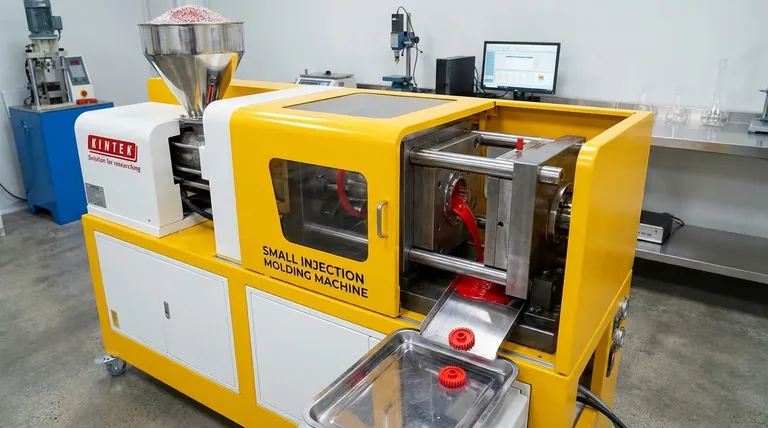
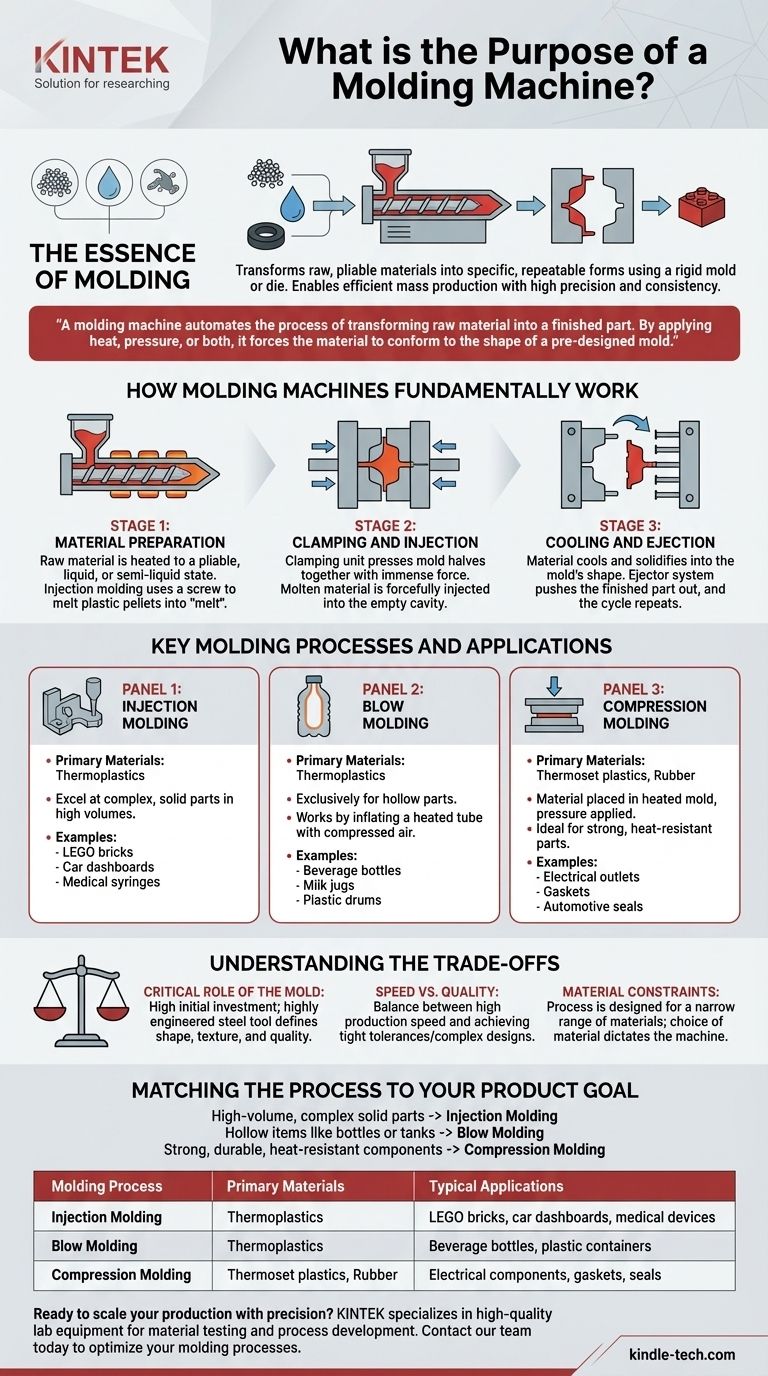
In essence, the purpose of a molding machine is to shape raw, pliable materials like plastic, rubber, or metal into a specific, repeatable form using a rigid frame known as a mold or die. These machines are the engines of modern mass production, allowing for the rapid creation of everything from simple bottle caps to complex automotive components with high precision and consistency.
A molding machine automates the process of transforming raw material into a finished part. By applying heat, pressure, or both, it forces the material to conform to the shape of a pre-designed mold, enabling the efficient mass production of identical items.

How Molding Machines Fundamentally Work
At their core, all molding machines follow a similar three-stage principle: prepare the material, shape it under force, and solidify the final part. Understanding this sequence is key to grasping their function.
Stage 1: Material Preparation
The process begins by getting the raw material into a pliable, liquid, or semi-liquid state. For the most common process, injection molding, this involves feeding plastic pellets from a hopper into a heated barrel where a screw melts and mixes them into a molten liquid called "melt."
Stage 2: Clamping and Injection
The machine's clamping unit presses two halves of the steel mold together with immense force. This ensures the mold remains sealed shut against the high pressure of the injection phase. The molten material is then forcefully injected from the barrel into the empty cavity of the mold, filling it completely.
Stage 3: Cooling and Ejection
Once the mold cavity is filled, the material begins to cool and solidify, taking on the shape of the mold. After a set cooling time, the clamping unit opens the mold, and an ejector system (usually a series of pins) pushes the finished part out. The cycle then immediately repeats.
Key Molding Processes and Their Applications
While the core principle is similar, different types of molding machines are specialized for creating different kinds of products.
Injection Molding
This is the most common process for thermoplastics. It excels at producing complex, solid parts in very high volumes with incredible precision.
Think of everyday items like LEGO bricks, computer mouse casings, car dashboards, and medical syringes.
Blow Molding
Blow molding is used exclusively to create hollow parts. It works by extruding a hollow tube of plastic (a parison) and then inflating it with compressed air inside a mold, much like blowing up a balloon.
This process is responsible for products like beverage bottles, milk jugs, and plastic drums.
Compression Molding
Often used for thermoset plastics and rubber, which harden irreversibly when heated. A pre-measured amount of material is placed directly into a heated mold cavity, and the mold is closed, applying pressure to force the material to fill the space.
This method is ideal for creating strong, heat-resistant parts such as electrical outlets, gaskets, and automotive seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The power of molding is undeniable, but it comes with critical considerations that dictate its use. The primary trade-off is between the high initial investment and the extremely low cost per part at scale.
The Critical Role of the Mold
The mold (or die) is the heart of the operation. It is a highly engineered, precision-machined steel tool that defines the final product's shape, texture, and quality. A complex mold can cost tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars and represents the largest single investment in the process.
Speed vs. Quality
Molding machines are designed for speed, with some cycles taking only a few seconds. However, producing high-precision parts with tight tolerances may require longer cooling times or more complex mold designs, slowing the cycle down. The balance between production speed and part quality is a constant engineering consideration.
Material Constraints
A specific molding machine and process are designed for a narrow range of materials. An injection molding machine for thermoplastics cannot be used for liquid silicone rubber, and a compression press for thermosets cannot perform blow molding. The choice of material fundamentally dictates the choice of machine.
Matching the Process to Your Product Goal
Choosing the right molding process is entirely dependent on the final product you need to create.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, complex solid parts: Injection molding is the unparalleled industry standard for its precision and speed.
- If your primary focus is hollow items like bottles or large tanks: Blow molding for smaller containers or rotational molding for larger items are your best options.
- If your primary focus is strong, durable, heat-resistant components: Compression molding with thermoset plastics or elastomers is the ideal choice.
Ultimately, a molding machine serves as the bridge between a raw material and a functional, finished product at an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Molding Process | Primary Materials | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Thermoplastics | LEGO bricks, car dashboards, medical devices |
| Blow Molding | Thermoplastics | Beverage bottles, plastic containers |
| Compression Molding | Thermoset plastics, Rubber | Electrical components, gaskets, seals |
Ready to scale your production with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for material testing and process development related to molding. Whether you're in R&D or quality control, our expertise can help you optimize your molding processes for better efficiency and part quality. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right equipment for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is the application of injection moulding machine? Powering Mass Production for Complex Parts
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production



















