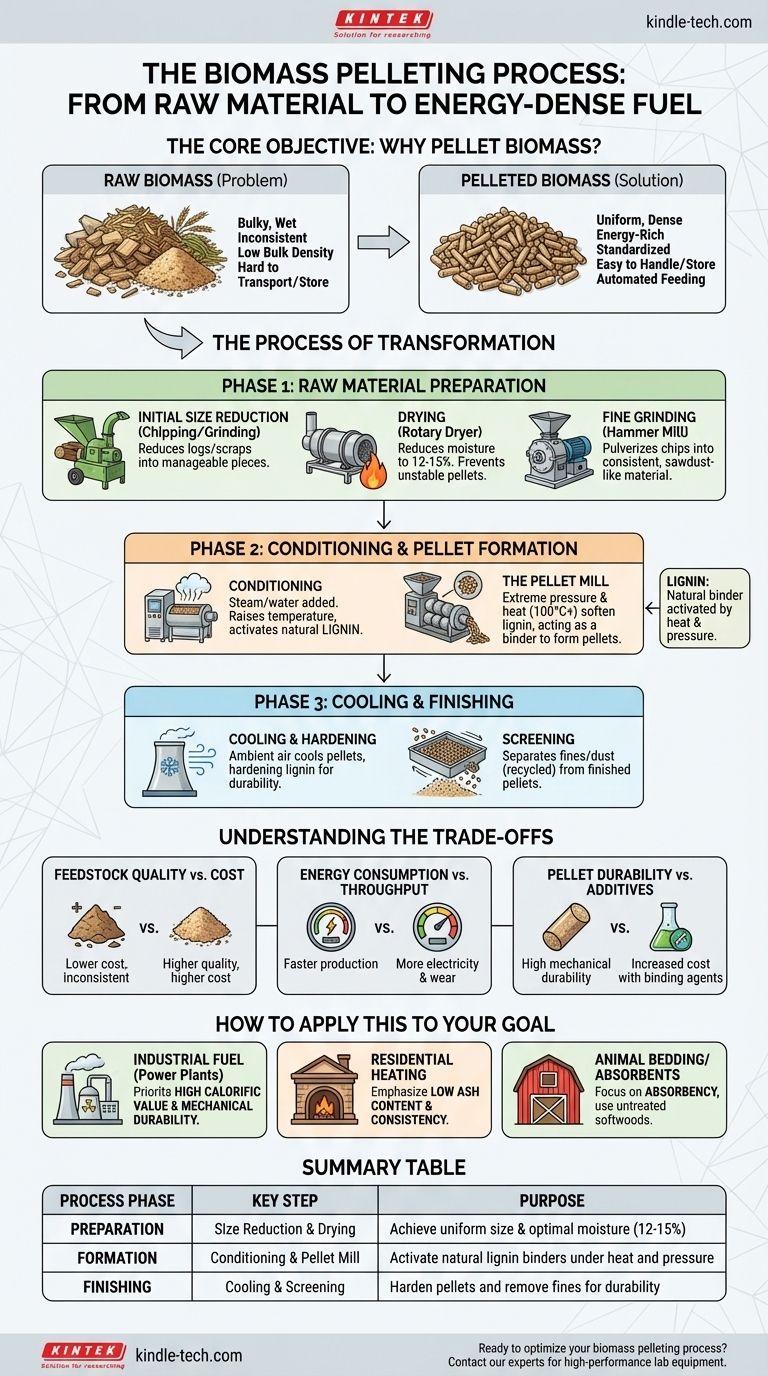
In short, the process of pelleting biomass is a multi-stage manufacturing operation that transforms raw, low-density organic material into dense, uniform, and energy-rich pellets. This involves systematically reducing the material's size, carefully controlling its moisture content, and then forcing it through a specialized die under extreme pressure and heat. The final steps involve cooling, hardening, and screening the pellets to ensure a high-quality, standardized final product.
The core purpose of pelleting is not merely compression; it is the transformation of inconsistent, difficult-to-handle raw biomass into a standardized, flowable, and energy-dense commodity fuel. This is achieved by manipulating moisture, heat, and pressure to activate natural binders within the material itself.

The Core Objective: Why Pellet Biomass?
Before examining the steps, it's critical to understand the goal. Raw biomass like wood chips, sawdust, or agricultural residue is often bulky, wet, and inconsistent, making it difficult to transport, store, and use efficiently.
The Problem with Raw Biomass
Raw biomass has low bulk density, meaning it takes up a lot of space for the energy it contains. This makes transportation and storage expensive and inefficient.
Its irregular shape and size also prevent it from being used in automated feeding systems, a requirement for modern power plants and heating systems.
The Value of Densification
Pelleting solves these problems by creating a uniform and dense product. A wood pellet has a much higher energy density than the sawdust it was made from.
This standardization allows biomass to be handled like other bulk commodities, such as corn or coal, enabling automated logistics and combustion.
The Step-by-Step Pelleting Process
The process can be broken down into three primary phases: material preparation, pellet formation, and finishing. Each step is critical for the final quality of the pellet.
Phase 1: Raw Material Preparation
This initial phase is arguably the most important, as it determines the success of all subsequent steps.
### H3: Initial Size Reduction (Chipping/Grinding)
The raw feedstock, such as logs or large wood scraps, is first processed through a chipper or grinder. This reduces the material into smaller, more manageable pieces.
### H3: Drying
This is a critical control point. The chipped material is then sent to a large rotary dryer to reduce its moisture content to a precise level, typically between 12-15%. Too much moisture creates soft, unstable pellets; too little prevents proper binding.
### H3: Fine Grinding (Hammer Milling)
After drying, the material is fed into a hammer mill. This machine uses rapidly swinging hammers to pulverize the chips into a fine, consistent, sawdust-like consistency, which is necessary for creating a dense, well-formed pellet.
Phase 2: Conditioning and Pellet Formation
This is the heart of the operation where the actual pellet is created.
### H3: Conditioning
The finely ground material enters a conditioner where steam or water is added. This step raises the temperature and slightly increases moisture, which helps to activate the natural lignin within the biomass.
### H3: The Pellet Mill
The conditioned material is then fed into the pellet mill. Inside, heavy rollers force the material through the holes of a thick, hardened steel ring called a pellet die. Think of it like a giant, industrial-strength pasta maker.
### H3: The Role of Lignin
The immense pressure and friction generate intense heat (often over 100°C / 212°F). This heat softens the lignin, a natural polymer in plant cell walls, causing it to act as a glue that binds the particles together as the pellet is extruded.
Phase 3: Cooling and Finishing
The pellets are not yet ready for use as they exit the die.
### H3: Cooling and Hardening
Pellets emerge from the mill hot, soft, and emitting steam. They are immediately transferred to a cooler, where ambient air is drawn over them. This process cools the pellets and hardens the lignin, giving the final product its characteristic durability.
### H3: Screening
Finally, the cooled pellets are passed over a screen. This separates out any fine material or dust (fines) from the finished product. These fines are typically recycled back into the production stream, ensuring minimal waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The pelleting process is a balance of competing factors that directly impact cost and quality.
Feedstock Quality vs. Cost
Using low-cost, inconsistent feedstock (like bark or agricultural waste) can reduce input costs but often requires more intensive preparation and can lead to higher ash content and lower pellet quality.
Energy Consumption vs. Throughput
Running a pellet mill faster increases production but also consumes significantly more electricity and can increase wear on the die and rollers. Pushing for maximum throughput can sometimes compromise pellet durability.
Pellet Durability vs. Additives
Achieving high mechanical durability is essential for reducing breakage during transport. While proper process control is key, some producers use binding agents like starch to improve durability, which adds to the operational cost.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your primary objective determines which aspects of the process are most critical.
- If your primary focus is producing industrial-grade fuel for power plants: Prioritize achieving a high calorific value and mechanical durability, even if it requires higher energy input during production.
- If your primary focus is creating residential heating pellets: Emphasize low ash content and consistency, which requires very clean feedstock and meticulous screening.
- If your primary focus is animal bedding or absorbents: Focus on using untreated softwoods and controlling the drying process to maximize absorbency, as energy content is not a concern.
Ultimately, successful biomass pelleting is a precise industrial process that transforms a low-value variable resource into a high-value standardized product.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Key Step | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Size Reduction & Drying | Achieve uniform particle size and optimal moisture (12-15%) |
| Formation | Conditioning & Pellet Mill | Activate natural lignin binders under heat and pressure |
| Finishing | Cooling & Screening | Harden pellets and remove fines for durability |
Ready to optimize your biomass pelleting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for testing and refining biomass materials. Whether you're developing industrial fuel pellets or specialized products like animal bedding, our solutions help you achieve precise moisture control, durability, and consistency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your pelleting goals with reliable, efficient laboratory technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of applying high pressure in dry cathode preparation? Achieve Peak Solid-State Battery Density
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic hot press in the assembly of solid-state photoelectrochemical cells?



















