Critically, the rate of electron beam evaporation is not a single value but a highly controllable variable that represents one of its primary advantages. While specific rates depend entirely on the material being deposited and the power applied, the process is renowned for being significantly faster than many other physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques, making it ideal for high-throughput industrial applications.
The core takeaway is that electron beam evaporation achieves high deposition rates by using a focused, high-energy electron beam to directly and efficiently heat the source material. This rate is precisely controlled by adjusting the beam's power, allowing it to vaporize even materials with very high melting points.
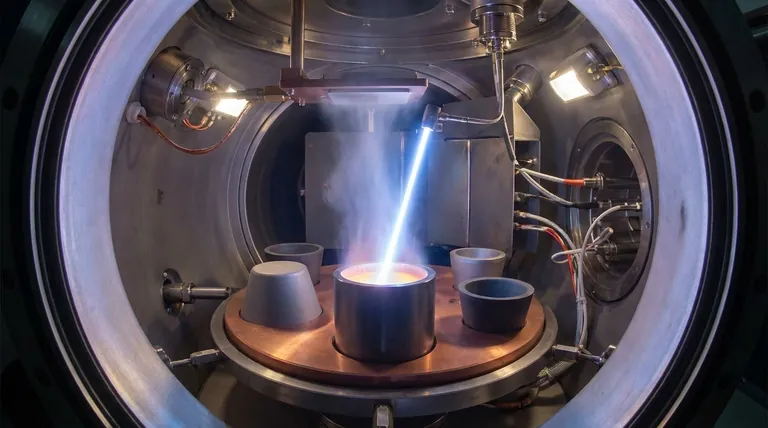

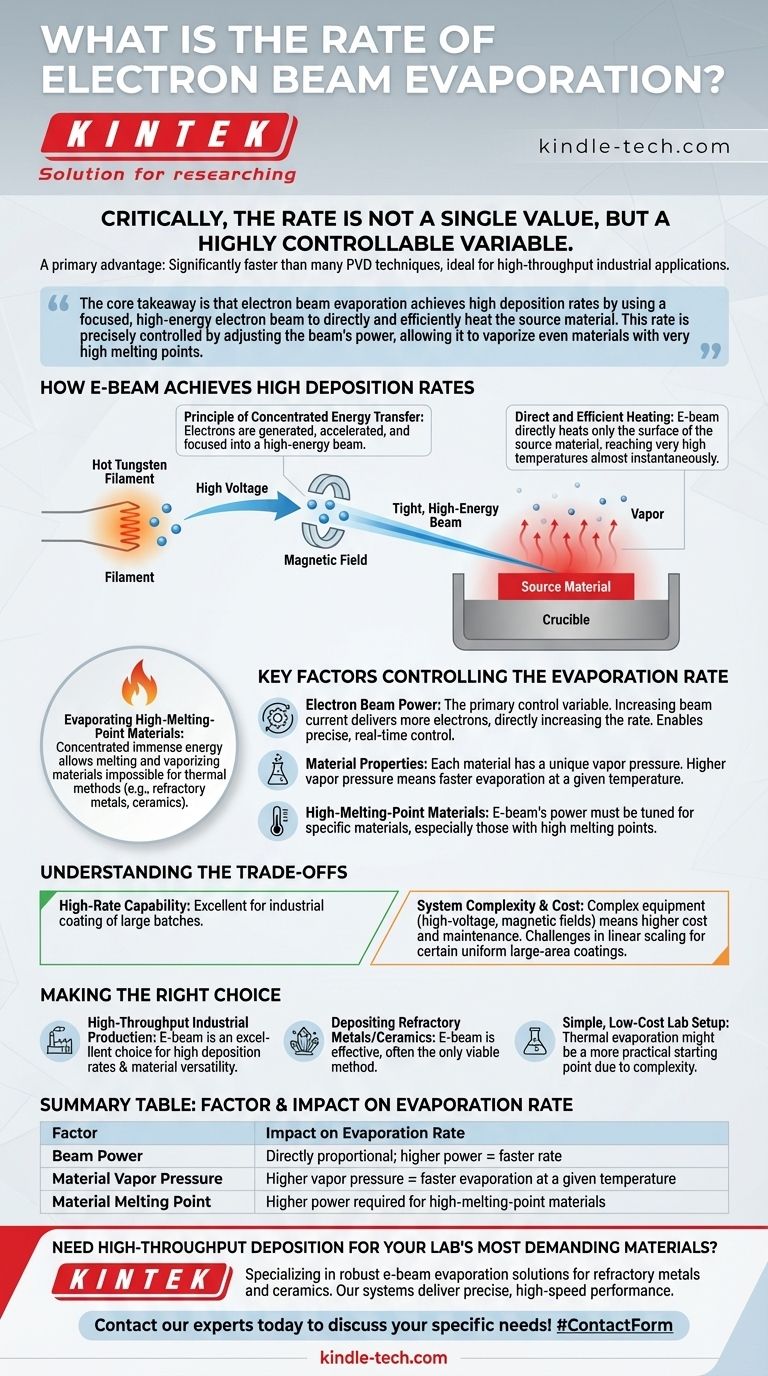
How E-Beam Evaporation Achieves High Deposition Rates
Electron beam (e-beam) evaporation is a PVD process that occurs in a high vacuum. Its ability to deposit films quickly and efficiently stems directly from its unique heating mechanism.
The Principle of Concentrated Energy Transfer
An e-beam system first generates electrons from a hot tungsten filament. A high voltage then accelerates these electrons, and a magnetic field focuses them into a tight, high-energy beam.
This beam is directed onto the source material held in a crucible, transferring its kinetic energy as intense, localized heat.
Direct and Efficient Heating
Unlike thermal evaporation, which heats the entire crucible and its contents, an e-beam directly heats only the surface of the source material. This direct energy transfer is extremely efficient.
This efficiency means less power is wasted and very high temperatures can be reached almost instantaneously, causing the material to rapidly evaporate or sublimate.
Evaporating High-Melting-Point Materials
The ability to concentrate immense energy into a small spot allows e-beam evaporation to melt and vaporize materials that are impossible to process with conventional thermal methods.
This makes it the preferred method for depositing refractory metals and ceramic coatings used in aerospace, semiconductor, and optical industries.
Key Factors Controlling the Evaporation Rate
The deposition rate is not a fixed property of the equipment but a parameter that is actively managed by controlling several key factors.
Electron Beam Power
The primary control variable is the power of the electron beam, which is a function of the acceleration voltage and the beam current.
Increasing the beam current delivers more electrons to the target, transferring more energy and directly increasing the evaporation rate. This allows for precise, real-time control over the film's growth.
Material Properties
Each material has a unique vapor pressure, which describes its tendency to transition from a solid or liquid to a gas at a given temperature.
Materials with higher vapor pressures will evaporate more quickly at the same temperature. The e-beam's power must be tuned to the specific properties of the source material to achieve a stable and desired deposition rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the high-rate capability of e-beam evaporation comes with specific operational considerations.
System Complexity and Cost
The equipment required to generate, accelerate, and precisely control an electron beam is complex. This includes high-voltage power supplies and magnetic field controls.
Consequently, e-beam systems are typically more expensive and require more maintenance than simpler deposition techniques.
Challenges in Linear Scaling
While excellent for industrial coating of large batches, the physics of the process can present challenges for certain types of linear or uniform large-area coating without sophisticated substrate manipulation.
This can make it less suitable for some specific lab applications compared to its widespread use in industrial processes like ophthalmic coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a deposition method requires aligning the technology's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: E-beam evaporation is an excellent choice due to its high deposition rates and material versatility.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or ceramics: E-beam is one of the most effective and often only viable methods for materials with high melting points.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost lab setup: The complexity and cost may be prohibitive, making a technique like thermal evaporation a more practical starting point.
Ultimately, understanding that the deposition rate is a powerful, controllable variable is the key to leveraging e-beam evaporation effectively.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Evaporation Rate |
|---|---|
| Beam Power | Directly proportional; higher power = faster rate |
| Material Vapor Pressure | Higher vapor pressure = faster evaporation at a given temperature |
| Material Melting Point | Higher power required for high-melting-point materials (refractory metals/ceramics) |
Need high-throughput deposition for your lab's most demanding materials?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust e-beam evaporation solutions perfect for depositing refractory metals and ceramics. Our systems are designed to deliver the precise, high-speed performance required for industrial and research applications.
Let us help you enhance your coating process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the container that holds the metal source material called in e-beam evaporation? Ensure Purity and Quality in Your Thin-Film Deposition
- Why are Boron Nitride Tubes selected as reaction vessels for Na3SbS4? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Synthesis
- How source material is evaporated during deposition? A Guide to Resistive vs. E-Beam Methods
- What is the principle of electron beam evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between thermal and electron beam evaporation? Unlock the Right Thin Film Deposition Method



















