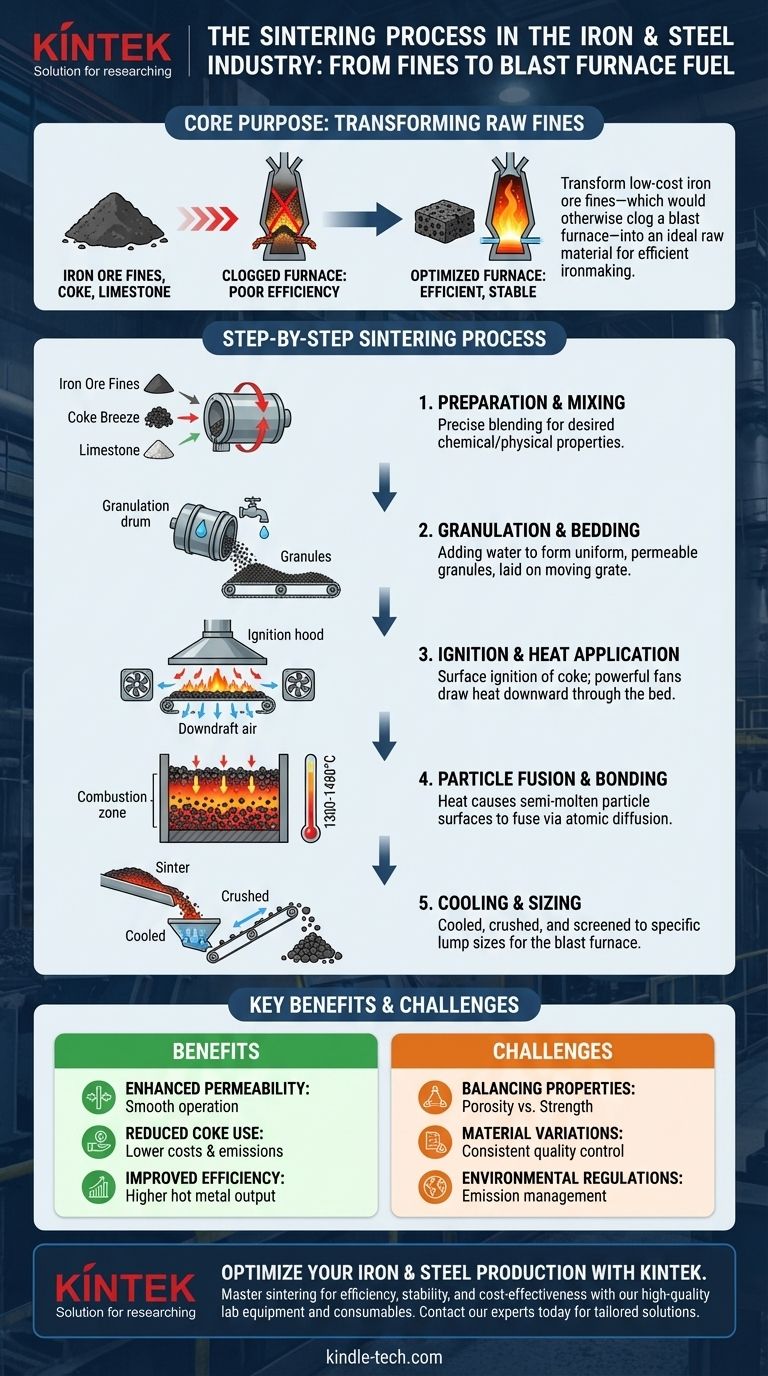
In the iron and steel industry, sintering is the critical process of agglomerating fine iron ore particles with other materials like coke and limestone into a coarse, porous mass called "sinter." This is done by heating the mixture to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together. The resulting sinter is the primary iron-bearing raw material fed into a blast furnace for iron production.
The core purpose of sintering is not to create a finished metal part, but to transform low-cost iron ore fines—which would otherwise clog a blast furnace—into an ideal raw material that ensures efficient, stable, and cost-effective ironmaking.

Why Sintering is Fundamental to Steel Production
Before detailing the process, it's essential to understand the problem sintering solves. A blast furnace relies on hot gases flowing upward through a column of raw materials to chemically reduce iron ore into liquid iron.
The Problem with Raw Iron Ore Fines
Modern mining produces a large quantity of fine iron ore particles. If these fine powders were charged directly into a blast furnace, they would pack together tightly.
This dense packing would severely restrict the flow of hot gases, effectively choking the furnace. The result would be poor efficiency, unstable operation, and a dramatic decrease in iron production.
The Solution: Creating Sintered Ore
Sintering converts these unusable fines into large, strong, and porous lumps. This "sintered ore" has the ideal properties for blast furnace operation.
The porous nature allows hot gases to pass through the material bed evenly, maximizing contact with the iron ore. The strength prevents the sinter from crumbling under the immense weight of the furnace charge.
Key Benefits for the Blast Furnace
A high-quality sinter directly improves blast furnace performance in several ways.
It enhances permeability, ensuring smooth and predictable furnace operation. It also reduces the required amount of coke, the expensive and carbon-intensive fuel used in ironmaking, and significantly improves the overall utilization and efficiency of the furnace.
The Step-by-Step Sintering Process
While the principle is simple fusion, the industrial process is a carefully controlled, continuous operation.
Step 1: Raw Material Preparation and Mixing
The process begins by precisely mixing the primary ingredients. The typical "sinter mix" includes iron ore fines, a solid fuel like coke breeze, and a fluxing agent like crushed limestone.
These materials are blended in specific ratios to ensure the final sinter has the desired chemical and physical properties.
Step 2: Granulation and Bedding
Water is added to the mix in a rotating drum to facilitate granulation. This causes the fine particles to stick together, forming small, quasi-spherical granules.
This granular mix is then laid down on a moving grate, called the sinter strand, to form a uniform, permeable bed.
Step 3: Ignition and Heat Application
The sinter strand moves under an ignition hood fired by gas. This intense heat ignites the coke breeze on the surface of the bed.
As the strand continues to move, powerful fans draw air down through the bed. This pulls the "combustion zone" downwards, layer by layer, through the entire mix, providing the heat needed for fusion.
Step 4: Particle Fusion and Bonding
The heat generated by the burning coke (reaching 1300-1480°C) is sufficient to cause the surfaces of the iron ore particles to become semi-molten.
This triggers atomic diffusion, allowing the particles to fuse together. The limestone acts as a flux, helping to bind the particles and form a strong, coherent mass.
Step 5: Cooling and Sizing
Once the combustion front reaches the bottom of the bed, the sintering process is complete. The hot, fused mass is discharged from the end of the strand.
This hot sinter is then cooled and subsequently crushed and screened to produce lumps within a specific size range required for optimal blast furnace charging.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Achieving high-quality sinter is a constant balancing act with significant operational challenges.
Balancing Permeability and Strength
The ideal sinter must be highly porous to allow for gas flow but also mechanically strong enough to resist degradation during handling and inside the blast furnace. These two properties are often in opposition, requiring precise control over the raw mix and heating process.
Managing Raw Material Quality
The chemical composition and physical characteristics of the iron ore, coke, and limestone can vary significantly. The sintering plant must constantly adjust its process parameters to compensate for these variations to produce a consistent final product.
Environmental Regulations
Sintering plants are a major source of atmospheric emissions, including dust, SOx, and NOx. Managing these emissions to comply with stringent environmental regulations requires significant investment in gas cleaning and pollution control technologies, adding a major layer of operational complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The quality of the sinter has a direct and measurable impact on the entire ironmaking value chain. Understanding its role helps prioritize operational focus.
- If your primary focus is blast furnace efficiency: Consistent, high-quality sinter is the most critical factor, as it directly reduces coke consumption and increases hot metal output.
- If your primary focus is operational stability: Prioritizing the strength and size consistency of the sinter ensures smooth gas flow within the furnace, preventing costly disruptions and unplanned downtime.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: Optimizing the sintering process allows the use of a wider range of lower-cost iron ore fines, significantly improving the economics of raw material procurement.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is foundational to achieving competitive, efficient, and stable modern iron production.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Inputs | Key Process | Key Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Prep | Iron ore fines, Coke breeze, Limestone | Precise mixing and blending | Uniform sinter mix |
| Granulation & Bedding | Sinter mix, Water | Granulation in a rotating drum; forming a bed on a moving grate | Permeable granular bed |
| Ignition & Heating | Ignition hood (gas-fired); downdraft air | Ignition of coke; combustion front moves downward through the bed | Initial particle fusion |
| Fusion & Bonding | Heat (1300-1480°C) | Surfaces of particles become semi-molten; atomic diffusion occurs | Strong, fused sinter mass |
| Cooling & Sizing | Hot sinter | Cooling, crushing, and screening | Sized sinter lumps for blast furnace |
Optimize Your Iron and Steel Production with KINTEK
Mastering the sintering process is crucial for maximizing blast furnace efficiency, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Whether your goal is to reduce coke consumption, enhance operational stability, or lower raw material costs, the right equipment and consumables are key.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support the precise control and analysis needed for optimal sintering. Our products help you monitor raw material quality, simulate process conditions, and ensure consistent, high-quality sinter output.
Ready to improve your sintering process and boost your bottom line? Contact our experts today to discover how KINTEK’s solutions can be tailored to your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















