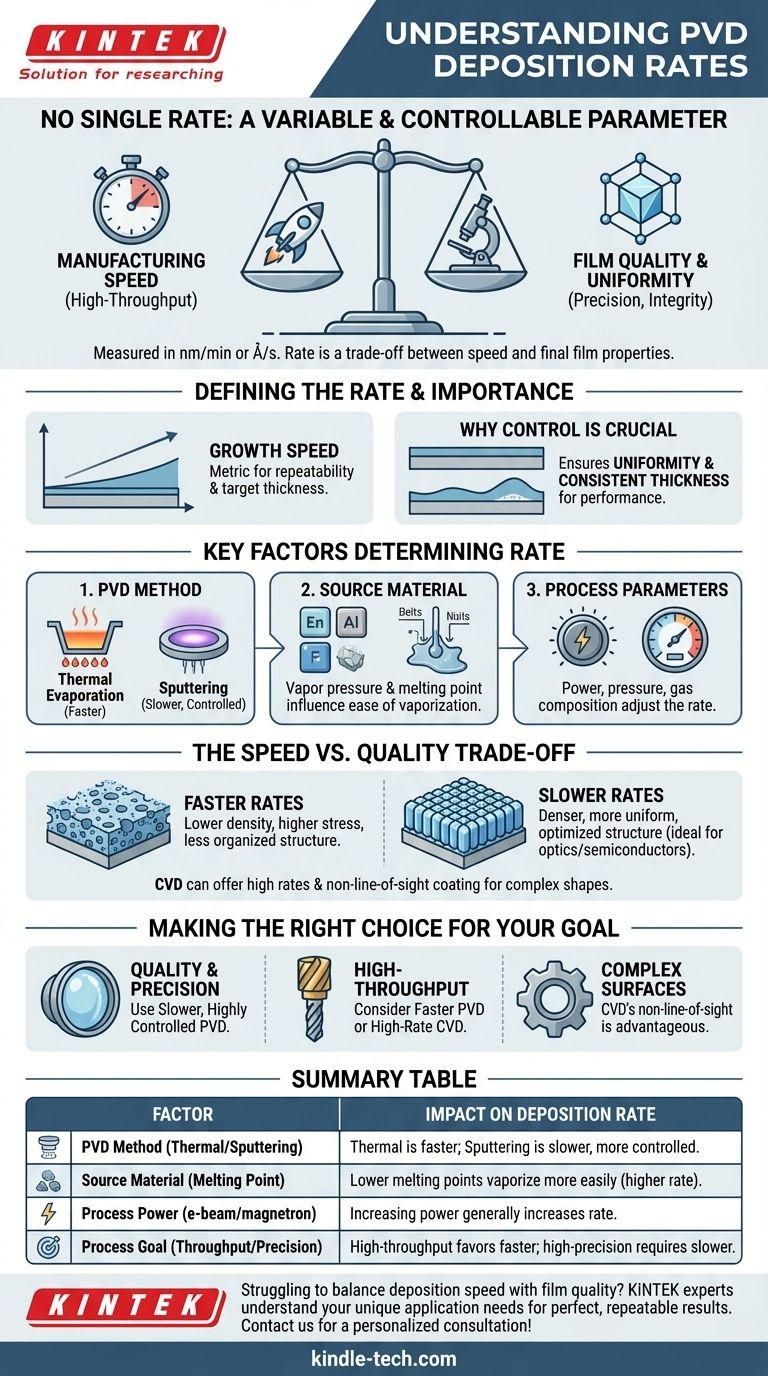
In short, there is no single rate for physical vapor deposition (PVD). The deposition rate is a highly variable and controllable parameter, defined as the speed at which a thin film is grown on a surface. It is typically measured in units of thickness per time, such as nanometers per minute (nm/min) or angstroms per second (Å/s), and is tailored to the specific application and desired film quality.
The core concept to understand is that the PVD rate is not a fixed number but a critical process variable. It represents a fundamental trade-off between manufacturing speed and the final quality, uniformity, and structural integrity of the deposited film.

Defining the PVD Rate
The deposition rate is one of the most important parameters in any PVD process. How it is defined and controlled directly impacts the outcome of the coating.
A Measure of Growth Speed
Deposition rate is a measurement of how quickly the thin film is produced on the substrate. This simple metric is vital for process repeatability and for achieving the target thickness of the final coating.
Why Control is Crucial
The rate of deposition must be carefully controlled. This ensures the uniformity and consistent thickness of the film across the entire substrate, which are critical factors determining the film's performance and overall quality.
Key Factors That Determine Deposition Rate
The actual rate you can achieve in a PVD system is not arbitrary. It is a direct result of the specific technique used, the material being deposited, and the precise operating parameters you set.
The PVD Method
Different PVD techniques have inherently different rate capabilities. For instance, thermal evaporation can often achieve very high deposition rates, making it suitable for applications like metallizing reflectors.
In contrast, sputtering, where atoms are ejected from a target by ion bombardment, is often a slower but more controlled and energetic process, yielding denser films.
The Source Material
Some materials simply vaporize or sputter more easily than others. A material's melting point, vapor pressure, and atomic mass all play a role in how readily it can be turned into a vapor and deposited, directly influencing the maximum achievable rate.
Process Parameters
Engineers use several levers to fine-tune the deposition rate. Increasing the power to an electron-beam source or a sputtering magnetron will typically increase the rate. Likewise, adjusting vacuum pressure and gas composition can significantly alter the deposition speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition rate is never just about going as fast as possible. The decision involves balancing speed against the required properties of the final film.
Speed vs. Quality
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Higher deposition rates can sometimes lead to films with lower density, higher internal stress, or a less organized crystal structure.
Slower deposition rates give the deposited atoms more time and energy to find optimal positions on the substrate surface. This often results in denser, more uniform, and higher-quality films, which is critical for optical and semiconductor applications.
PVD vs. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The references note that Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) can achieve comparatively high deposition rates in certain scenarios.
CVD relies on chemical reactions on the substrate surface and is not a line-of-sight process. This allows it to coat complex shapes evenly, which can be a significant advantage over the directional nature of PVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate deposition rate requires understanding your ultimate priority, whether it's raw production speed, film perfection, or coating complexity.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality and precision: You will likely need a slower, highly controlled PVD process to achieve the required uniformity for optical or electronic layers.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput protective coatings: A faster PVD method or a high-rate CVD process might be more suitable for applications like coating tools or aerospace parts.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces: The non-line-of-sight advantage of CVD may be more important than the absolute deposition rate of any single process.
Ultimately, controlling the deposition rate is about deliberately balancing manufacturing efficiency with the specific film characteristics your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Deposition Rate |
|---|---|
| PVD Method | Thermal Evaporation is typically faster; Sputtering is slower but more controlled. |
| Source Material | Materials with lower melting points/vapor pressure vaporize more easily (higher rate). |
| Process Power | Increasing power (e-beam, magnetron) generally increases the rate. |
| Process Goal | High-throughput coatings favor faster rates; high-precision films require slower rates. |
Struggling to balance deposition speed with film quality for your project? The experts at KINTEK understand that the 'right' PVD rate is unique to your application, whether you're developing semiconductor layers, precision optics, or durable protective coatings. We specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables to achieve perfect, repeatable results. Let's optimize your process—contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















