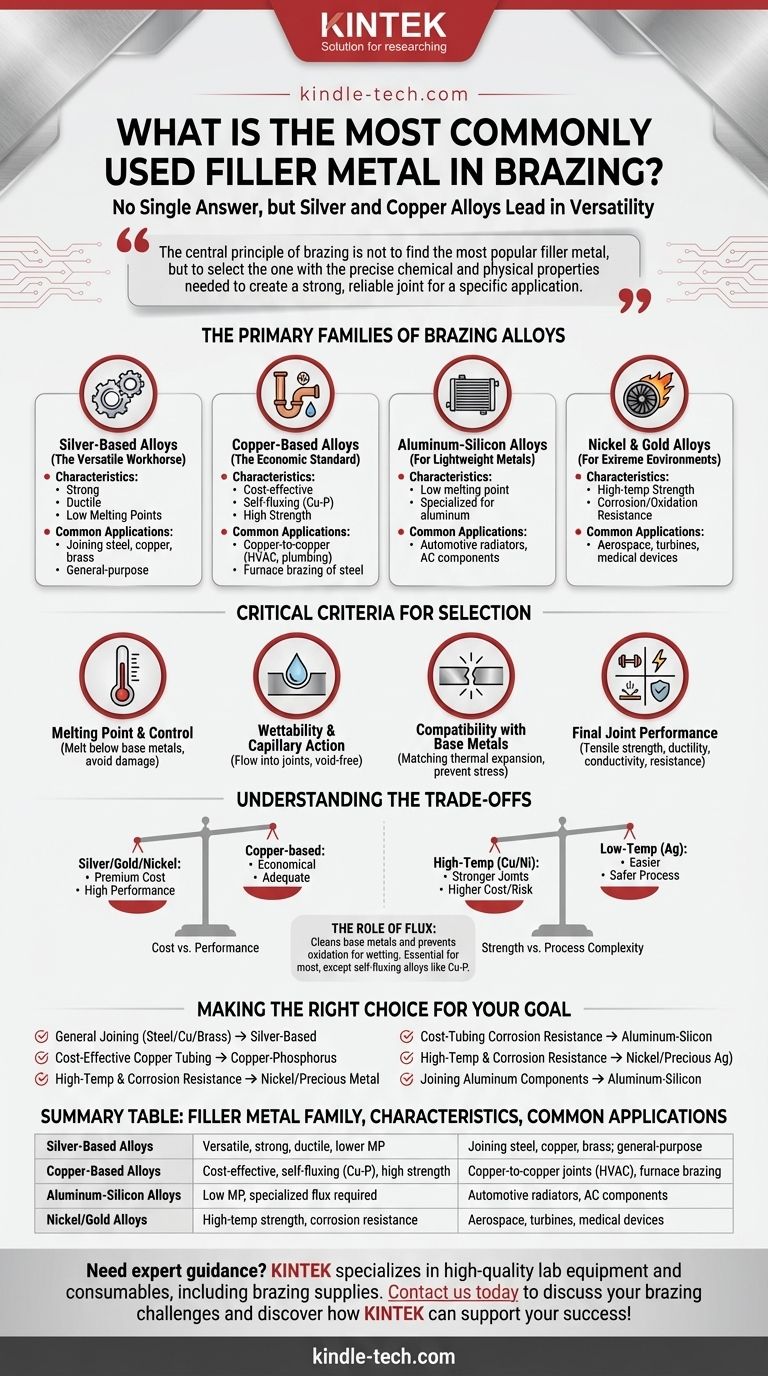
While there is no single "most common" filler metal for all applications, alloys based on silver and copper are the most widely used and versatile choices in brazing. The selection of a specific alloy, however, is not a matter of popularity but a critical engineering decision based on the base metals being joined, the required service temperature, and the desired strength of the final joint.
The central principle of brazing is not to find the most popular filler metal, but to select the one with the precise chemical and physical properties needed to create a strong, reliable joint for a specific application. This choice is dictated by metallurgy, not trends.

The Primary Families of Brazing Alloys
The vast majority of brazing applications are served by a few key families of filler metals, each with distinct advantages and use cases.
Silver-Based Alloys (The Versatile Workhorse)
Silver alloys, often combined with copper and zinc, are extremely popular due to their versatility. They offer strong, ductile joints and have relatively low melting points, which reduces the risk of heat damage to the base materials. They can be used to join most ferrous and non-ferrous metals, except aluminum and magnesium.
Copper-Based Alloys (The Economic Standard)
This family includes copper-zinc (brass), copper-phosphorus, and nearly pure copper fillers. Copper-phosphorus alloys are an industry standard for joining copper to copper (like in plumbing or HVAC) because they are self-fluxing, eliminating an extra step. Copper and brass fillers are widely used for brazing steel and cast iron in furnace applications.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys (For Lightweight Metals)
Brazing aluminum requires a specialized approach. Aluminum-silicon filler metals have melting points just below that of the aluminum base metals, allowing for strong joints in applications like automotive radiators and air conditioning components.
Nickel and Gold Alloys (For Extreme Environments)
For applications demanding superior strength at high temperatures or exceptional corrosion and oxidation resistance, nickel, gold, and palladium-based alloys are the solution. Their high cost reserves them for critical components in the aerospace, turbine, and medical industries.
The Critical Criteria for Selecting a Filler Metal
An expert's choice of filler metal is guided by a clear set of technical requirements, not just familiarity.
Melting Point and Temperature Control
The filler metal must melt at a temperature lower than the base metals being joined. This is the fundamental rule of brazing. The melting point must also be high enough to provide adequate strength in the final application, but not so high that the brazing process itself damages or weakens the base metals through excessive grain growth.
Wettability and Capillary Action
Wettability is the ability of the molten filler to flow over and adhere to the surfaces of the base metals. Good wetting allows the filler to be drawn into the tight gap between the parts via capillary action, ensuring a complete, void-free joint.
Compatibility with Base Metals
The filler must be metallurgically compatible with the base metals. A key factor is the linear expansion coefficient. If the filler and base metals expand and contract at vastly different rates during heating and cooling, it can build up internal stress, leading to joint failure or cracking.
Final Joint Performance
The final joint must meet the demands of the product. This includes mechanical properties like tensile strength and ductility, as well as functional requirements like electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. The filler metal is a primary determinant of these final characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filler metal always involves balancing competing factors.
Cost vs. Performance
The most significant trade-off is often cost. Silver, gold, and nickel alloys provide exceptional performance but come at a premium. For many applications, a more economical copper-based alloy provides perfectly adequate strength and reliability.
Strength vs. Process Complexity
Higher-temperature fillers like pure copper or nickel alloys often create stronger joints. However, they require higher process temperatures, which increases energy costs and the risk of distorting or damaging the base parts. Lower-temperature silver alloys are often easier and safer to work with.
The Role of Flux
Most brazing operations require the use of flux, a chemical compound that cleans the base metals and protects them from oxidation during heating, which is essential for proper wetting. The choice of flux is directly tied to the filler metal, base metal, and brazing temperature. The exception is self-fluxing alloys like copper-phosphorus on copper parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your filler metal based on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose joining of steel, copper, or brass: A silver-based alloy offers the best combination of strength, lower process temperature, and versatility.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective brazing of copper tubing: A copper-phosphorus alloy is the industry standard, providing strong joints without the need for a separate flux.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance: Nickel or precious metal alloys are required to meet the demands of these extreme service environments.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum components: You must use a specialized aluminum-silicon filler metal and a compatible flux designed specifically for aluminum.
Ultimately, the right filler metal is the one that creates a sound metallurgical bond that meets the precise service demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Family | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Silver-Based Alloys | Versatile, strong, ductile, lower melting point | Joining steel, copper, brass; general-purpose brazing |
| Copper-Based Alloys | Cost-effective, self-fluxing (Cu-P), high strength | Copper-to-copper joints (HVAC, plumbing), furnace brazing of steel |
| Aluminum-Silicon Alloys | Low melting point (for aluminum), specialized flux required | Automotive radiators, air conditioning components, aluminum structures |
| Nickel/Gold Alloys | High-temperature strength, corrosion/oxidation resistance | Aerospace, turbines, medical devices, extreme environments |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect brazing filler metal for your laboratory or production needs? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including brazing supplies, to ensure your joints are strong, reliable, and meet precise specifications. Our team can help you choose the right alloy for your base metals and application requirements. Contact us today to discuss your brazing challenges and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
- Versatile PTFE Solutions for Semiconductor and Medical Wafer Processing
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
People Also Ask
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What is the function of high-temperature metal filaments in HFCVD? Catalyzing Diamond Growth Success
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
















