In short, the purpose of PVD coating is to deposit an extremely thin, hard film onto a surface to dramatically improve its performance. This is not simply a paint or a plating; it is a molecular-level process that enhances a material's durability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and overall appearance.
The core function of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is to transform the surface of a standard component into a high-performance material, tailoring its properties for specific, demanding applications without altering the underlying object.

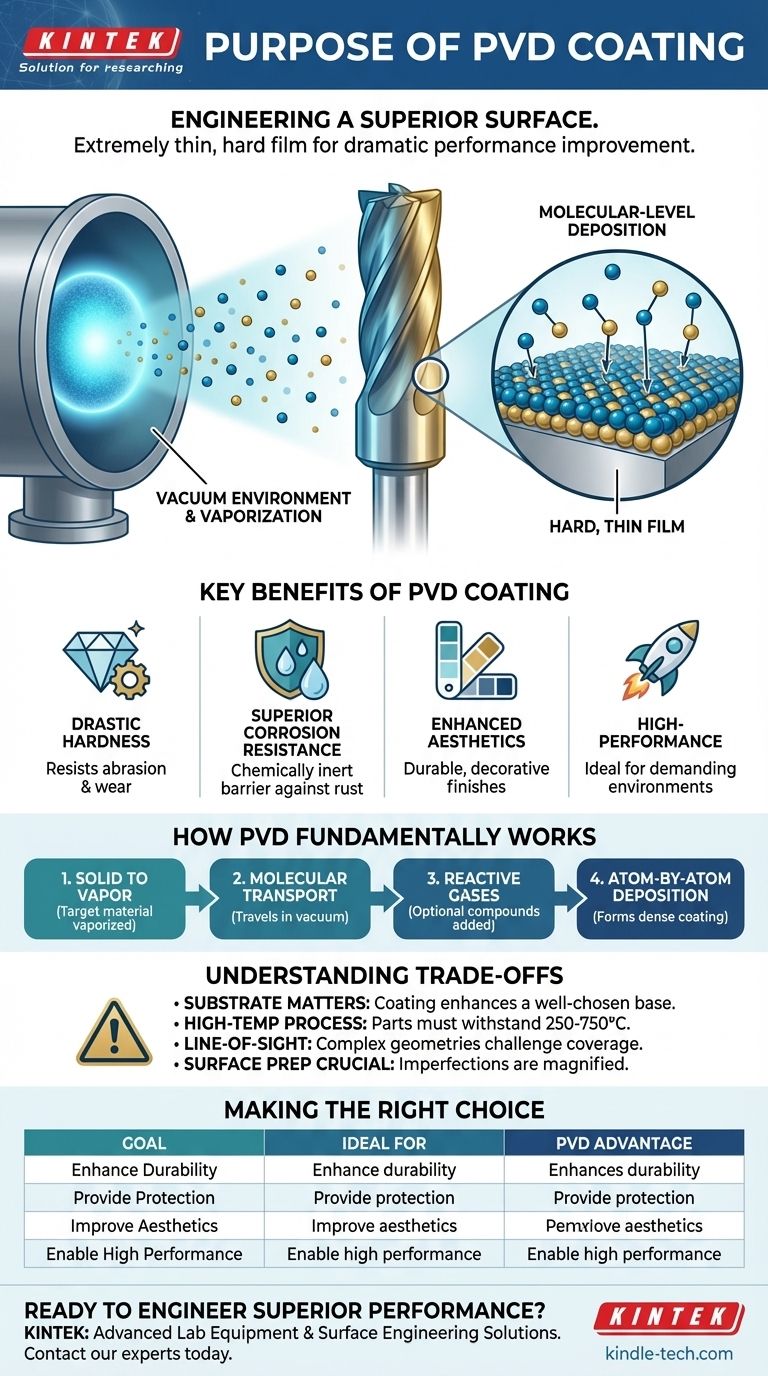
How PVD Fundamentally Works
To understand the purpose of PVD, you must first understand the process. It is a sophisticated technique that takes place entirely within a high-vacuum chamber.
The Vacuum Environment
The entire PVD process occurs under a vacuum. This is critical because it removes atmospheric particles that could otherwise interfere with the process, ensuring the purity and quality of the final coating.
From Solid to Vapor
A solid source material, known as the target, is converted into a vapor. This is achieved through physical methods like high-energy sputtering or cathodic arc evaporation, which bombard the target and release atoms from its surface.
Molecular-Level Deposition
These vaporized atoms travel across the vacuum chamber and condense onto the surface of the component being coated. Because this happens atom by atom, the resulting film is incredibly dense, uniform, and forms an exceptionally strong bond with the substrate.
Creating New Compounds
During the deposition process, reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen can be introduced. These gases combine with the metal vapor to form specific ceramic compound coatings (like Titanium Nitride), allowing for a wide range of tailored physical and tribological properties.
The Key Benefits of a PVD Coating
Applying a PVD coating is an engineering decision designed to achieve specific performance outcomes that the base material alone cannot provide.
Drastic Improvement in Hardness
The primary benefit is a significant increase in surface hardness. This makes components highly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and wear, extending their functional lifespan dramatically.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
PVD coatings are chemically inert and incredibly dense. This creates an effective barrier that protects the underlying material from oxidation, corrosion, and attack from various chemicals.
Enhanced Aesthetic Finishes
Beyond performance, PVD provides a durable and consistent decorative finish. It allows for a variety of colors and textures on materials like stainless steel, which are far more resilient than traditional methods like painting or electroplating.
High-Performance in Demanding Environments
The combination of hardness, stability, and a low coefficient of friction makes PVD-coated parts ideal for demanding applications, such as high-temperature cutting tools where performance and longevity are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is tied to specific process requirements and limitations.
The Substrate Material is Paramount
The final properties of the coated part are a combination of the coating and the base material. A PVD coating will not fix a weak or unsuitable substrate; it can only enhance the properties of a well-chosen foundation.
It's a High-Temperature Process
PVD requires high temperatures, often ranging from 250°C to 750°C. Therefore, the component being coated must be able to withstand this thermal load without deforming or losing its essential properties.
It is a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vaporized atoms travel in a straight line, coating complex internal geometries or deeply recessed areas can be challenging. Parts often need to be carefully positioned and rotated to ensure even coverage.
Surface Preparation is Crucial
The final PVD finish will replicate the texture of the underlying surface. The process cannot hide or fix imperfections. A flawless, highly polished finish requires a flawlessly prepared surface before coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select PVD coating when your goal is to engineer a superior surface for a specific task.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: PVD is an excellent choice for tools, bearings, and components subjected to high friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is environmental protection: The inert, dense barrier provided by PVD offers a superior defense against corrosion and chemical attack.
- If your primary focus is a premium aesthetic: PVD offers a wide range of stable, vibrant colors and finishes that are far more durable than plating or painting.
Ultimately, PVD coating empowers you to engineer the surface of a component for a specific performance outcome without changing the core material itself.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of PVD Coating | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance Durability | Drastically increases surface hardness and wear resistance. | Cutting tools, bearings, industrial components. |
| Provide Protection | Creates a dense, inert barrier against corrosion and chemicals. | Medical devices, marine hardware, automotive parts. |
| Improve Aesthetics | Offers durable, consistent colors and finishes. | Consumer electronics, architectural hardware, luxury goods. |
| Enable High Performance | Combines low friction with stability in extreme environments. | Aerospace components, high-temperature tooling. |
Ready to engineer superior performance into your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise in PVD coating technologies can help you achieve unparalleled durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finishes for your laboratory or manufacturing needs.
Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your specific applications. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















