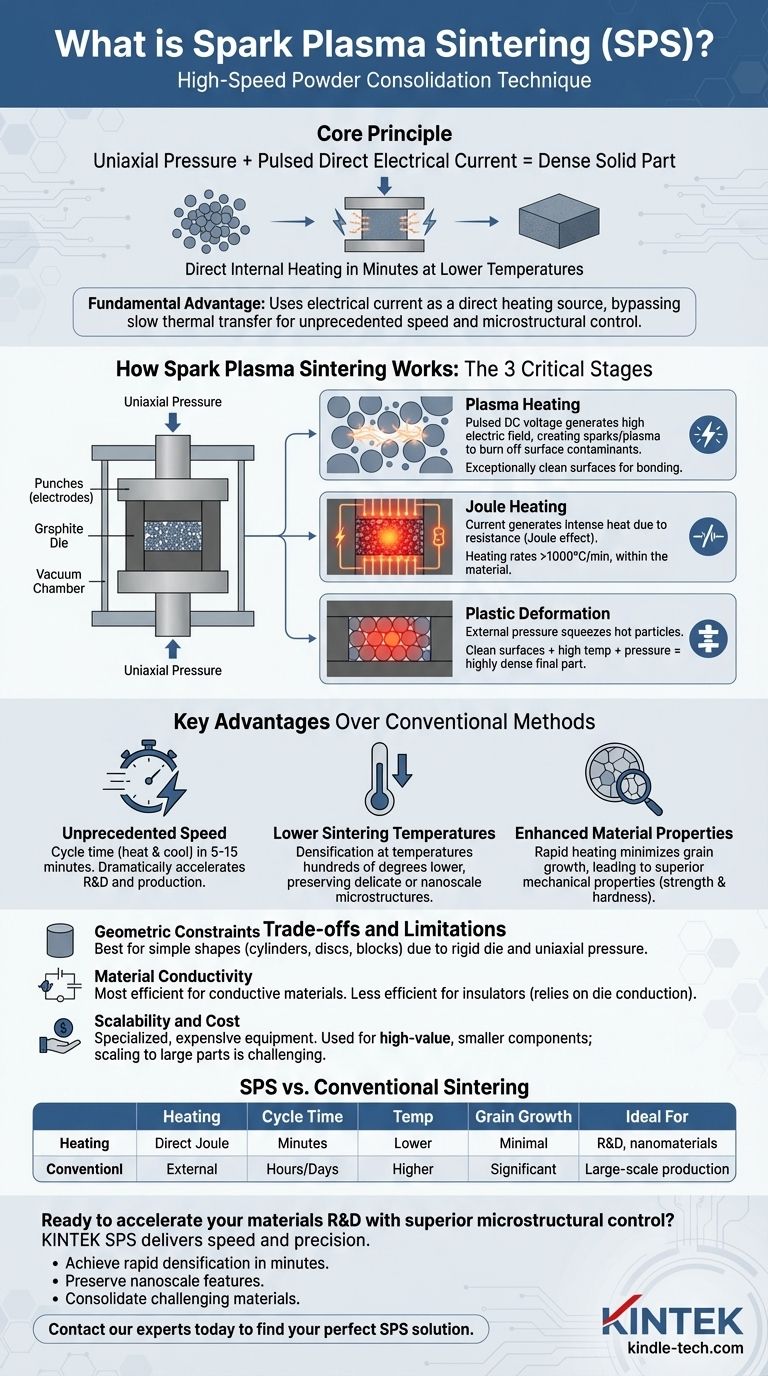
At its core, spark plasma sintering (SPS) is a high-speed powder consolidation technique that uses a combination of uniaxial pressure and a pulsed direct electrical current to transform loose powder into a dense, solid part. Unlike conventional furnaces that slowly bake materials from the outside, SPS passes current directly through the conductive mold and the powder itself, causing rapid and uniform internal heating. This direct energy application allows for sintering in just minutes, at temperatures hundreds of degrees lower than traditional methods.
The fundamental advantage of SPS is its use of electrical current as a direct heating source. This bypasses the slow, inefficient thermal transfer of conventional furnaces, enabling unprecedented speed and control over the final material's microstructure.

How Spark Plasma Sintering Actually Works
To understand the power of SPS, it's essential to look beyond the name and examine the distinct physical processes that occur in rapid succession. The method relies on a specialized apparatus and a unique combination of thermal, electrical, and mechanical forces.
The Core Components
The SPS system consists of a few key parts. The powdered material is loaded into a conductive die, typically made of graphite. This die is then placed between two punches, which also act as electrodes. The entire assembly is housed in a vacuum chamber and subjected to mechanical pressure from a press while a high-power supply delivers the pulsed electrical current.
The Three Critical Stages
The process that turns loose powder into a solid object can be broken down into three overlapping stages.
-
Plasma Heating: When the pulsed DC voltage is first applied, the gaps between individual powder particles can create a high electric field. This can generate a momentary spark or plasma discharge across these voids. This effect is crucial for burning off surface contaminants and oxides from the powder particles, creating exceptionally clean surfaces that are ready to bond.
-
Joule Heating: As the current flows through the conductive graphite die and the powder compact, it generates intense heat due to electrical resistance. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is the primary source of thermal energy in the process. Because the heat is generated within the material itself, heating rates can be extremely high—sometimes over 1000°C per minute.
-
Plastic Deformation: While the powder is being rapidly heated, the external uniaxial pressure is constantly applied. This mechanical force squeezes the now-hot and softened particles together. The combination of clean particle surfaces, high temperature, and immense pressure forces the material to consolidate, eliminating the porous spaces between particles and resulting in a highly dense final part.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Methods
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several significant advantages over traditional sintering techniques like hot pressing or furnace sintering.
Unprecedented Speed
The most significant advantage is speed. While conventional sintering can take many hours, an entire SPS cycle—from heating to cooling—can be completed in as little as 5 to 15 minutes. This dramatically accelerates research, development, and production cycles.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
Because the electrical effects help activate the particle surfaces, densification can be achieved at much lower overall temperatures. Sintering hundreds of degrees below the material's normal requirement is common, which is critical for preserving delicate or nanoscale microstructures.
Enhanced Material Properties
The rapid heating and short duration at high temperatures minimize undesirable effects like grain growth. Keeping the grains in the material small and uniform often leads to superior mechanical properties, such as increased strength and hardness in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Its unique operating principle introduces specific constraints that are critical to understand.
Geometric Constraints
The use of a rigid die and uniaxial (single-axis) pressure means that SPS is primarily suited for producing simple shapes. Cylinders, discs, and rectangular blocks are common, but creating complex, three-dimensional parts is not feasible with standard setups.
Material Conductivity
The process is most efficient when the material itself has some electrical conductivity, allowing for direct Joule heating of the powder. While insulating materials like many ceramics can still be sintered, the process relies solely on thermal conduction from the hot graphite die, making it less efficient than for conductive materials.
Scalability and Cost
SPS equipment is highly specialized and generally more expensive than a conventional furnace. The process is also typically used for producing smaller, high-value components rather than large-scale, mass-produced parts. Scaling up to very large dimensions presents significant technical challenges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on your project's specific objectives, material, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid material discovery and R&D: SPS is the ideal choice due to its incredibly fast cycle times, allowing for quick iteration.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures or fine-grained microstructures: The low sintering temperatures and short processing times of SPS are essential to prevent grain growth.
- If your primary focus is consolidating difficult-to-sinter materials: The combination of pressure, heat, and electrical surface activation in SPS can densify advanced composites and alloys that fail to consolidate with other methods.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering offers unparalleled control over material microstructure through the direct and efficient application of electrical energy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Direct Joule heating & plasma discharges | External, radiative heating |
| Cycle Time | Minutes (5-15 min typical) | Hours to days |
| Sintering Temperature | Lower (by hundreds of degrees) | Higher |
| Grain Growth | Minimal due to short processing time | Significant |
| Ideal For | R&D, nanomaterials, difficult-to-sinter materials | Large-scale production, simpler materials |
Ready to accelerate your materials R&D with superior microstructural control?
Spark Plasma Sintering from KINTEK delivers the speed and precision your lab needs for advanced materials development. Our SPS systems enable you to:
- Achieve rapid densification in minutes, not hours.
- Preserve nanoscale features with low-temperature processing.
- Consolidate challenging materials like advanced composites and alloys.
As your partner in lab equipment, KINTEK specializes in providing the tools that drive innovation. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect SPS solution for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification


















