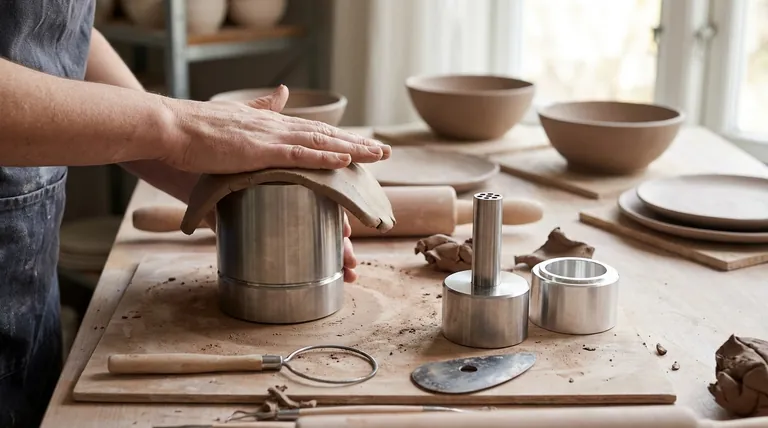
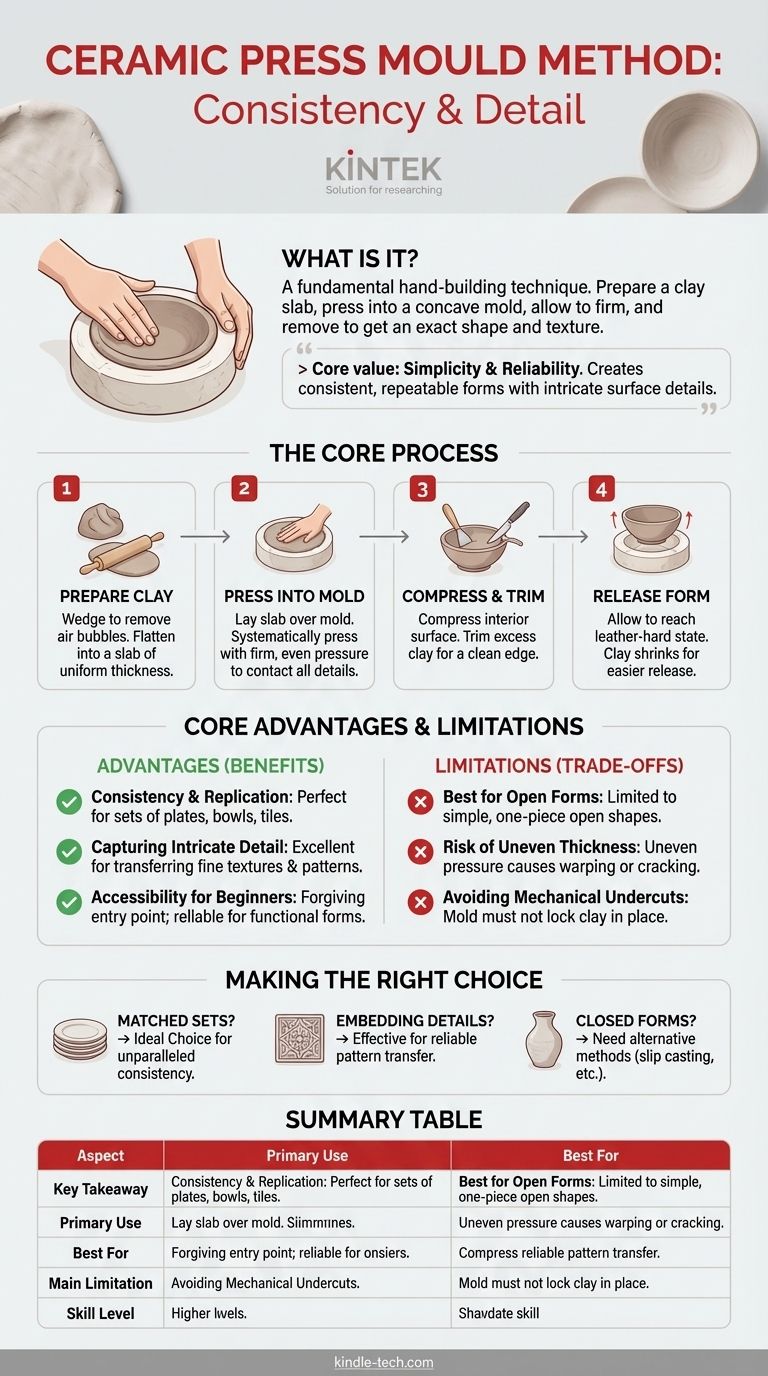
In ceramics, the press mold method is a fundamental hand-building technique used to shape clay. It involves preparing a slab or coil of clay and manually pressing it into a concave mold, forcing the clay to take on the mold's exact shape and texture. Once the clay has firmed up slightly, it is removed, leaving a positive impression of the mold's interior.
The core value of the press mold technique lies in its simplicity and reliability. It empowers artists to create consistent, repeatable forms with intricate surface details that would be difficult or time-consuming to achieve by other hand-building methods.

How Press Molding Works: The Core Process
Press molding is a direct and intuitive process. The quality of the final piece depends entirely on careful preparation and consistent pressure during the forming stage.
Step 1: Preparing the Clay
Before you begin, the clay must be properly wedged to remove air bubbles and ensure a uniform consistency. The clay is then flattened into a slab of even thickness, which is crucial for preventing cracks during drying and firing.
Step 2: Pressing Clay Into the Mold
The clay slab is carefully laid over the mold. Using your fingers, thumbs, or a soft rib, you systematically press the clay down, starting from the center and working your way outwards. The goal is to apply firm, even pressure to ensure the clay makes full contact with every detail of the mold's surface.
Step 3: Compressing and Trimming
Once the clay is fully pressed in, it's important to compress the interior surface to strengthen the clay walls. Any excess clay is then trimmed from the rim with a knife or needle tool to create a clean, level edge.
Step 4: Releasing the Form
The piece is left in the mold until the clay stiffens to a leather-hard state. At this stage, it is firm enough to hold its shape but still contains enough moisture to be handled without breaking. As the clay dries, it shrinks slightly, which helps it pull away from the mold for easier release.
The Core Advantages of Using Press Molds
This technique is a workshop staple for several key reasons, benefiting both beginners and experienced professionals.
Consistency and Replication
The primary advantage of a press mold is its ability to produce multiple, near-identical pieces. This makes it the perfect method for creating sets of plates, bowls, tiles, or any other repeated form.
Capturing Intricate Detail
Press molds excel at transferring fine textures and complex patterns to the clay surface. Any detail carved into the mold, from subtle fabric textures to sharp geometric lines, will be cleanly imprinted onto the final piece.
Accessibility for Beginners
Unlike the potter's wheel, which requires significant practice to master, press molding offers a much more forgiving entry point into ceramics. It provides a reliable way to create successful, functional forms early in one's learning journey.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the press mold technique is not suited for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Best Suited for Open Forms
A simple, one-piece press mold is designed to create open forms like bowls, platters, or shallow dishes. Creating a closed form, like a sphere or a bottle, would require a more complex, multi-part mold and is often better suited to other techniques like slip casting.
Risk of Uneven Thickness
If the clay is not pressed in with careful, consistent pressure, the walls of the piece can end up being unevenly thick. These thicker and thinner sections will dry and shrink at different rates, creating stress that can lead to warping or cracking in the kiln.
Avoiding Mechanical Undercuts
The design of the mold is critical. The mold's interior must not have any undercuts—areas where the form curves back on itself—as these will lock the clay piece in place and make it impossible to remove without damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Use these points to determine if press molding is the best approach for your specific ceramic goal.
- If your primary focus is creating a matched set of dishes or tiles: Press molding is the ideal choice for its unparalleled consistency and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is embedding complex, detailed surface textures: A press mold is one of the most effective ways to reliably transfer patterns onto clay.
- If your primary focus is making a closed or narrow-necked form (like a vase): You will likely need to combine press-molded parts or explore slip casting or coil-building instead.
Mastering the press mold unlocks a reliable and versatile method for bringing consistent, detailed forms to life in your ceramic work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Creating consistent, repeatable forms like plates, bowls, and tiles. |
| Best For | Transferring intricate surface details and patterns onto clay. |
| Main Limitation | Best suited for open forms; not ideal for closed or narrow-necked shapes. |
| Skill Level | Highly accessible for beginners, offering a forgiving entry into ceramics. |
Ready to bring your ceramic visions to life with precision and consistency?
The press mould method is a cornerstone of reliable ceramic production. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying the high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables that artists and studios need to perfect their craft. Whether you're scaling up production or ensuring every piece meets your exacting standards, the right tools make all the difference.
Let us help you equip your studio for success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your creative process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a stainless steel pressure die ensure the quality of the electrolyte layer? Unlock Precision Battery Assembly
- What functions do high-purity graphite molds serve for IZO targets? Ensure Density and Prevent Sintering Cracks
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- Why are high-strength graphite molds essential for vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Your Diamond/Copper Composites



















