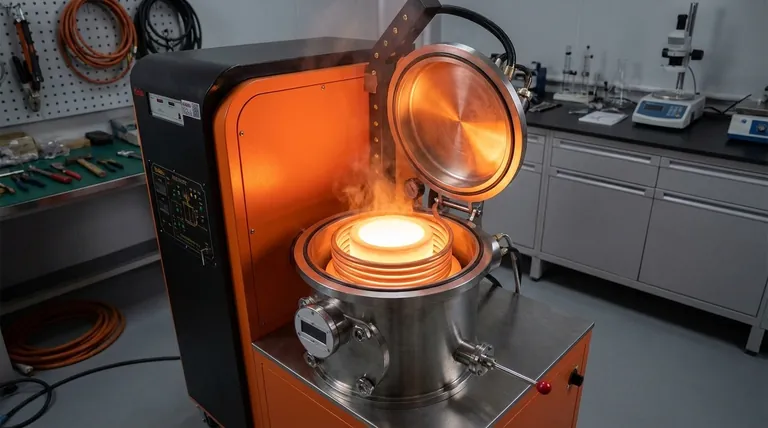
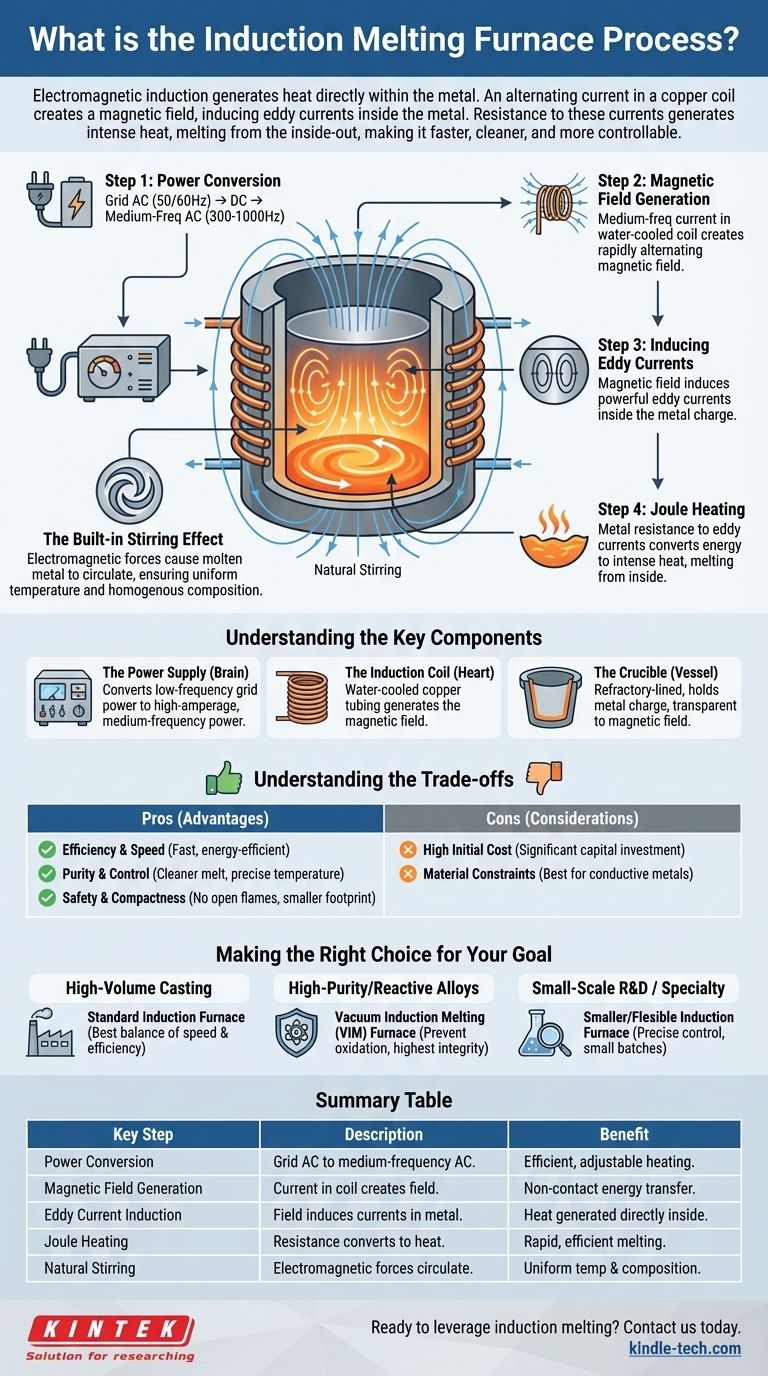
The induction melting process uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal itself. An alternating current passes through a copper coil, creating a powerful and rapidly reversing magnetic field. This field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, inside the metal charge, and the metal's own resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt without any direct contact from a flame or heating element.
Unlike traditional furnaces that heat a material from the outside-in, an induction furnace uses a magnetic field to create internal electrical currents that melt the metal from the inside-out. This fundamental difference makes the process significantly faster, cleaner, and more controllable.

The Core Principle: From Electricity to Molten Metal
The entire process is a chain of energy conversions, engineered for maximum efficiency. Each step plays a critical role in transforming grid electricity into the heat required for melting.
Step 1: Power Conversion
The process begins with a standard three-phase, low-frequency (50/60Hz) alternating current (AC) from the power grid. A specialized power supply first converts this AC into direct current (DC).
It then converts the DC back into a single-phase, medium-frequency AC, typically between 300Hz and 1000Hz. This adjustable, medium-frequency current is the key to efficient induction heating.
Step 2: Generating the Magnetic Field
This engineered medium-frequency current is fed into an induction coil, which is usually made of hollow copper tubing. As the current flows through the coil, it generates a strong, rapidly alternating magnetic field in the space within the coil where the crucible sits.
Step 3: Inducing Eddy Currents
The magnetic field passes through the metal charge placed inside the crucible. According to Faraday's law of induction, the changing magnetic field induces powerful circular electrical currents—known as eddy currents—within the metal.
The metal charge essentially becomes the secondary coil of a transformer, with the induction coil acting as the primary.
Step 4: Joule Heating
The induced eddy currents flow through the metal, which has its own natural electrical resistance. This resistance impedes the flow of the currents, converting the electrical energy directly into thermal energy through a process called Joule heating.
Because this heat is generated inside the metal itself, melting is exceptionally rapid and efficient, with minimal heat loss to the surrounding environment.
The Built-in Stirring Effect
A unique advantage of this process is the natural stirring action. The electromagnetic forces that create the eddy currents also cause the molten metal to move and circulate.
This inherent stirring ensures the melt achieves a uniform temperature and a homogenous chemical composition, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Understanding the Key Components
An induction furnace system is relatively simple in concept, consisting of three primary components working in concert.
The Power Supply
This is the "brain" of the system. It is a sophisticated solid-state unit responsible for the crucial task of converting low-frequency grid power into the high-amperage, medium-frequency power required by the induction coil.
The Induction Coil
This is the "heart" of the furnace. It's a precisely wound coil of copper tubing that creates the magnetic field. It is almost always water-cooled to dissipate the immense heat generated by the high electrical currents flowing through it.
The Crucible
This is the refractory-lined vessel that holds the metal charge. It must be made from a material that can withstand extreme temperatures and is transparent to the magnetic field, allowing the field to pass through and couple with the metal inside.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction melting involves specific advantages and considerations that make it suitable for certain applications over others.
Pro: Efficiency and Speed
Because heat is generated directly within the material, the process is incredibly fast and energy-efficient compared to methods that rely on external combustion or heating elements. Start-up and melting times are significantly shorter.
Pro: Purity and Control
There are no combustion byproducts (like gas or soot) to contaminate the metal, resulting in a cleaner melt. The power input can be precisely controlled, allowing for accurate temperature management and superior metallurgical results.
Pro: Safety and Compactness
The lack of open flames or massive external heat sources creates a safer and cooler working environment. The furnaces themselves are also more compact than traditional furnaces of equivalent capacity.
Con: High Initial Cost
The sophisticated power supply units and precision-engineered coils represent a significant capital investment compared to simpler fuel-fired furnace technologies.
Con: Material Constraints
Induction melting is most effective for electrically conductive metals. While non-conductive materials can be melted in a conductive (e.g., graphite) crucible, the process is indirect and less efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your material requirements, production scale, and quality standards.
- If your primary focus is high-volume casting of standard metals (e.g., iron, steel, aluminum): A standard medium-frequency induction furnace offers the best balance of speed, efficiency, and cleanliness for foundry operations.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, reactive alloys (e.g., titanium, nickel-based superalloys): A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure the highest material integrity.
- If your primary focus is small-scale R&D or specialty precious metals: A smaller, more flexible induction furnace allows for precise control over small batches and unique alloys with minimal material loss.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of internal heating is the key to leveraging the precision, speed, and cleanliness of induction melting technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Power Conversion | Grid AC is converted to medium-frequency AC. | Enables efficient and adjustable heating. |
| Magnetic Field Generation | Current in the copper coil creates an alternating magnetic field. | Non-contact energy transfer to the metal. |
| Eddy Current Induction | The magnetic field induces electrical currents (eddy currents) inside the metal. | Heat is generated directly within the material. |
| Joule Heating | Metal resistance converts electrical energy into intense heat. | Rapid, efficient melting from the inside out. |
| Natural Stirring | Electromagnetic forces circulate the molten metal. | Ensures uniform temperature and composition. |
Ready to leverage the precision and efficiency of induction melting in your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction melting furnaces designed for speed, purity, and control. Whether you are involved in R&D, producing high-purity alloys, or high-volume metal casting, our solutions help you achieve superior results with cleaner melts and significant energy savings.
Contact us today to discuss your specific metal processing needs and discover how our technology can enhance your operations.
Get in touch via our Contact Form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is plasma arc melting? Achieve Unmatched Purity for High-Performance Metals
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What metals can be melted with induction? From Steel to Gold, Discover the Versatility
- What is a channel type induction furnace? A Guide to Efficient Metal Holding & Melting
- What is the primary function of a Vacuum Induction Furnace in 15Cr12MoVWN steel melting? Ensure Purity and Precision
- What is induction heating for industrial use? A Guide to Fast, Clean, and Precise Heat
- How does magnetic field heat metal? Achieve Precise Thermal Control with Induction Heating
- What is the primary function of an induction melting furnace? Achieving Homogeneity in Fe-Cr-Ni Alloys



















