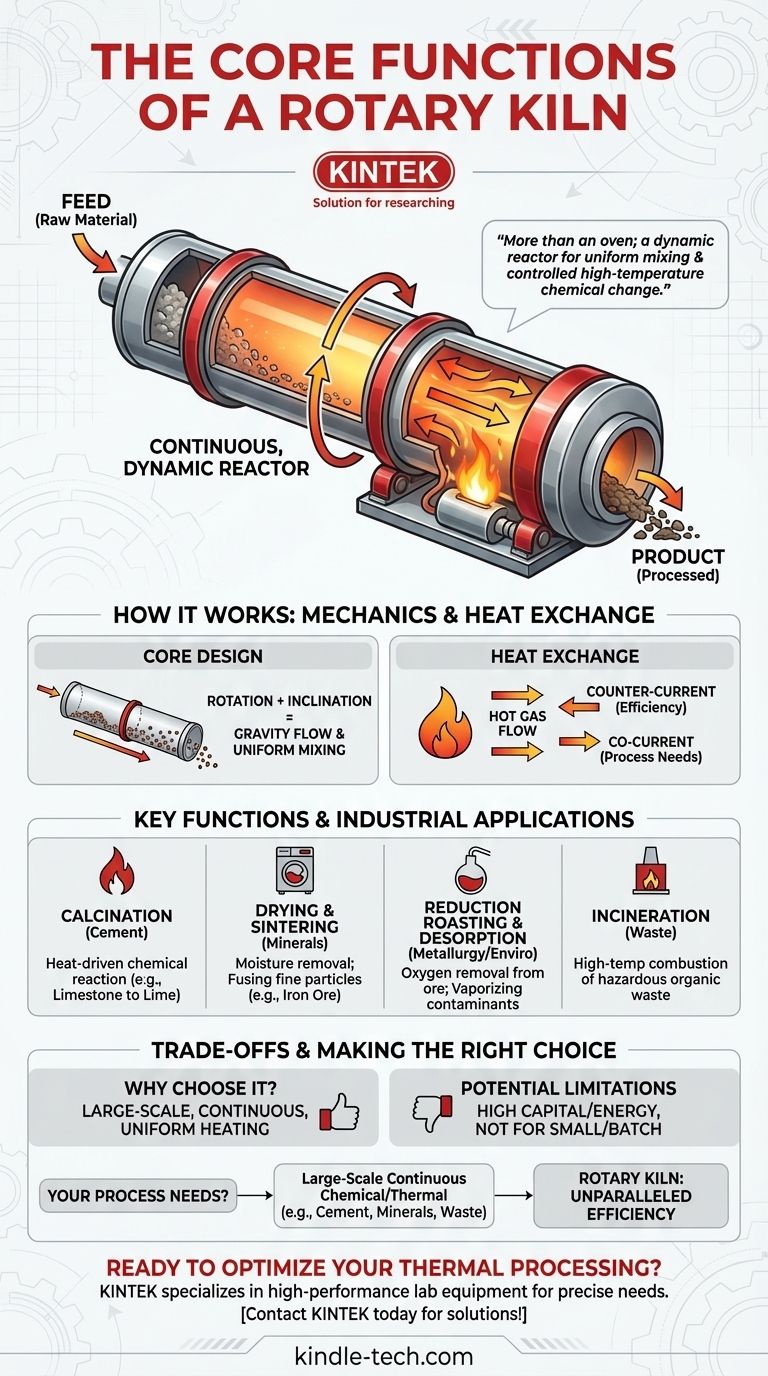
A rotary kiln is far more than a simple oven. Its primary function is to serve as a dynamic, continuous reactor that uses rotation and inclination to uniformly mix and transport materials through a controlled, high-temperature environment, making it indispensable for industries like cement manufacturing.
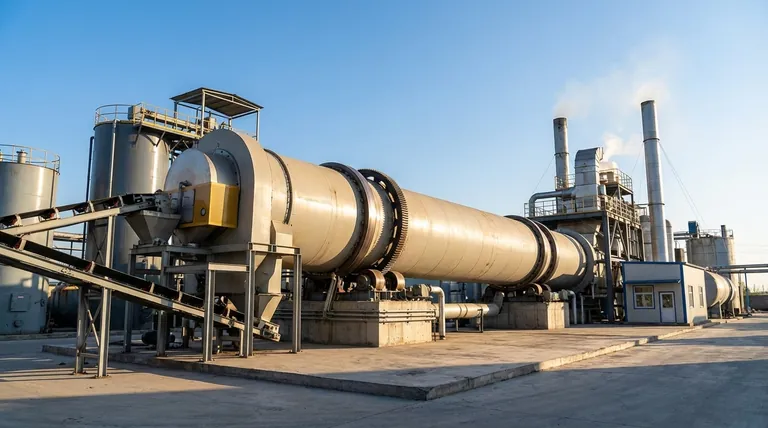

How a Rotary Kiln Works
A rotary kiln’s function is dictated by its unique design. Understanding its mechanics reveals why it is so effective for specific industrial processes.
The Core Design: An Inclined, Rotating Cylinder
A rotary kiln is a long, cylindrical vessel tilted at a slight angle. This inclination is critical.
As the kiln slowly rotates, the raw material fed into the higher end tumbles and gradually moves down toward the lower end due to gravity and the rotational motion.
This constant tumbling and mixing is key, as it ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source for consistent processing.
The Mechanism of Heat Exchange
The kiln functions as a massive heat exchanger. Hot gases are passed through the cylinder, transferring thermal energy to the solid material.
These gases can be generated by a large burner flame inside the lower end of the kiln or from an external furnace.
The flow of these gases can be either counter-current (opposite the material flow) for maximum thermal efficiency or co-current (same direction as material flow), depending on the specific process requirements.
Key Functions and Industrial Applications
The kiln's ability to create a controlled, high-temperature environment enables it to perform several critical functions across various industries.
Calcination
This is arguably the most common and vital function. Calcination is a process that uses heat to drive a chemical reaction, such as decomposing a compound.
The most prominent example is in the cement industry, where limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated in a rotary kiln to produce lime (calcium oxide), a primary ingredient in cement clinker.
Drying and Sintering
A rotary kiln can act as a high-capacity dryer, removing moisture from bulk materials.
It is also used for sintering or induration, where heat is used to fuse fine particles into a solid, strong mass without melting them completely. This is common in processing iron ore pellets.
Reduction Roasting and Thermal Desorption
In metallurgy, kilns are used for reduction roasting, a process that uses heat and a reducing agent to remove oxygen from metal ores.
In environmental applications, they are used for thermal desorption, where heat vaporizes contaminants from soil or other solid materials for remediation.
Incineration
The high temperatures and long residence time in a rotary kiln make it highly effective for the combustion and destruction of organic materials, including hazardous waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary kiln is a specialized piece of equipment. Its selection is based on a clear understanding of its strengths and limitations.
Why Choose a Rotary Kiln?
The primary advantage is its ability to process large volumes of solid material continuously.
Its design ensures uniform heating and excellent mixing, which is critical for achieving consistent product quality in processes like cement production.
Potential Limitations
Rotary kilns are enormous pieces of machinery that represent a significant capital investment and have high energy consumption.
They are not well-suited for small-scale or batch-type processes, where a simpler furnace might be more economical and efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a rotary kiln is directly tied to the scale and requirements of your thermal processing needs.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous chemical transformation (like cement production): The rotary kiln is the industry standard due to its unparalleled efficiency in uniform heating and material transport.
- If your primary focus is high-volume drying or agglomeration of minerals: A rotary kiln provides the robust, continuous operation needed to process bulk materials effectively.
- If your primary focus is waste destruction or soil remediation: The kiln's ability to thoroughly mix and expose materials to sustained high temperatures makes it a highly effective and reliable solution.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln’s function is to provide a controlled, dynamic, and powerful environment for transforming materials on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Industry Application |
|---|---|
| Calcination | Cement Production (Limestone to Lime) |
| Drying & Sintering | Mineral Processing (Iron Ore Pellets) |
| Reduction Roasting | Metallurgy (Metal Ore Processing) |
| Thermal Desorption | Environmental Remediation |
| Incineration | Hazardous Waste Destruction |
Ready to Optimize Your Industrial Thermal Processing?
Whether you're in cement production, mineral processing, or environmental remediation, the right equipment is critical for efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and industrial R&D sectors.
Let our experts help you select the ideal thermal processing solutions for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how we can support your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity



















