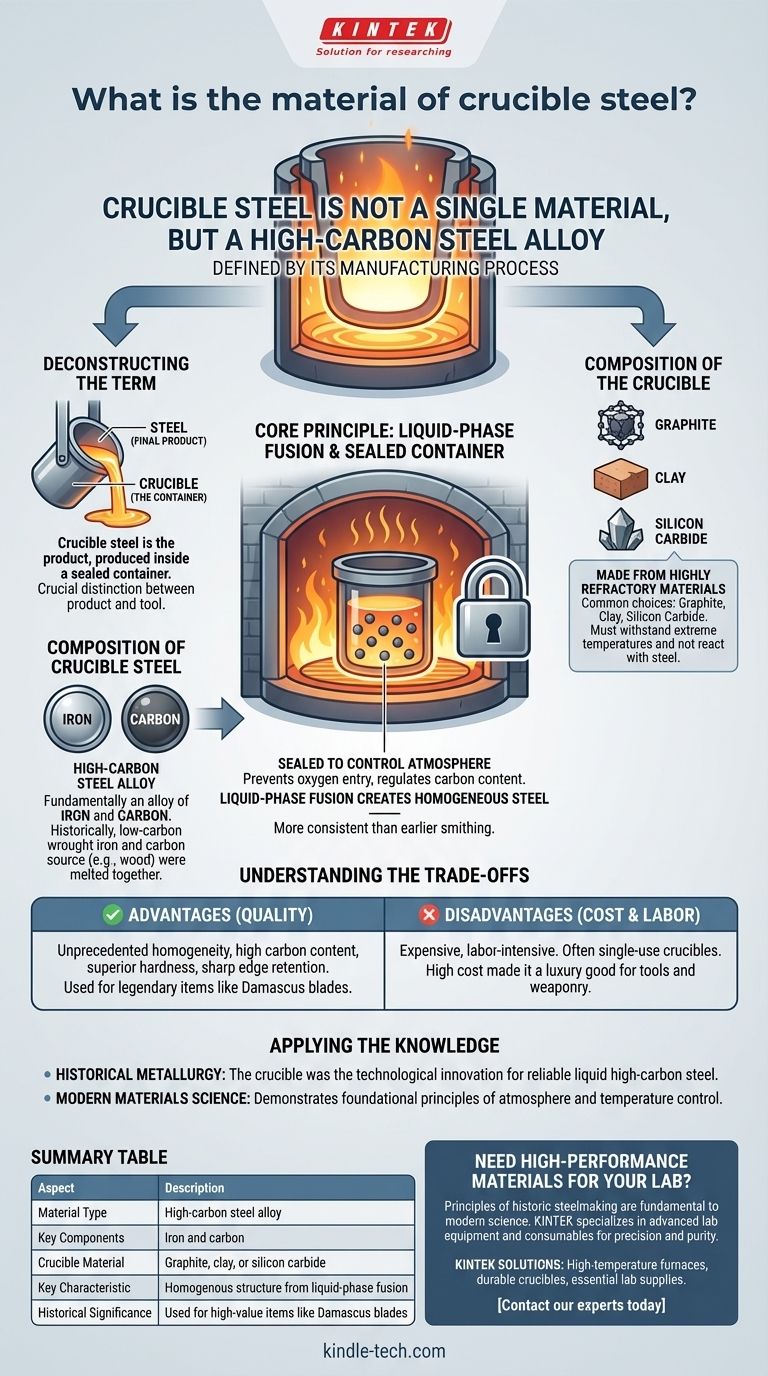
Crucible steel is not a single material, but a high-carbon steel defined by its manufacturing process. It is produced by melting iron and carbon-rich materials together inside a sealed, high-temperature container called a crucible, resulting in a homogenous steel alloy.
The term "crucible steel" can be confusing. It refers to the steel produced in a crucible, not the material of the crucible itself. The crucible is the tool; the steel is the product. Understanding the relationship between the two is key to understanding the material's significance.

Deconstructing the Term: Steel vs. Crucible
The name "crucible steel" describes a manufacturing technology, not a specific chemical formula. It's crucial to distinguish between the final product (the steel) and the container used to make it (the crucible).
The Composition of Crucible Steel
Crucible steel is fundamentally an alloy of iron and carbon. Historically, producers would place low-carbon wrought iron into the crucible along with a source of carbon.
This carbon source was often organic material, such as wood, leaves, or other plant matter. The intense heat of the furnace would cause the iron to absorb carbon from these materials, transforming it into high-carbon steel.
The Composition of the Crucible
The crucible itself is the critical piece of technology in this process. It must be a container capable of withstanding extreme temperatures without melting, reacting with, or contaminating the steel inside.
Crucibles are made from highly refractory (heat-resistant) materials. Common choices include graphite, clay, and silicon carbide, selected for their ability to maintain structural integrity well above the melting point of steel.
The Core Principle of the Crucible Process
The process was a revolutionary step in metallurgy, allowing for the creation of steel with properties that were previously unattainable. The crucible was central to this achievement.
Why a Sealed Container is Essential
The process requires a closed environment. A lid seals the crucible, preventing oxygen from entering and gases from escaping.
This controlled atmosphere is vital for regulating the carbon content of the final steel, ensuring a consistent and predictable result. Early methods, like those for producing Indian wootz steel, involved breaking the crucible open after it cooled to retrieve the solid ingot of steel.
The Role of Raw Ingredients
The inputs were simple but precise. Craftsmen would fill the crucible with a carefully measured charge of wrought iron and a carbon source.
By melting these components together into a liquid state, the carbon would distribute evenly throughout the iron. This liquid-phase fusion creates a far more homogenous steel than earlier smithing techniques, which only heated iron to a semi-solid state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The crucible method produced a superior metal, but it came with significant costs and limitations that made it a specialist material for centuries.
The Advantage: Unprecedented Quality
The primary benefit of crucible steel was its homogeneity and high carbon content. This resulted in a metal that could be hardened to a greater degree, hold a sharper edge, and exhibit consistent properties throughout.
Legendary materials like wootz steel, known for its use in Damascus blades, were products of this advanced crucible process.
The Disadvantage: A Destructive Process
The main drawback was the cost and labor. The crucibles were expensive to produce and, in many historical processes, were single-use.
Since the crucible had to be broken to extract the cooled steel ingot, the cost of the container was part of the cost of every single batch. This made crucible steel a luxury good, reserved for high-value items like tools and weaponry.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding crucible steel is about appreciating a pivotal moment in the history of materials science. The principles pioneered here laid the groundwork for modern steelmaking.
- If your primary focus is historical metallurgy: The key takeaway is that the crucible was the technological innovation that allowed for the first reliable production of liquid-phase, high-carbon steel.
- If your primary focus is modern materials science: The crucible process demonstrates the foundational principles of atmosphere and temperature control that are now essential to all modern, high-purity alloy production.
Ultimately, the crucible was the breakthrough vessel that allowed metallurgists to finally master the creation of high-quality, homogenous steel.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Type | High-carbon steel alloy |
| Key Components | Iron and carbon |
| Crucible Material | Graphite, clay, or silicon carbide |
| Key Characteristic | Homogenous structure from liquid-phase fusion |
| Historical Significance | Used for high-value items like Damascus blades |
Need High-Performance Materials for Your Lab?
The principles of precise temperature and atmosphere control used in historic crucible steelmaking are fundamental to modern materials science. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to achieve similar precision and purity in your own research and production.
Whether you require high-temperature furnaces, durable crucibles, or other essential lab supplies, our expertise ensures you get reliable, consistent results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your materials science projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What not to do with a crucible? Avoid These Common Mistakes to Ensure Safety and Longevity
- What is the application of crucible? A Guide to High-Temperature Melting and Analysis
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles necessary for liquid lead corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Data
- What is a graphite crucible used for? Mastering High-Temperature Melting and Casting
- What crucible is best for melting gold? Choose the Right Tool for a Clean, Efficient Melt
- What is the role of an alumina crucible in LLZ calcination? Ensure High Purity in Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- Why use nickel or alumina crucibles for KOH activation? Ensure high-purity activated carbon synthesis results.



















