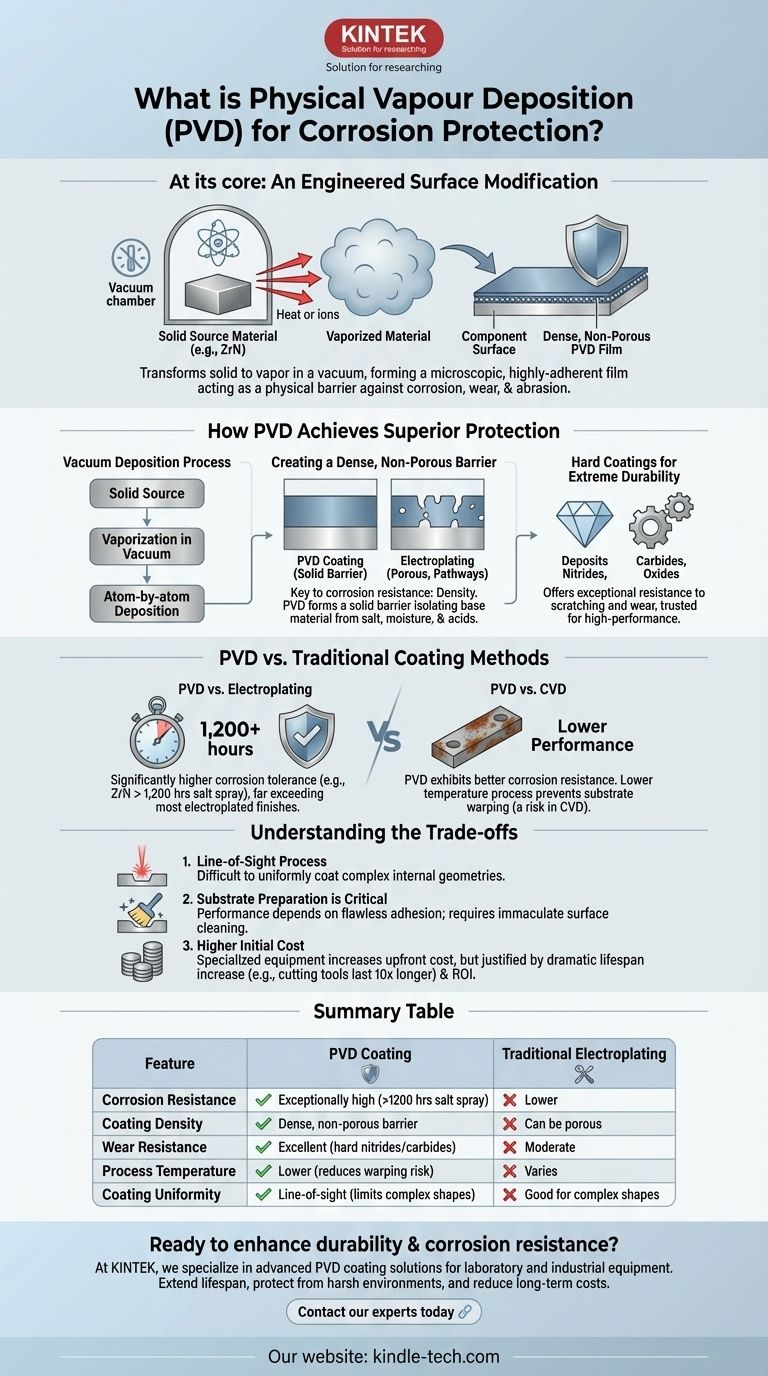
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based coating process that transforms a solid material into a vapor, which then condenses onto a component's surface to form a thin, highly-adherent film. This microscopic layer acts as a physical barrier, significantly enhancing the part's resistance to corrosion, wear, and abrasion.
While many finishing processes can provide surface protection, PVD stands apart. It should be understood not just as a coating, but as an engineered surface modification that delivers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional methods like electroplating.
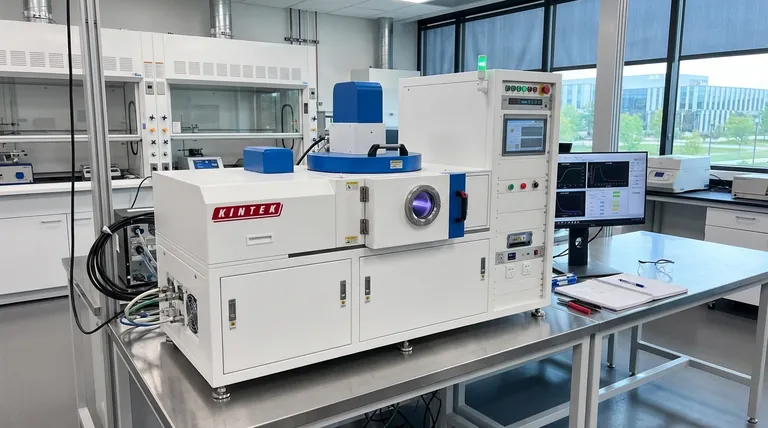

How PVD Achieves Superior Protection
PVD is not a single technique but a family of processes. Methods like sputter deposition and cathodic arc deposition all operate under the same core principle of vaporizing and depositing material in a vacuum.
The Vacuum Deposition Process
First, the components to be coated are placed in a vacuum chamber. A solid source material, such as a metal or ceramic like Zirconium Nitride, is then vaporized through heat or bombardment with ions.
This vaporized material travels through the vacuum and deposits atom-by-atom onto the components, forming a film that is exceptionally dense and uniform.
Creating a Dense, Non-Porous Barrier
The key to PVD's corrosion resistance is the density of the film. Unlike electroplating, which can be porous and create pathways for corrosion to begin, a PVD coating creates a solid, non-porous barrier.
This barrier effectively isolates the base material from corrosive elements like salt, moisture, and acidic compounds.
Hard Coatings for Extreme Durability
PVD is used to deposit extremely hard and durable materials, including nitrides, carbides, and oxides. These hard coatings not only resist chemical attack but also provide exceptional resistance to scratching and wear.
This dual benefit of corrosion and wear resistance is why PVD is trusted for high-performance applications.
PVD vs. Traditional Coating Methods
When evaluating surface treatments, it's crucial to compare PVD against older, more established methods.
The Advantage Over Electroplating
PVD demonstrates a significantly higher tolerance for corrosion than electroplating. Tests show that PVD coatings like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) can surpass 1,200 hours of neutral salt spray testing.
This level of performance far exceeds that of most electroplated finishes, making PVD more effective at preventing rust and degradation over the long term.
The PVD vs. CVD Distinction
PVD is also frequently compared to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While both are advanced techniques, PVD coatings generally exhibit better corrosion resistance.
Furthermore, PVD is a lower-temperature process, which prevents any potential warping or changes to the underlying properties of the substrate—a risk in high-temperature CVD processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
A key physical principle of PVD is its "line-of-sight" nature. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, which can make it difficult to uniformly coat complex internal geometries or deeply recessed areas.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The performance of a PVD coating is entirely dependent on the adhesion to the substrate. The component's surface must be immaculately cleaned and prepared before entering the vacuum chamber to ensure a flawless bond.
Higher Initial Cost
The specialized equipment and vacuum environment make PVD a more costly process upfront compared to traditional methods. This cost, however, is often justified by the dramatic increase in a component's lifespan and reliability.
For example, PVD-coated cutting tools can last up to 10 times longer than uncoated tools, providing a clear return on investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right coating requires balancing performance requirements, component geometry, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion and wear resistance: PVD is the superior technical choice, especially for critical components in harsh environments where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: You must carefully evaluate if PVD can achieve the required coverage or if an alternative like electroless plating is more suitable.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume production for non-critical parts: Traditional methods like electroplating may offer a more cost-effective solution, despite the lower performance.
Ultimately, choosing PVD is an investment in the long-term reliability and performance of your components.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Traditional Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptionally high (>1200 hrs salt spray) | Lower |
| Coating Density | Dense, non-porous barrier | Can be porous |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent (hard nitrides/carbides) | Moderate |
| Process Temperature | Lower (reduces substrate warping risk) | Varies |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (can limit complex geometries) | Good for complex shapes |
Ready to enhance your components' durability and corrosion resistance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coating solutions for laboratory and industrial equipment. Our coatings can dramatically extend the lifespan of your critical components, protecting them from harsh environments and reducing long-term costs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD coatings can solve your specific corrosion and wear challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















