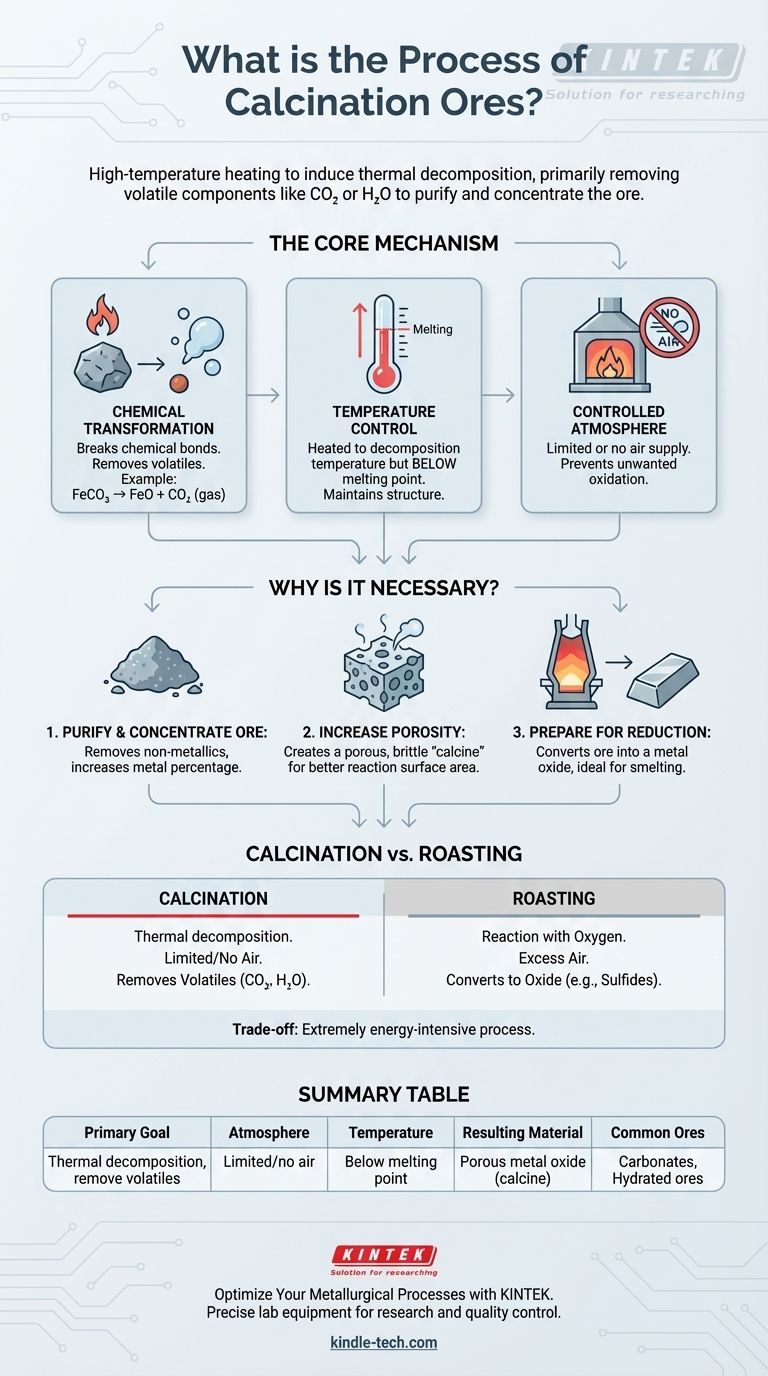
Calcination is a high-temperature heating process used to bring about a chemical change in ores and other solid materials. Its primary purpose is to remove volatile components, such as carbon dioxide or water, from the ore. For example, heating limestone (calcium carbonate) drives off carbon dioxide gas, leaving behind lime (calcium oxide).
The core purpose of calcination is not simply to heat an ore, but to induce its thermal decomposition. This purifies and concentrates the ore, making it more porous and chemically suitable for the next stage of metal extraction, which is typically reduction.
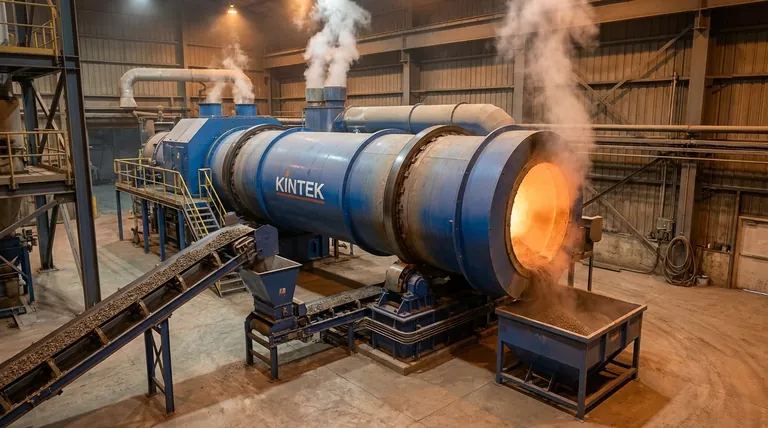

The Core Mechanism: What Happens During Calcination?
Calcination is a foundational process in metallurgy and materials science. Understanding its core mechanism requires looking at the chemical reaction, the role of temperature, and the specific atmospheric conditions used.
The Chemical Transformation
The heat applied during calcination provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds within the ore. This causes the material to decompose into two or more simpler substances.
A primary outcome is the removal of a volatile component, which escapes as a gas, leaving a more concentrated solid behind. Common examples for different ore types include:
- Carbonate Ores:
FeCO₃ (Siderite) → FeO (Iron(II) Oxide) + CO₂ (gas) - Hydrated Ores:
Al₂O₃·2H₂O (Bauxite) → Al₂O₃ (Alumina) + 2H₂O (gas)
The Critical Role of Temperature
The process requires heating the ore to a temperature high enough to initiate decomposition but below its melting point.
If the ore were to melt, its structure would change entirely, defeating the purpose of creating a porous, reactive solid for the next stage. Each mineral has a specific decomposition temperature that must be precisely maintained.
The Controlled Atmosphere
A defining feature of calcination is that it is typically carried out in the absence or a limited supply of air.
This prevents unwanted oxidation of the ore. The goal is purely decomposition, not a reaction with oxygen from the atmosphere.
Why is Calcination a Necessary Step?
Metallurgists don't perform this energy-intensive process without good reason. Calcination serves several critical functions that make subsequent metal extraction more efficient.
To Purify and Concentrate the Ore
By driving off components like water and carbon dioxide, the process removes non-metallic substances. This significantly increases the percentage of the desired metal in the remaining material, making it more concentrated.
To Increase Porosity
As gases escape from the solid ore, they leave behind a network of tiny pores. This makes the resulting material, known as the "calcine," much more porous and brittle.
This increased surface area is crucial because it allows reducing gases (like carbon monoxide in a blast furnace) to penetrate and react with the ore more effectively and quickly.
To Prepare for Smelting (Reduction)
Ultimately, calcination converts the ore into a form—usually a metal oxide—that is ideally suited for reduction. A porous, concentrated oxide is far easier to convert into a pure metal than the original, raw ore.
Understanding Key Distinctions and Trade-offs
To fully grasp calcination, it's essential to distinguish it from a similar process and acknowledge its primary industrial challenge.
Calcination vs. Roasting
These two terms are often confused, but they describe fundamentally different chemical objectives.
- Calcination is thermal decomposition, done in limited or no air. The goal is to remove volatiles like H₂O or CO₂.
- Roasting is a reaction with oxygen, done in excess air. The goal is to convert an ore (often a metal sulfide) into a metal oxide. For example:
2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂.
The Energy Cost
Heating vast quantities of ore to hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius is an extremely energy-intensive process. The cost of fuel is a significant economic factor in any large-scale smelting operation and is the primary trade-off of this essential step.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right thermal treatment depends entirely on the chemical nature of the ore you are processing.
- If your primary focus is carbonate or hydrated ores: Calcination is the essential first step to drive off CO₂ or H₂O and produce the metal oxide.
- If your primary focus is sulfide ores: Roasting, not calcination, is the correct process to convert the sulfide into an oxide by reacting it with oxygen.
- If your primary focus is oxide ores that are already pure: Neither process may be needed, and the ore can proceed directly to reduction.
Calcination is the fundamental preparatory step that transforms raw ore into a refined material ready for the final creation of pure metal.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition to remove volatile components (e.g., CO₂, H₂O) |
| Atmosphere | Limited or no air to prevent unwanted oxidation |
| Temperature | Heated below the melting point of the ore |
| Resulting Material | Purified, porous metal oxide (calcine) ready for reduction |
| Common Ore Types | Carbonate ores (e.g., limestone) and Hydrated ores (e.g., bauxite) |
Optimize Your Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Understanding the precise thermal treatment your materials require is critical for efficient metal extraction and purification. Whether your operations involve calcination, roasting, or other high-temperature processes, having the right laboratory equipment is essential for research, development, and quality control.
KINTEK specializes in supplying robust and precise lab furnaces, reactors, and consumables designed to meet the demanding needs of metallurgical and materials science laboratories. Our equipment ensures accurate temperature control and atmospheric conditions, helping you achieve consistent, reliable results.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your specific ore processing and metal extraction goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















