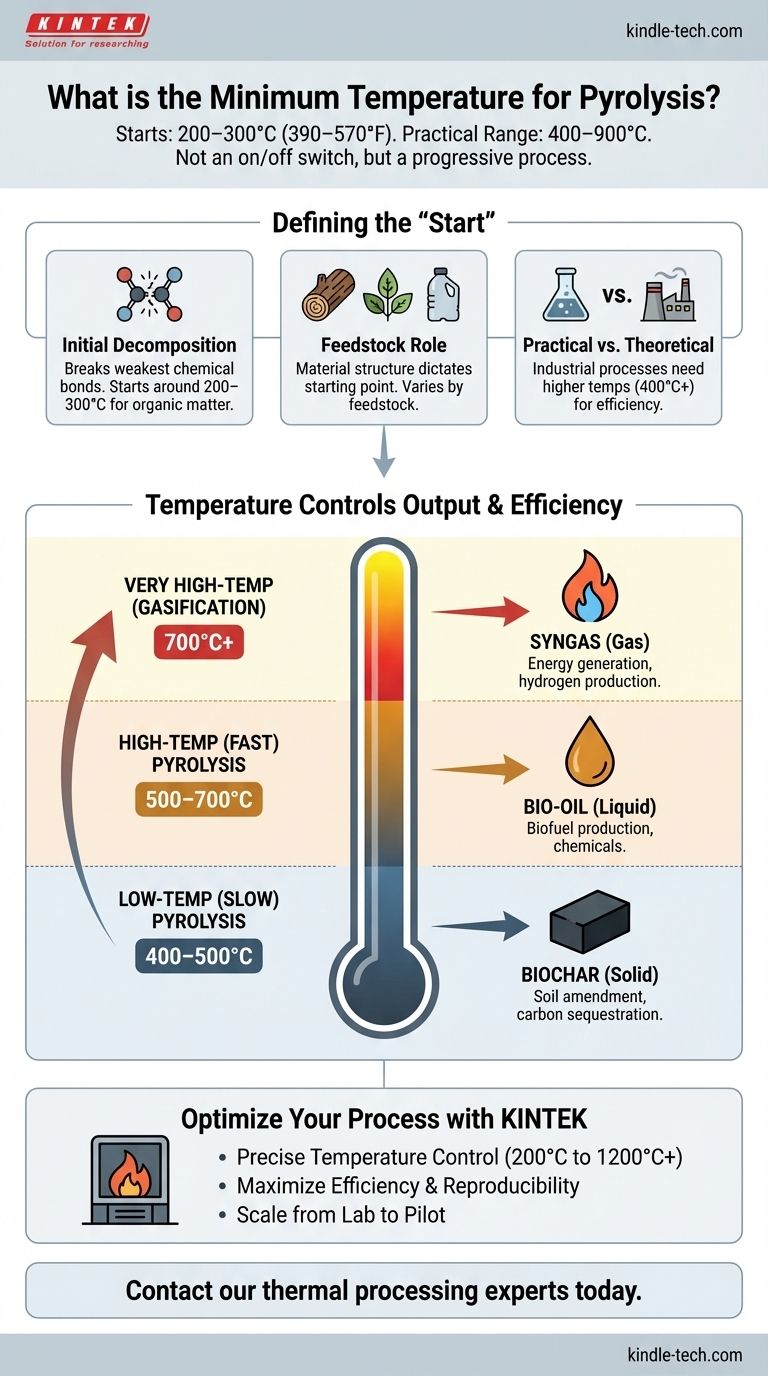
To be precise, the minimum temperature for pyrolysis to begin is generally between 200–300°C (390–570°F), but this is highly dependent on the specific material being heated. This initial stage involves the breakdown of the least stable chemical compounds within the feedstock. However, effective and practical pyrolysis for industrial applications typically requires much higher temperatures, often in the range of 400-900°C.
The key is to understand that pyrolysis isn't an on/off switch at a single temperature. Instead, it's a process that starts at a lower temperature threshold and then accelerates and changes its output as the temperature increases.

What Defines the "Start" of Pyrolysis?
The term "minimum temperature" can be misleading without context. It refers to the point where thermal decomposition first begins, not the optimal temperature for a desired outcome.
Initial Decomposition
Pyrolysis begins when enough thermal energy is introduced to start breaking the weakest chemical bonds in a material.
For organic matter like wood or biomass, this process starts in the 200-300°C range. The first components to break down are typically less stable polymers like hemicellulose.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
There is no single universal minimum temperature for pyrolysis because every material has a different chemical structure.
Materials with less stable bonds will begin to decompose at lower temperatures, while more stable materials require more energy. Wood is a common benchmark, but plastics or other forms of biomass will have their own unique starting points.
Practical vs. Theoretical Minimums
While decomposition may start around 250°C, this process is often slow and incomplete.
Industrial processes use higher temperatures (400°C and above) to ensure a rapid and efficient conversion of the entire feedstock into the desired products, whether that be biochar, bio-oil, or syngas.
Understanding the Temperature Trade-offs
The temperature you choose is the single most important variable controlling the final products of pyrolysis. This is not a mistake to be made; it is a parameter to be controlled.
Low-Temperature (Slow) Pyrolysis
Operating at the lower end of the effective range (approx. 400-500°C) with a slow heating rate maximizes the production of solid biochar.
The longer residence time allows carbon atoms to rearrange into stable, solid structures rather than vaporizing into gases and liquids.
High-Temperature (Fast) Pyrolysis
Using higher temperatures (approx. 500-700°C) with a very rapid heating rate cracks the molecules into smaller vapors. When these vapors are cooled and condensed quickly, they form a liquid bio-oil.
This process minimizes the chance for the vapors to undergo secondary reactions or form solid char.
Very High-Temperature (Gasification)
At extremely high temperatures (typically above 700°C), the process favors breaking down all components into the simplest gaseous molecules.
This maximizes the yield of non-condensable gases known as syngas (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide).
Matching Temperature to Your Desired Outcome
Your target temperature should be dictated entirely by the product you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar yield: Operate at lower temperatures (around 400-500°C) with slow heating rates.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil yield: Use moderate-to-high temperatures (around 500-650°C) with very fast heating rates.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas production: Employ very high temperatures (700°C+) to ensure complete thermal cracking into gaseous components.
Ultimately, temperature is the primary lever you can pull to control the output and efficiency of any pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Typical Temperature Range | Primary Product | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature (Slow) | 400-500°C | Biochar (Maximized) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| High-Temperature (Fast) | 500-700°C | Bio-Oil (Maximized) | Biofuel production, chemicals |
| Very High-Temperature | 700°C+ | Syngas (Maximized) | Energy generation, hydrogen production |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Precise temperature control is critical for achieving your desired product yield, whether it's biochar, bio-oil, or syngas. KINTEK provides robust and reliable lab furnaces and pyrolysis reactors designed for exact temperature management and consistent results.
Our equipment helps researchers and engineers like you:
- Accurately control pyrolysis temperatures from 200°C to 1200°C+.
- Maximize efficiency and reproducibility in your experiments or processes.
- Scale your operations with confidence from lab to pilot plant.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your needs. Get in touch via our contact form to request a quote or schedule a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
















