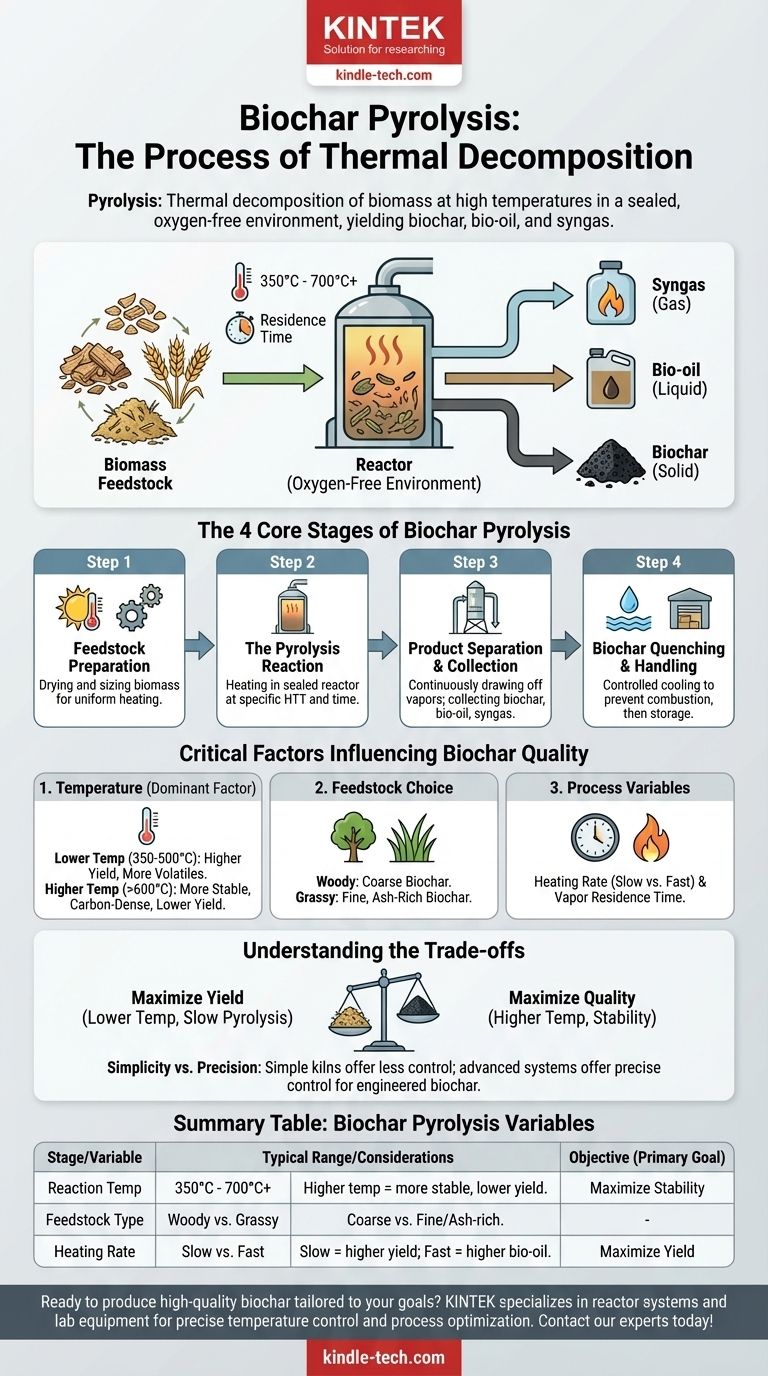
In essence, pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition that transforms biomass, such as wood or agricultural waste, into biochar. This is achieved by heating the material to high temperatures in a sealed, oxygen-free or oxygen-limited environment. Without oxygen, the biomass does not combust; instead, it breaks down into a stable, carbon-rich solid (biochar), along with liquid (bio-oil) and gas (syngas) co-products.
The core principle of biochar production is not merely heating biomass, but precisely controlling the conditions of that heating process. The final yield and characteristics of your biochar are directly determined by key variables, with temperature being the single most influential factor.
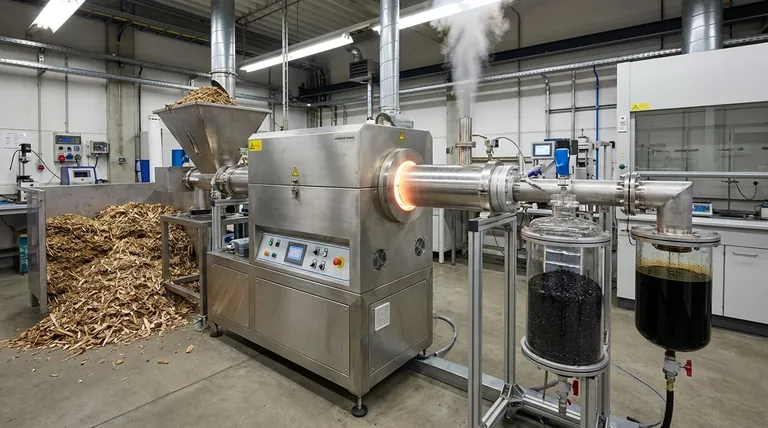

The Core Stages of Biochar Pyrolysis
The transformation from raw biomass to finished biochar follows a clear, multi-stage process. Each step presents an opportunity to influence the final product's quality.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The process begins with the raw organic material, or feedstock. This can include a wide range of materials like pine wood, wheat straw, green waste, or even dried algae.
This initial stage involves preparing the biomass for the reactor, which may include drying to reduce moisture content and chipping or grinding to create a uniform particle size for even heating.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reaction
The prepared feedstock is fed into a reactor, which is then sealed to eliminate oxygen. The biomass is heated to a specific pyrolysis temperature, typically ranging from 350°C to 700°C or higher.
The material is held at this highest treatment temperature (HTT) for a specific residence time. During this phase, volatile compounds are driven off as gases and vapors, leaving behind the solid, carbon-dense biochar.
Step 3: Product Separation and Collection
As the biomass decomposes, it separates into three distinct products: solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, and syngas.
An effective pyrolysis plant has separate mechanisms to continuously draw off the hot vapors and gases. These can be condensed to capture the bio-oil or used as fuel to sustain the reaction, while the solid biochar remains in the primary chamber.
Step 4: Biochar Quenching and Handling
Once the reaction is complete, the hot biochar must be cooled down in a controlled manner. This process, known as quenching, prevents it from combusting upon exposure to oxygen.
After quenching, the stable biochar is collected, stored, and prepared for its intended application, whether in agriculture, filtration, or construction.
Critical Factors Influencing Biochar Quality
Simply completing the steps is not enough; mastering the process means understanding the variables that control the outcome.
The Dominant Role of Temperature
The highest treatment temperature (HTT) has the greatest overall influence on biochar properties. Lower temperatures (350-500°C) tend to produce a higher yield of biochar, but the char itself has more volatile matter.
Higher temperatures (>600°C) produce a lower biochar yield but result in a more stable, carbon-dense product with a higher surface area.
The Impact of Feedstock Choice
The starting material matters. Woody biomass generally produces a coarse, blocky biochar, while grassy feedstocks like straw result in a finer, more ash-rich biochar. The feedstock's inherent chemical structure sets the baseline for the final product's characteristics.
Other Process Variables
While secondary to temperature, factors like heating rate and vapor residence time also play a role. Slow pyrolysis, which involves a slow heating rate, maximizes the yield of biochar, often achieving up to 30% yield by dry weight. Fast pyrolysis prioritizes bio-oil production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Producing biochar is a balancing act between competing objectives. There is no single "best" method, only the best method for a specific goal.
Yield vs. Quality
There is an inherent trade-off between the quantity of biochar produced and its specific qualities.
A process optimized for maximum yield (e.g., slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures) will not produce the most stable, high-carbon biochar. Conversely, targeting high carbon stability with high temperatures will inevitably reduce your total solid yield.
Simplicity vs. Precision
Simple, low-cost pyrolysis systems (like kilns or batch reactors) can produce quality biochar but offer limited control over temperature and heating rate.
Highly instrumented, continuous-flow systems offer precise control over all variables, enabling consistent production of engineered biochar. However, this precision comes with significantly higher capital and operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To produce the right biochar, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar yield for soil volume: Employ slow pyrolysis with lower peak temperatures (around 450-550°C).
- If your primary focus is creating a highly stable biochar for long-term carbon sequestration: Use higher peak temperatures (above 600°C), accepting a lower overall yield.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse and wet waste streams: Invest in robust feedstock drying and preparation equipment ahead of the pyrolysis unit.
Understanding these controlling factors empowers you to engineer the pyrolysis process to create a biochar with the exact properties you require.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Variable | Typical Range/Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction | Pyrolysis Temperature | 350°C - 700°C+ (Higher temp = more stable biochar, lower yield) |
| Feedstock | Biomass Type | Woody (coarse biochar) vs. Grassy (fine, ash-rich biochar) |
| Process | Heating Rate | Slow Pyrolysis (maximizes biochar yield) vs. Fast Pyrolysis (maximizes bio-oil) |
| Objective | Primary Goal | Maximize Yield (lower temp) vs. Maximize Stability/Carbon Sequestration (higher temp) |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar tailored to your specific goals?
Whether your focus is maximizing yield for soil amendment or creating a highly stable product for carbon sequestration, the right lab equipment is crucial for precise temperature control and process optimization. KINTEK specializes in reactor systems and lab equipment for pyrolysis research and development, helping you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your biochar production needs and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity



















