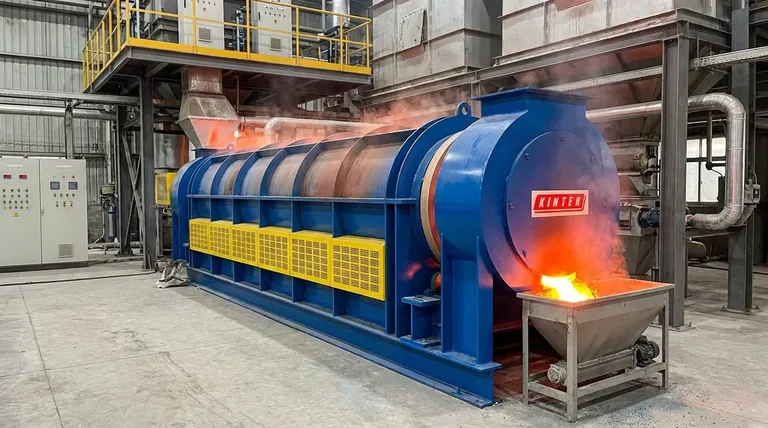
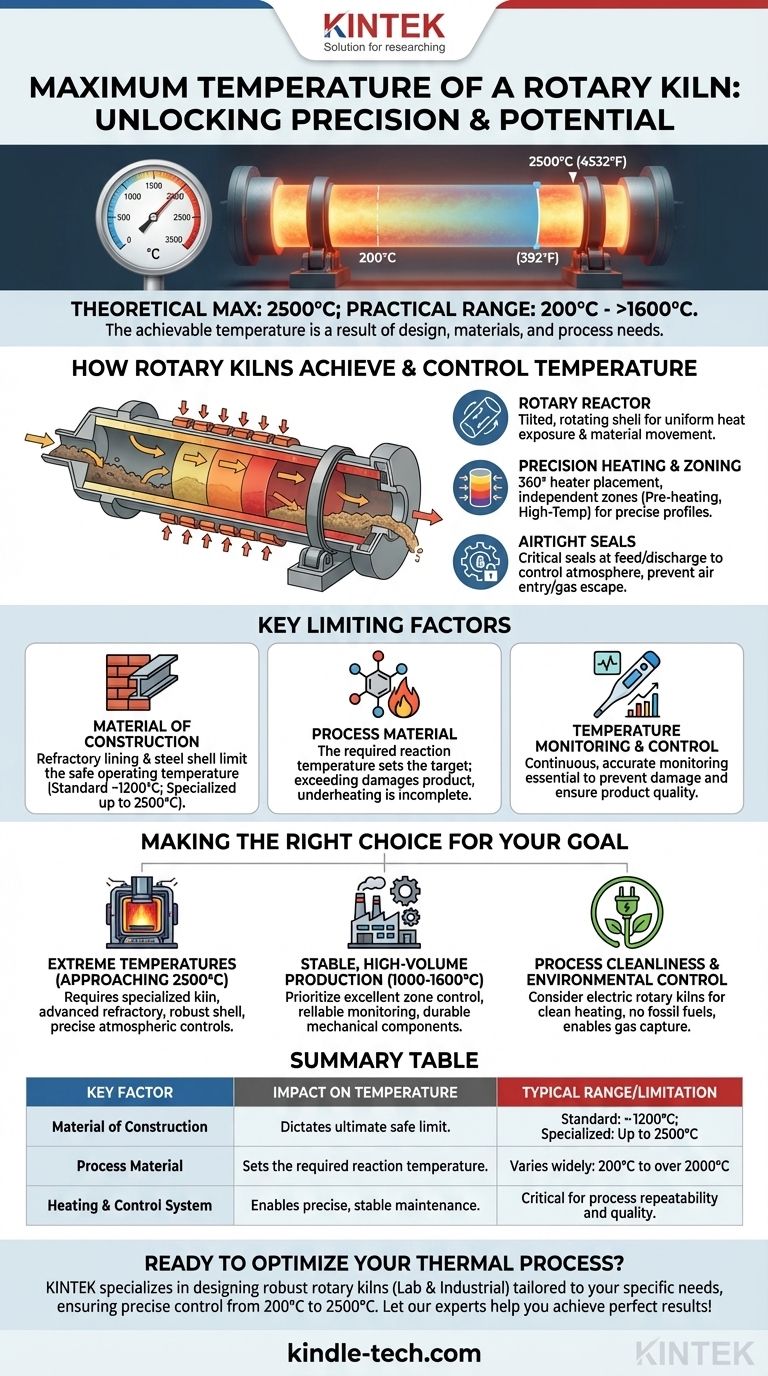
In principle, a rotary kiln can be designed to reach temperatures as high as 2500°C (4532°F). However, this figure represents the upper limit of specialized applications, while most industrial processes operate within a wide range, starting from a low of 200°C (392°F). The achievable temperature in any specific kiln is a direct result of its design, materials of construction, and the thermal requirements of the material being processed.
While a rotary kiln's theoretical temperature ceiling is high, the practical and effective operating temperature is not a single number. It is a carefully controlled parameter dictated by the kiln's physical limits and the precise thermodynamic needs of your specific industrial process.

How Rotary Kilns Achieve and Control Temperature
A rotary kiln is fundamentally a thermal processing machine. Its ability to achieve and maintain precise, high temperatures stems from its core design and a system of integrated components working in unison.
The Central Role of the Rotary Reactor
The heart of the system is the rotary reactor—a long, cylindrical shell, tilted at a slight angle. This rotation and incline ensure that material continuously tumbles and moves from the feed end to the discharge end, promoting uniform heat exposure.
This design is engineered to drive specific chemical reactions or phase changes that require significant thermal energy for kinetic or thermodynamic reasons.
Precision Heating and Zoning
Modern kilns utilize advanced heating controls. A 360° heater placement allows for exceptionally even heat transmission into the material bed.
Furthermore, the kiln is often divided into distinct zones, such as a pre-heating zone and a high-temperature heating zone. Each zone can have its temperature set and controlled independently, allowing for a precise heating profile that matches the exact needs of the process.
The Importance of Airtight Seals
At high temperatures, controlling the process atmosphere is critical. High-quality seals at the feed and discharge ends are essential to prevent unwanted air from entering the kiln or process gases from escaping.
This airtightness ensures process stability, prevents raw material from scattering, and is crucial for applications that require an inert or specific reactive atmosphere.
Understanding the Key Limiting Factors
The maximum operational temperature is less about a theoretical number and more about the practical constraints of the system. Several factors dictate the safe and effective temperature limit.
Material of Construction
The ultimate temperature limit of any kiln is determined by the materials used to build it. The steel outer shell and, more importantly, the internal refractory lining must be able to withstand the target temperature without mechanical failure or chemical degradation. Specialized, high-temperature applications require advanced refractory materials.
The Material Being Processed
The process dictates the temperature, not the other way around. The goal is to heat the product to the optimal point required for the desired reaction, be it calcination, sintering, or reduction. Exceeding this temperature can damage the product, while failing to reach it results in an incomplete process.
Temperature Monitoring and Control
Achieving high temperatures is useless without the ability to control them. Continuous and accurate temperature monitoring is crucial for stable production. Any deviation from the optimal temperature curve must be detected and corrected promptly to prevent damage to the kiln or loss of product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "maximum temperature" you should be concerned with is the one that optimizes your specific process safely and efficiently. Use these guidelines to frame your requirements.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (approaching 2500°C): You will require a highly specialized kiln with advanced refractory materials, a robust shell design, and precise atmospheric controls.
- If your primary focus is stable, high-volume production (e.g., 1000-1600°C): Prioritize a system with excellent zone control, reliable temperature monitoring, and durable mechanical components like riding rings and trunnion wheels.
- If your primary focus is process cleanliness and environmental control: Consider an electric rotary kiln, which offers a clean heating alternative to fossil fuels and enables the capture of process gases like CO2.
Ultimately, the right temperature is the one that is precisely controlled to meet the specific kinetic and thermodynamic demands of your material.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Temperature | Typical Range / Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Material of Construction | Dictates the ultimate safe operating limit. | Standard kilns: ~1200°C; Specialized kilns: Up to 2500°C. |
| Process Material | The required reaction temperature sets the target. | Varies widely, from 200°C to over 2000°C. |
| Heating & Control System | Enables precise, stable temperature maintenance. | Critical for process repeatability and product quality. |
Ready to optimize your thermal process? The right rotary kiln temperature is critical for your product's success. KINTEK specializes in designing and supplying robust lab and industrial rotary kilns tailored to your specific material and temperature requirements, ensuring precise control from 200°C to 2500°C. Let our experts help you achieve perfect results—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















