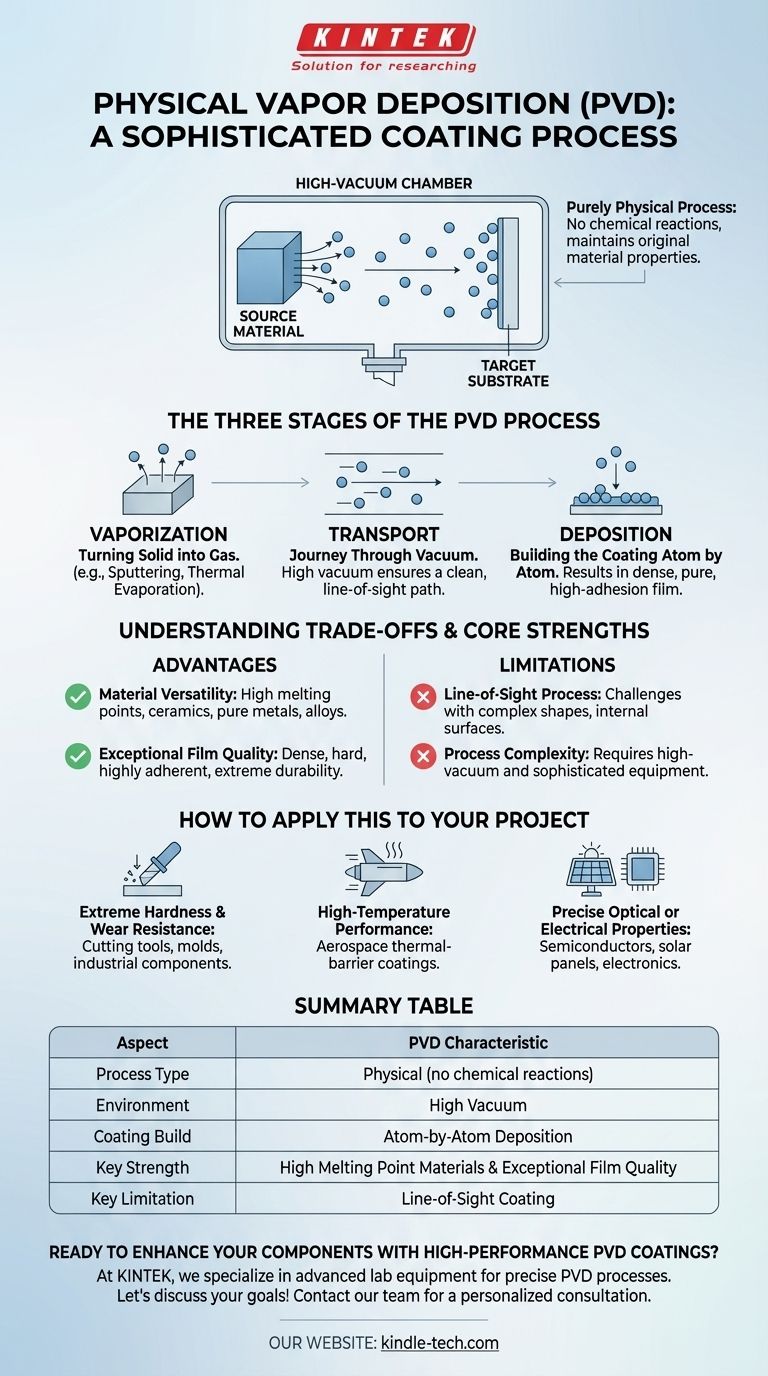
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating process that operates within a high-vacuum environment. It involves taking a solid source material, converting it into a vapor, and then allowing that vapor to travel and condense onto a target object, or substrate, to form an exceptionally thin and high-performance film. The coating is built atom by atom, resulting in a layer with superior adhesion and purity.
The defining characteristic of PVD is that it is a purely physical process. Unlike chemical methods, PVD transfers material from a source to a surface without any chemical reactions, ensuring the deposited film maintains the fundamental properties of the original material.

The Three Stages of the PVD Process
To understand how PVD works, it's best to break it down into its three fundamental stages. Each step occurs under a very high vacuum to prevent contamination and ensure a clean, direct path for the material.
1. Vaporization: Turning Solid into Gas
The process begins by converting a solid source material, known as the target, into a gaseous vapor. This is the primary distinction between different PVD methods.
Common vaporization techniques include sputtering, where the target is bombarded with high-energy ions, and thermal evaporation, where the material is heated until its atoms evaporate. More advanced methods may use an electron beam or a laser to achieve vaporization.
2. Transport: The Journey Through Vacuum
Once the atoms are freed from the solid target, they travel through the vacuum chamber. The high vacuum is critical because it removes other gas molecules that could collide with the vaporized atoms or contaminate the final film.
This ensures the material travels in a straight, line-of-sight path from the source directly to the substrate.
3. Deposition: Building the Coating Atom by Atom
When the vaporized atoms reach the surface of the substrate, they condense back into a solid state. This forms a thin, tightly bonded film.
Because this process happens on an atomic level, the resulting coating is often extremely dense, pure, and has excellent adhesion to the underlying surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Core Strengths
While PVD is a powerful technique, it is essential to understand both its advantages and its inherent limitations to determine if it is the right choice for a specific application.
Key Advantage: Material Versatility
PVD excels at depositing materials with very high melting points and ceramics that are difficult or impossible to process using other methods. This makes it ideal for creating high-performance coatings from a wide range of pure metals and alloys.
Key Advantage: Exceptional Film Quality
The atomistic deposition process results in coatings that are dense, hard, and highly adherent. This is why PVD is trusted for applications requiring extreme durability, from aerospace components to industrial cutting tools.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vaporized atoms travel in a straight line, PVD is a line-of-sight technique. This can make it challenging to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with internal surfaces or hidden features.
Limitation: Process Complexity
PVD requires a high-vacuum environment and sophisticated equipment to generate the energy for vaporization. This makes it a more complex and often higher-cost process compared to conventional coating methods like painting or electroplating.
How to Apply This to Your Project
PVD is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The decision to use it should be driven by the specific performance requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: PVD is the industry standard for applying hard, corrosion-resistant coatings to cutting tools, molds, and other components used in harsh industrial environments.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: PVD is used to apply dense, thermal-barrier coatings on aerospace components, enhancing their durability and ability to withstand extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is precise optical or electrical properties: The purity and thin-film control of PVD make it essential for manufacturing semiconductors, solar panels, and other advanced electronic components.
Ultimately, PVD is a key enabling technology for creating materials with properties that far exceed what their bulk form can offer.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (no chemical reactions) |
| Environment | High Vacuum |
| Coating Build | Atom-by-Atom Deposition |
| Key Strength | High Melting Point Materials & Exceptional Film Quality |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-Sight Coating |
Ready to enhance your components with high-performance PVD coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD processes. Whether you are developing cutting tools, aerospace components, or sophisticated electronics, our solutions deliver the superior adhesion, hardness, and purity your project demands.
Let's discuss how our expertise can help you achieve your specific coating goals. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















