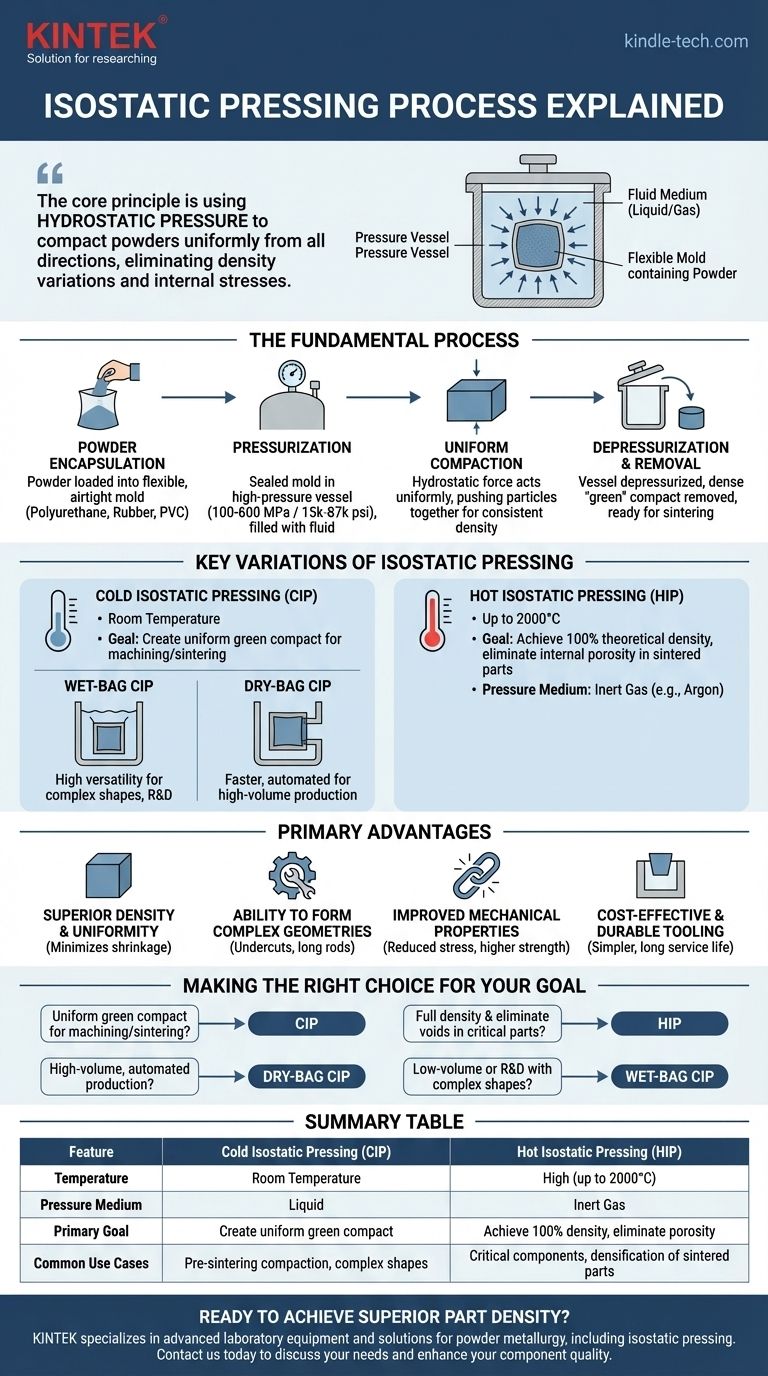
Isostatic pressing is a powder metallurgy process that forms a solid component by subjecting a powder sealed within a flexible mold to uniform, high pressure. This pressure is transmitted through a fluid medium—either a liquid or a gas—ensuring that the compressive force is applied equally from all directions. The result is a highly uniform, dense "green" compact ready for subsequent processing like sintering.
The core principle behind isostatic pressing is the use of hydrostatic pressure to compact powders. Unlike traditional pressing which applies force from one or two directions, this method eliminates density variations and internal stresses, making it ideal for creating complex, high-performance parts.
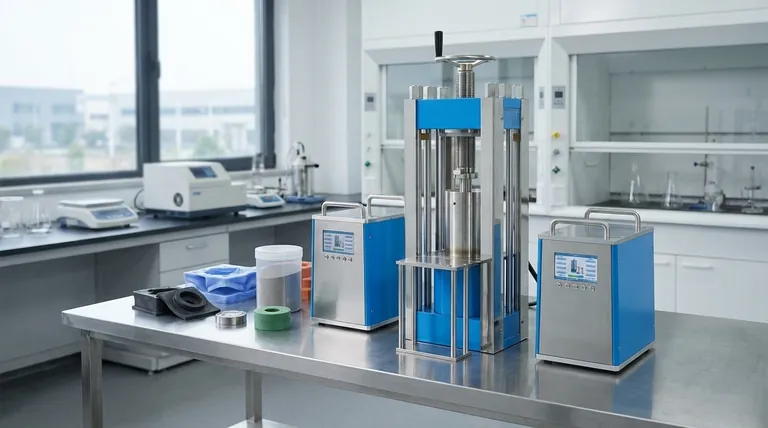

The Fundamental Process Explained
The effectiveness of isostatic pressing stems from a basic principle of fluid dynamics: pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
Step 1: Powder Encapsulation
The process begins by loading a precisely measured amount of powder into a flexible, airtight mold or bag. This mold is typically made from materials like polyurethane, rubber, or PVC and is designed to be the inverse shape of the desired part.
Step 2: Pressurization
The sealed mold is placed inside a high-pressure vessel. The vessel is then filled with a fluid, and pumps increase the pressure to the required level, typically ranging from 100 to 600 MPa (15,000 to 87,000 psi).
Step 3: Uniform Compaction
The hydrostatic pressure from the fluid acts uniformly on the entire surface of the flexible mold. This force is transmitted through the mold to the powder particles, pushing them closer together and creating a solid object with consistent density throughout.
Step 4: Depressurization and Removal
After holding at the target pressure for a set duration, the vessel is carefully depressurized. The compacted part, now known as a "green" compact, is removed from the mold. It is solid enough to be handled but typically requires a subsequent thermal treatment (sintering) to achieve its final strength.
Key Variations of Isostatic Pressing
The general process can be categorized into two main types, differentiated by temperature, and a further two methods based on how the mold is handled.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is performed at or near room temperature. Its primary purpose is to create a green compact with sufficient strength and uniform density for machining or sintering.
Wet-Bag vs. Dry-Bag CIP
Within CIP, there are two common techniques. The wet-bag method involves submerging the sealed mold directly into the pressurizing fluid in the vessel, offering high versatility for complex shapes and R&D. The dry-bag method integrates the mold into the pressure vessel itself, allowing for faster, more automated loading and unloading suitable for high-volume production.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) combines intense heat (up to 2,000°C) with high pressure. An inert gas, typically argon, is used as the pressure medium instead of a liquid. HIP is used not only to compact powders but also to eliminate any remaining internal porosity in already-sintered parts, achieving 100% theoretical density.
Understanding the Primary Advantages
Isostatic pressing is chosen over conventional methods for several critical reasons that directly impact final part quality.
Superior Density and Uniformity
The most significant advantage is the creation of a part with high and even density. This minimizes shrinkage and distortion during the final sintering stage, a common problem with uniaxial pressing which creates density gradients.
Ability to Form Complex Geometries
Because pressure is applied from all sides, the process can produce parts with complex shapes, high length-to-diameter ratios (like long rods or tubes), and undercuts that are impossible to achieve with rigid die pressing.
Improved Mechanical Properties
The uniform compaction reduces internal stress within the component. This results in products with higher strength and excellent machinability compared to those made by other methods.
Cost-Effective and Durable Tooling
The flexible molds are often simpler and less expensive to manufacture than the hardened steel dies required for conventional pressing. They also tend to have a long service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific method you choose depends entirely on your end goal, production volume, and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform green compact for further machining or sintering: Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is the most direct and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving full theoretical density and eliminating all internal voids in a critical component: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the necessary final processing step.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated production of a consistent part: The dry-bag CIP method is optimized for speed and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or R&D with many different complex shapes: The wet-bag CIP method offers the greatest flexibility.
Ultimately, isostatic pressing provides an unparalleled capability for producing dense, uniform components from powdered materials that are vital for high-performance applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Room Temperature | High (up to 2000°C) |
| Pressure Medium | Liquid | Inert Gas (e.g., Argon) |
| Primary Goal | Create uniform green compact | Achieve 100% density, eliminate porosity |
| Common Use Cases | Pre-sintering compaction, complex shapes | Critical components, densification of sintered parts |
Ready to achieve superior part density and complex geometries with isostatic pressing?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including solutions for powder metallurgy processes like isostatic pressing. Whether you are developing new materials in R&D or optimizing high-volume production, our expertise can help you select the right pressing method and equipment to enhance your component quality and performance.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- Why Use an Isostatic or High-Precision Hydraulic Press for Li/LLZO/Li Batteries? Master Solid-State Interfaces
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- Why is isostatic pressing better than regular uniaxial pressing when manufacturing ceramics? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes
- What is cold sintering? A Low-Energy Path to Novel Composite Materials
- What advantages does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) offer for solid-state batteries? Superior Density & Uniformity
- What is the specific function of a cold isostatic press in the sintering process of LiFePO4? Maximize Battery Density
- What is the dry bag process? A Guide to High-Speed Isostatic Pressing



















