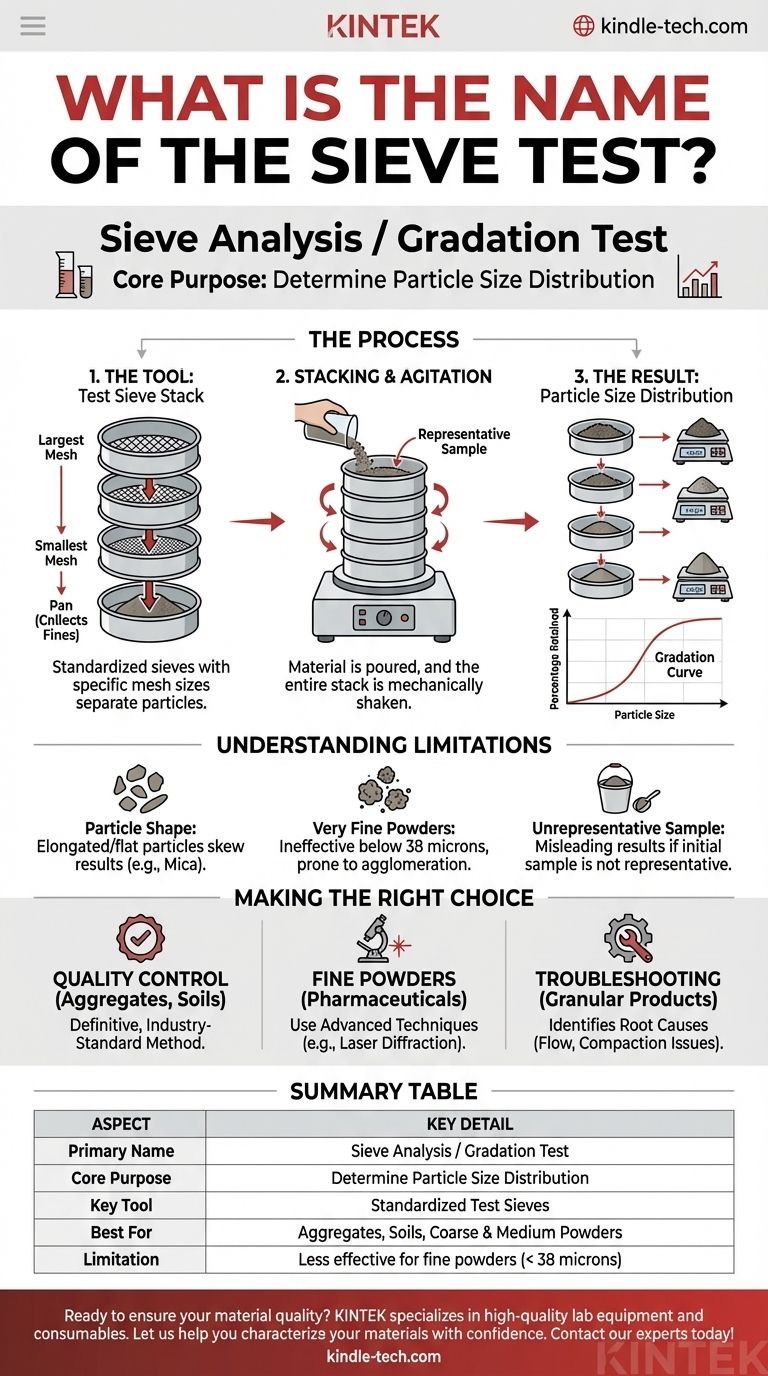
The test you are asking about is most commonly known as a sieve analysis or a gradation test. This fundamental procedure uses a series of interlocking sieves with specific mesh sizes to separate a granular material sample and determine its particle size distribution.
The name of the test is simple, but its purpose is profound. A sieve analysis is not just about separating particles; it is about quantifying the particle size distribution of a material, which is a critical predictor of its physical behavior, quality, and suitability for a specific application.
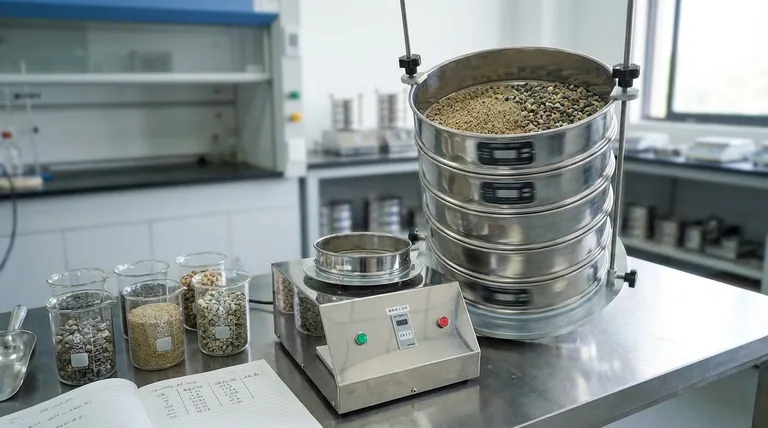

What is a Sieve Analysis?
A sieve analysis is a straightforward, mechanical method used across countless industries to characterize the size of particles within a sample. The process reveals the proportion of a material, by weight, that falls within different size ranges.
The Tool: The Test Sieve
At the heart of the analysis is the test sieve. As described, this is a highly precise instrument consisting of a wire mesh screen with uniform openings, held taut within a rigid, circular frame.
Sieves are manufactured to meet strict industry standards (like those from ASTM or ISO) that define the exact opening size, wire diameter, and frame dimensions. This standardization ensures that results are repeatable and comparable anywhere in the world.
The Process: Stacking and Agitation
The procedure involves creating a stack of test sieves. The sieve with the largest mesh opening is placed on top, followed by progressively smaller ones. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
A pre-weighed, representative sample of the material is poured into the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated, usually by a mechanical shaker, for a set period. This shaking allows particles to work their way down through the stack until they are retained on a sieve with openings smaller than their diameter.
The Result: Particle Size Distribution
After agitation, the material retained on each individual sieve is carefully weighed. By calculating the percentage of the total weight retained on each screen, you can generate a particle size distribution curve. This graph is the ultimate output of the test, providing a visual fingerprint of the material's gradation.
Understanding the Limitations
While sieve analysis is a foundational and reliable technique, it is essential to recognize its limitations to ensure accurate interpretation.
Particle Shape Skews Results
Sieve analysis inherently assumes that particles are generally spherical. Elongated or flat particles may pass through a mesh opening end-on or diagonally, causing them to be reported as smaller than they functionally are. This can be a significant factor for materials like mica flakes or certain crushed aggregates.
Ineffective for Very Fine Powders
For extremely fine materials (typically below 38 microns, or a No. 400 sieve), mechanical sieving becomes impractical. Tiny particles tend to agglomerate (stick together) due to electrostatic forces and moisture, preventing them from passing through the fine mesh. Other methods, such as laser diffraction or air jet sieving, are required for these powders.
The Risk of an Unrepresentative Sample
The results of a sieve analysis are only as good as the sample you start with. If the initial sample is not properly collected and is not representative of the entire bulk material, the resulting data will be misleading, even if the test procedure is performed perfectly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of a sieve analysis lies in applying it to the correct problem. Its purpose is to provide clear, quantitative data for quality control and material characterization.
- If your primary focus is quality control for construction aggregates, soils, or food grains: A sieve analysis is the definitive, industry-standard method for ensuring your material meets project or safety specifications.
- If your primary focus is characterizing fine pharmaceutical powders or advanced materials: Sieve analysis is a preliminary step at best; you must use more advanced particle sizing techniques like laser diffraction for accurate results.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a production issue with a granular product: A sieve analysis can quickly reveal if a change in particle size distribution is the root cause of problems with flow, compaction, or mixing.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of sieve analysis allows you to translate a simple pile of raw material into a precise and actionable dataset.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Name | Sieve Analysis / Gradation Test |
| Core Purpose | Determine Particle Size Distribution |
| Key Tool | Standardized Test Sieves |
| Best For | Aggregates, Soils, Coarse & Medium Powders |
| Limitation | Less effective for fine powders (< 38 microns) |
Ready to ensure your material quality and consistency? A precise sieve analysis is the first step. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including certified test sieves and shakers, to deliver accurate particle size data for your laboratory.
Let us help you characterize your materials with confidence.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















