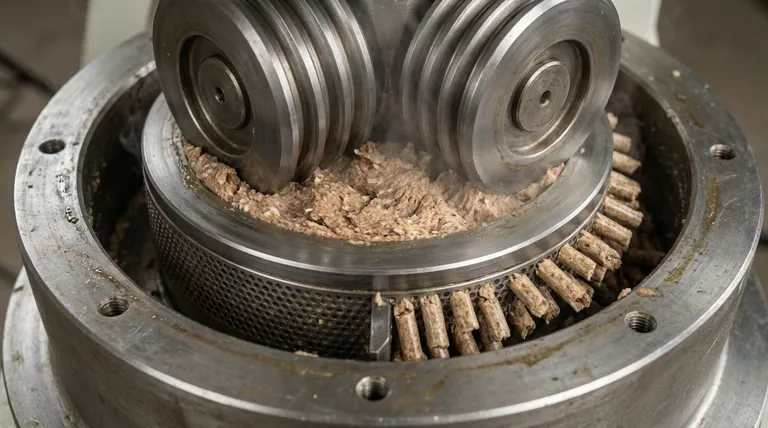
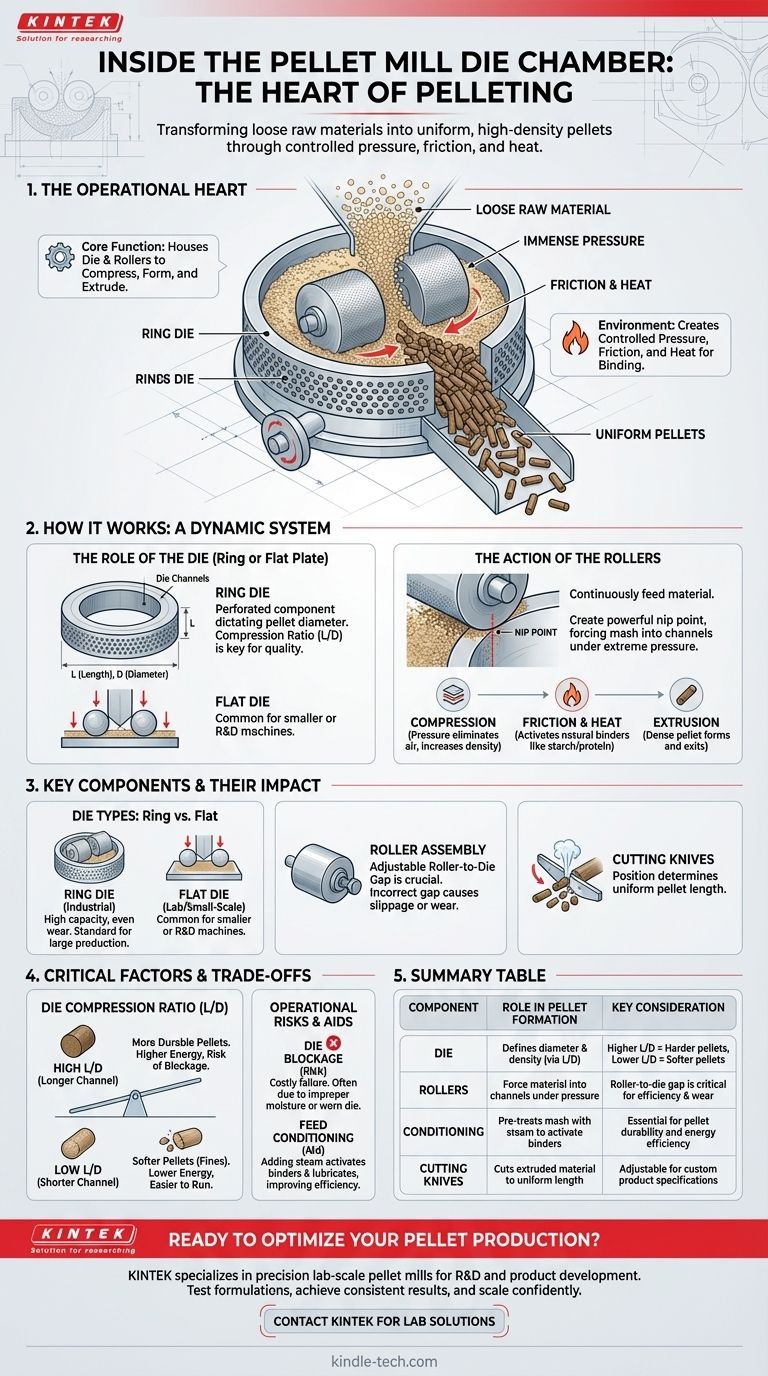
At its core, the pellet mill die chamber is the operational heart of the pelleting process, where loose raw materials are transformed into dense, uniform pellets. This chamber houses the two critical components—the die and the rollers—which work in tandem under immense pressure to compress, form, and extrude the final product.
The purpose of the die chamber is not merely to contain the material, but to create a highly controlled environment of pressure, friction, and heat. It is this environment that forces the physical and chemical changes necessary to bind loose particles into durable, high-density pellets.

How the Die Chamber Functions
To understand the chamber, you must understand the interplay between its core components and the material being processed. It is a dynamic system, not a simple press.
The Role of the Die
The die is a thick, perforated metal component, typically in the shape of a ring or a flat plate. These perforations, known as die channels, dictate the final diameter of the pellets.
The die's thickness is just as critical as the hole diameter. This relationship, known as the compression ratio (L/D)—the length of the die channel (L) divided by its diameter (D)—is a primary factor in determining pellet quality.
The Action of the Rollers
Inside the chamber, one or more rollers rotate, continuously feeding raw material (mash) to the inner surface of the die. The gap between the rollers and the die is minimal, creating a powerful nip point.
This action forces the mash into the die channels under extreme pressure. It's this compressive force that initiates the pelleting process.
The Physics of Pellet Formation
As the material is forced through the die channels, three crucial things happen. First, immense pressure compacts the particles, eliminating air pockets and increasing density.
Second, intense friction between the material and the die channel walls generates significant heat. This heat helps to activate natural binders within the feed, such as starches (gelatinization) and proteins (denaturation), which act as a natural glue.
Finally, the now-compacted and heated material is extruded from the other side of the die as a dense, cylindrical pellet.
Key Components and Their Impact
The specific design of the components within the chamber directly influences the efficiency and output of the entire pellet mill.
Ring Die vs. Flat Die
Ring dies, where the die is a vertical ring and rollers press from the inside out, are the standard for high-capacity industrial applications like animal feed production. They offer higher throughput and more even wear.
Flat dies, where a flat plate die lies horizontally and rollers press down from above, are typically found on smaller-scale or lab-scale machines.
Roller Assembly
The rollers are not fixed. They are designed to be adjustable, allowing operators to set the precise roller-to-die gap. An incorrect gap can lead to slippage (too large) or premature wear on both the roller and the die (too small).
The Cutting Knives
As the dense spaghetti-like strands of material exit the die, adjustable knives are positioned to cut them to a specific, uniform length. The speed and position of these knives determine the final length of the pellet.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
The die chamber's performance is a balancing act. Optimizing for one variable often means compromising on another.
Die Compression Ratio (L/D)
A high compression ratio (a long channel relative to its diameter) creates more friction and pressure. This results in highly durable, dense pellets but requires more energy, increases wear, and raises the risk of blockages.
A low compression ratio is easier to run and requires less energy, but may produce softer pellets that are more prone to breaking apart (fines).
The Risk of Die Blockage
A plugged die is a common and costly operational failure. It occurs when material gets stuck and hardens inside the die channels, stopping production. This is often caused by improper raw material moisture, an incorrect feed formulation, or a worn-out die.
The Impact of Feed Conditioning
The die chamber does not work in isolation. The state of the raw material entering the chamber is paramount. The process of conditioning—adding steam to the mash to elevate its temperature and moisture content before it enters the die chamber—is critical for activating binders and lubricating the die, making the entire process more efficient and effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Optimizing the die chamber's function depends entirely on your production priorities.
- If your primary focus is pellet durability: Prioritize a higher die compression ratio (L/D) and ensure proper steam conditioning to activate natural binders and create a stronger pellet.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Use a well-maintained die with a moderate compression ratio and precisely optimize the roller-to-die gap to ensure efficient material flow without slippage.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Ensure your raw material is conditioned to the ideal moisture and temperature, as this acts as a lubricant and reduces the frictional load on the main drive motor.
By understanding the die chamber, you transform it from a "black box" into a controllable system, giving you direct command over your final product quality.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Pellet Formation | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Die | Defines pellet diameter and density via compression ratio (L/D) | Higher L/D = harder pellets, lower L/D = softer pellets |
| Rollers | Force material into die channels under extreme pressure | Roller-to-die gap is critical for efficiency and wear |
| Conditioning | Pre-treats mash with steam to activate natural binders | Essential for pellet durability and energy efficiency |
| Cutting Knives | Cuts extruded material to precise, uniform pellet length | Adjustable for custom product specifications |
Ready to Optimize Your Pellet Production?
Understanding the die chamber is the first step to achieving superior pellet quality, durability, and throughput. The right equipment is critical for your success.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab-scale pellet mills and consumables, perfect for R&D, product development, and small-scale production. Whether you're developing new animal feed formulas, creating biomass fuels, or producing specialty pellets, our equipment gives you direct control over the entire process.
We help you:
- Test formulations with exact control over compression ratios and conditioning.
- Achieve consistent results with robust, reliable machinery.
- Scale your process confidently from the lab to production.
Contact us today to find the perfect pellet mill solution for your laboratory needs. Let's discuss how we can enhance your pelleting process.
[#ContactForm Contact KINTEK Now]
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory manual hydraulic pellet press for FTIR? Enhance Your Spectral Data
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the significance of applying 200 MPa of pressure with a laboratory hydraulic pellet press for composite ceramics?
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for Li3V2(PO4)3 pellets? Optimize Solid-State Sintering for Li-ion Materials
- How does a laboratory hydraulic pellet press contribute to SiCw/2024 aluminum composite preforms? Optimize Densification



















