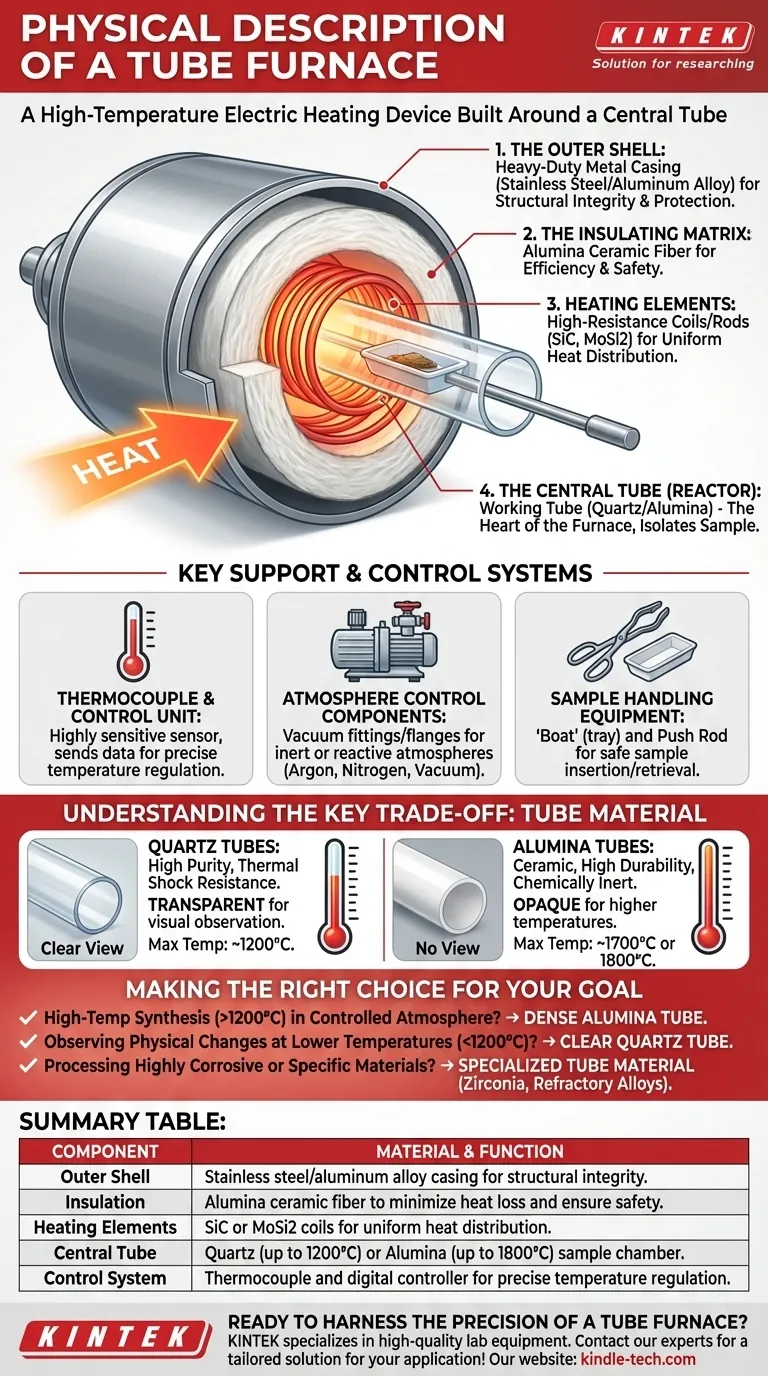
At its core, a tube furnace is a high-temperature electric heating device built around a central, cylindrical tube. It consists of a protective outer shell, a layer of thermal insulation, heating elements that encircle the tube, and a control system that uses a thermocouple for precise temperature regulation. Samples are placed inside this central tube, which can be made from materials like quartz or alumina, to be heated in a highly controlled environment.
A tube furnace is essentially a thermal "sleeve" designed for one primary purpose: to apply precise and uniform heat to a sample isolated within a central working tube. Its physical design is a layered system of shell, insulation, and heating elements, all focused on creating a stable, high-temperature zone inside that tube.

The Core Anatomy of a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace's construction can be understood as a series of concentric layers, each serving a distinct function. We can break it down from the outside in.
The Outer Shell
The outermost layer is a heavy-duty metal casing, typically made of stainless steel or a strong aluminum alloy.
This shell provides structural integrity and protects the internal components from the external environment. Its corrosion-resistant properties ensure durability.
The Insulating Matrix
Just inside the shell lies a thick layer of thermal insulation, often composed of alumina ceramic fiber.
This material is critical for both safety and efficiency. It prevents the extreme internal heat from escaping, keeping the outer shell cool to the touch and minimizing energy loss.
The Heating Elements
Embedded within the insulation are the heating elements. These are the components that actually generate the heat.
They are typically high-resistance coils or rods made from materials like resistance wire, silicon carbon (SiC), or silicon molybdenum (MoSi2). These elements completely surround the central cavity, ensuring uniform heat distribution.
The Central Tube (The Reactor)
At the very center is the working tube, which serves as the sample chamber or reactor. This is the heart of the furnace.
The tube is a separate, often removable component that isolates the sample from the heating elements. This allows for processing under vacuum or in a controlled gas atmosphere. The ends of the tube extend beyond the furnace body to allow for fittings.
Key Support and Control Systems
The furnace body is only part of the complete system. Several external components are required for it to function as a precise scientific instrument.
The Thermocouple and Control Unit
A thermocouple, a highly sensitive temperature sensor, is placed very close to or touching the central tube.
It constantly sends temperature data back to a digital control unit. This feedback loop allows the controller to precisely adjust the power sent to the heating elements, maintaining a stable temperature.
Atmosphere Control Components
The ends of the central tube are sealed with vacuum fittings or flanges.
These fittings allow for the connection of a vacuum pump to remove air or for the introduction of specific gases (like argon or nitrogen). This enables material processing in inert or reactive atmospheres.
Sample Handling Equipment
Samples are not placed directly into the hot tube. They are first put into a small tray, known as a "boat," which is often made of ceramic or metal.
A long push rod is then used to safely slide the boat into the center of the tube's hot zone and to retrieve it after processing is complete.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Tube Material
The single most important physical variable in a tube furnace is the material of the central tube itself. The choice dictates the furnace's operational limits and capabilities.
Quartz Tubes
Quartz tubes are common due to their high purity and excellent thermal shock resistance. Their key feature is transparency, which allows for visual observation of the sample during heating.
However, quartz is typically limited to temperatures around 1200°C and can react with certain alkaline materials at high temperatures.
Alumina Tubes
Alumina (a ceramic) is an opaque material used for higher temperature applications, often up to 1700°C or 1800°C.
It is highly durable and chemically inert, making it ideal for processing a wide range of materials. However, it is more brittle than quartz and does not allow for visual monitoring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The physical characteristics of the furnace directly inform its best use case. When selecting or specifying a tube furnace, your primary application is the most important factor.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (>1200°C) in a controlled atmosphere: You need a furnace equipped with a dense alumina tube and appropriate gas/vacuum fittings.
- If your primary focus is observing physical changes at lower temperatures (<1200°C): A furnace with a clear quartz tube is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly corrosive or specific materials: You must select a specialized tube material, such as zirconia or a refractory metal alloy, designed for that chemical environment.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is a versatile tool whose physical design enables precise thermal control over a sample in a perfectly isolated environment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material & Function |
|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Stainless steel/aluminum alloy casing for structural integrity. |
| Insulation | Alumina ceramic fiber to minimize heat loss and ensure safety. |
| Heating Elements | SiC or MoSi2 coils for uniform heat distribution. |
| Central Tube | Quartz (up to 1200°C) or Alumina (up to 1800°C) sample chamber. |
| Control System | Thermocouple and digital controller for precise temperature regulation. |
Ready to harness the precision of a tube furnace in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including tube furnaces designed for precise temperature control and uniform heating. Whether you need a system for high-temperature synthesis, material observation, or processing in controlled atmospheres, our experts can help you select the perfect configuration. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















