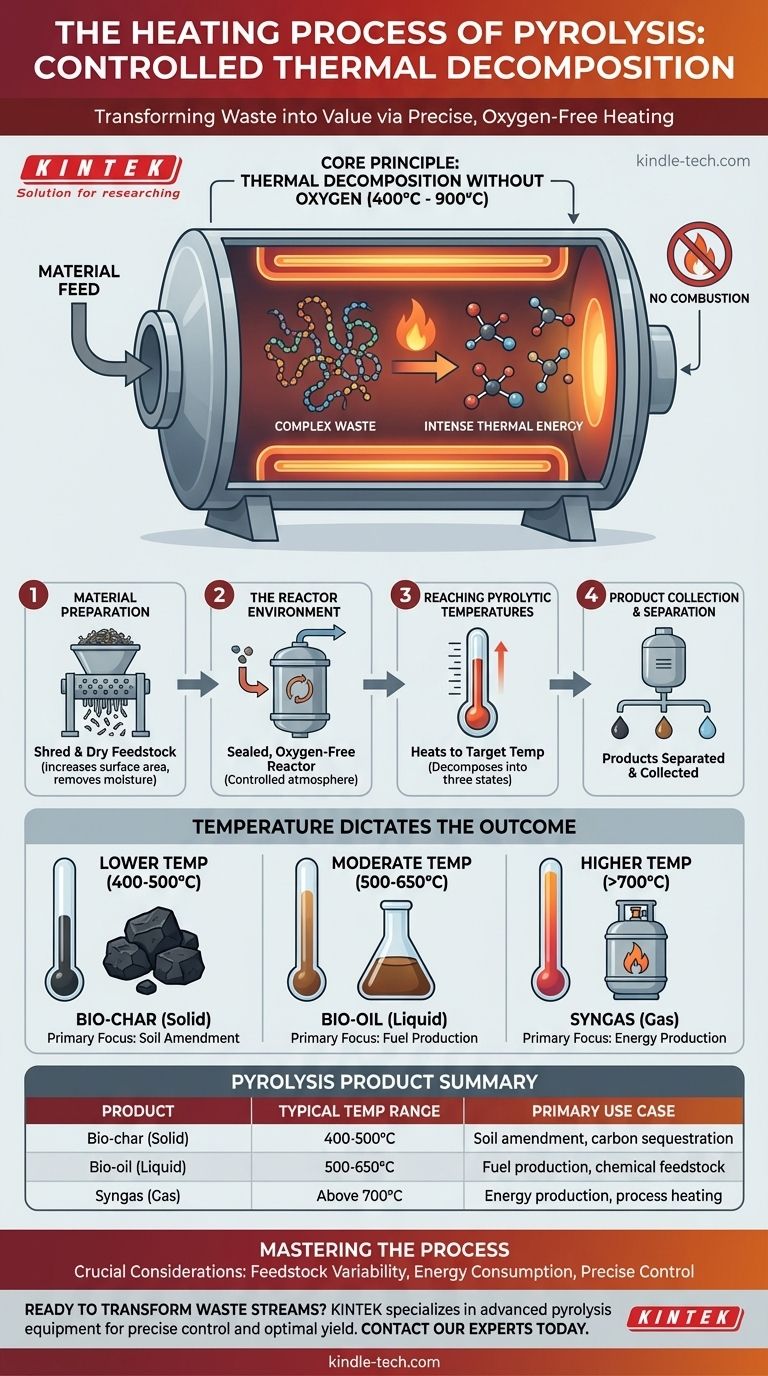
In essence, the heating process in pyrolysis is the controlled thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C, within a reactor that is completely devoid of oxygen. This absence of oxygen is the critical factor that prevents the material from burning (combusting) and instead forces its complex molecules to break apart into simpler, valuable substances like syngas, bio-oil, and bio-char.
The core principle to understand is that pyrolysis heating is not burning. It is a precise, oxygen-free thermal process designed to deconstruct a material at a molecular level, transforming it from a low-value waste into a high-value resource.
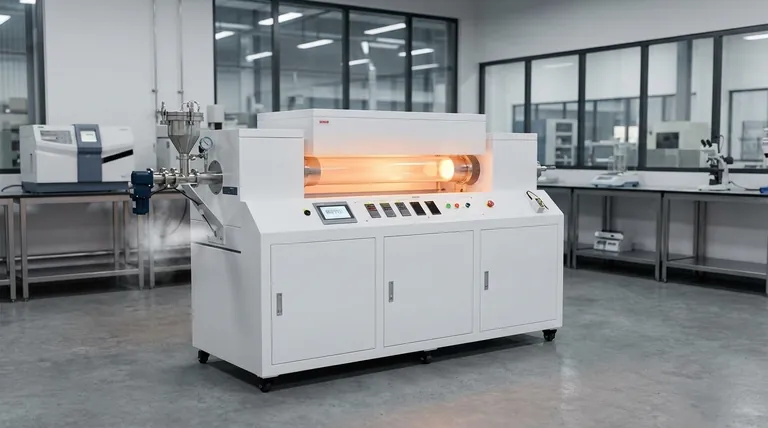

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
To truly grasp pyrolysis, you must understand the interplay between heat and the controlled atmosphere. The process hinges on applying intense thermal energy while strictly preventing combustion.
Why No Oxygen is Critical
Without oxygen, combustion cannot occur. Instead of burning and releasing energy as fire, the material's chemical bonds become unstable from the heat and simply break. This fundamental distinction is what separates pyrolysis from incineration.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat provides the necessary energy to sever the long, complex polymer chains found in materials like plastic, tires, or biomass (cellulose and lignin). As these chains break down into smaller, more volatile molecules, they vaporize, leaving behind a solid carbon residue.
Temperature Dictates the Outcome
The final product distribution is highly dependent on the temperature inside the reactor. A lower temperature might favor the production of solid bio-char, while higher temperatures tend to yield more syngas and bio-oil. The specific target temperature is set based on the desired output.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Heating Stage
While the heating itself happens inside the reactor, it's a single step in a larger, integrated workflow.
Step 1: Material Preparation
Before heating can begin, the raw feedstock (like plastic waste or biomass) is often shredded and dried. This increases the surface area for more efficient heat transfer and removes moisture that can interfere with the process.
Step 2: The Reactor Environment
The prepared material is fed into a sealed, oxygen-free reactor. This is the heart of the pyrolysis plant where the controlled heating takes place.
Step 3: Reaching Pyrolytic Temperatures
The reactor heats the material to its target temperature, typically between 400°C and 900°C. As the material decomposes, it separates into three primary states.
- Solid: A carbon-rich residue called bio-char.
- Liquid: Vapors that are condensed to form bio-oil (also called pyrolysis oil).
- Gas: Non-condensable gases known as syngas.
Step 4: Product Collection and Separation
These three products are then separated and collected. The bio-char is typically removed from the bottom of the reactor, while the gas and vapor mixture is piped out to be cooled, separating the liquid bio-oil from the syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Applying this process effectively requires a clear understanding of its operational realities and limitations.
Feedstock Variability
Different materials decompose differently. The plastics in municipal waste require a different heating profile and pre-treatment than wood chips or agricultural residue. The process must be tuned to the specific feedstock being used.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of up to 900°C is an energy-intensive process. A portion of the syngas produced during pyrolysis is often used to power the system itself, but the overall energy balance is a critical factor in the economic viability of a plant.
The Need for Precise Control
Success in pyrolysis depends on precise control systems. Any deviation in temperature, pressure, or the introduction of oxygen can dramatically alter the output, reduce efficiency, and introduce safety risks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The heating parameters you choose are directly tied to the product you want to create.
- If your primary focus is producing bio-char for soil amendment: This typically requires slower heating rates at the lower end of the temperature range (around 400-500°C).
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil for fuel: This is often achieved with very fast heating rates to moderate temperatures (around 500-650°C).
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for energy production: This generally demands the highest process temperatures (above 700°C) to further break down molecules into their gaseous components.
Ultimately, mastering the heating process is the key to unlocking the specific value hidden within a given waste stream.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Typical Temperature Range | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-char (Solid) | 400-500°C | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | 500-650°C | Fuel production, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas (Gas) | Above 700°C | Energy production, process heating |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and pilot-scale pyrolysis equipment designed for precise temperature control and optimal product yield. Whether your goal is to produce bio-char, bio-oil, or syngas, our reactors are engineered for efficiency and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis solutions can meet your specific research and processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the characteristics of the slipping, slumping, and rolling modes of bed motion? Optimize Your Rotary Process
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















