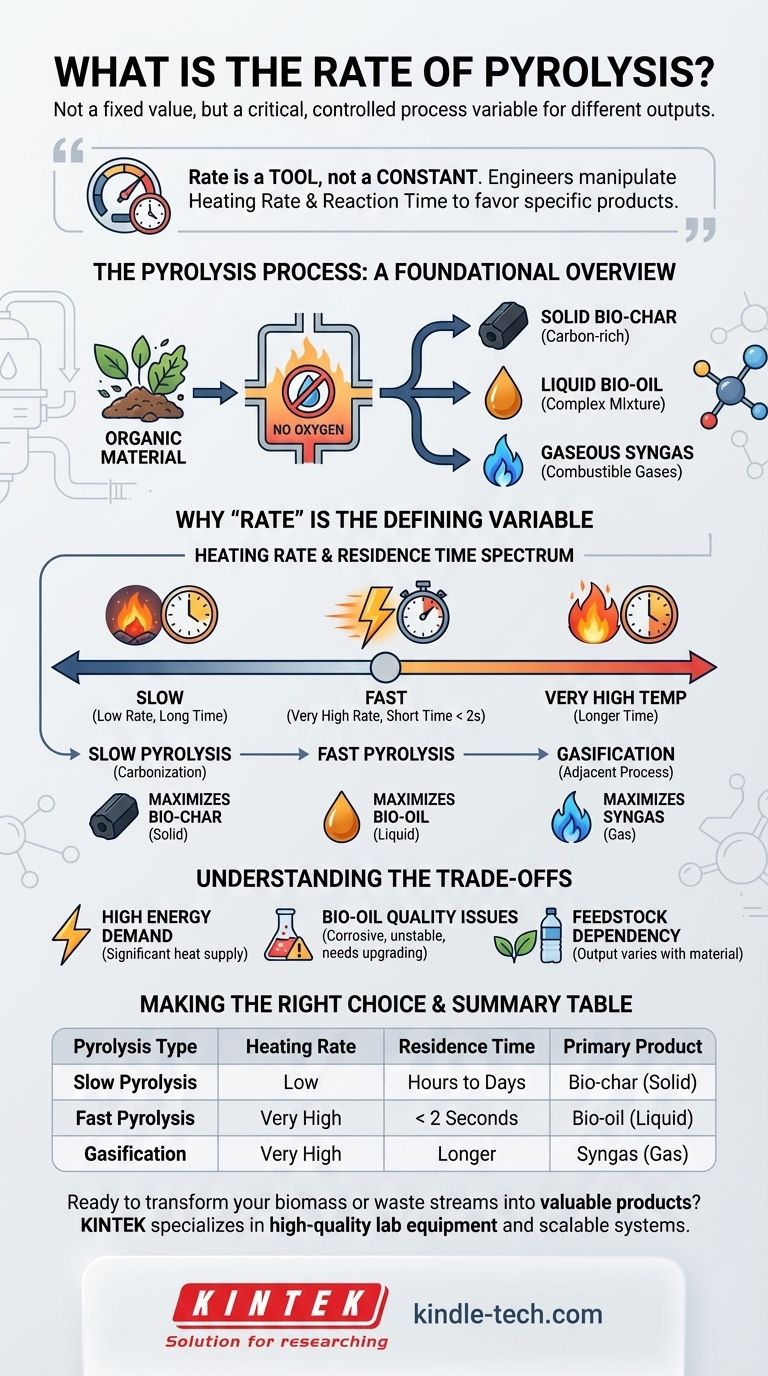
The rate of pyrolysis is not a single, fixed value. Instead, it is a critical process variable that is deliberately controlled to produce different outputs. The "rate" is determined by the heating rate and temperature, which defines the type of pyrolysis being performed—ranging from slow processes that take hours to fast processes completed in seconds.
The central concept to grasp is that the "rate" of pyrolysis is a tool, not a constant. Engineers manipulate the heating rate and reaction time to intentionally favor the production of either solid bio-char, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas, depending on the desired outcome.
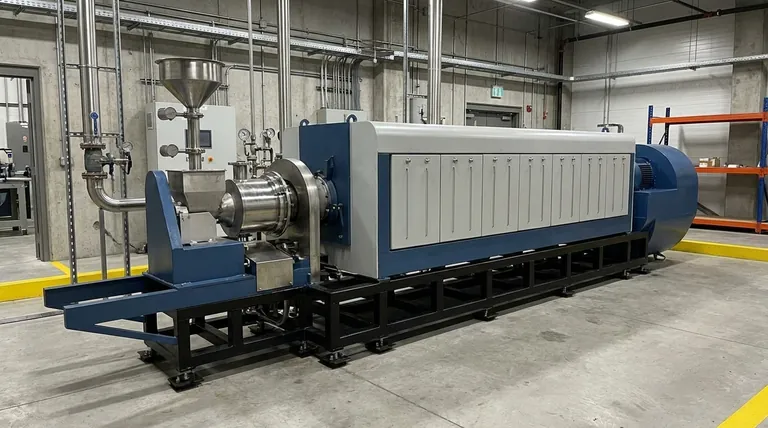

The Pyrolysis Process: A Foundational Overview
What is Thermochemical Decomposition?
Pyrolysis is the thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
By preventing combustion, this process breaks down complex materials like biomass, plastics, or tires into simpler, more valuable products.
The Three Primary Outputs
The process fractionates the feedstock into three distinct products: a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
- Bio-char (or Coke): A solid, carbon-rich material.
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A complex liquid mixture of oxygenated organic compounds.
- Syngas (or Pyrolysis Gas): A mixture of non-condensable, combustible gases.
The proportion of these three outputs is a direct result of the process conditions, especially the rate.
Why "Rate" is the Defining Variable
The speed at which the material is heated (heating rate) and the time it spends at peak temperature (residence time) are the most important factors. These two variables define the different modes of pyrolysis.
Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis uses very high heating rates and short residence times (typically less than two seconds) to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil.
The goal is to rapidly break down the material and immediately quench the vapors to prevent them from breaking down further into gases. The reference to an ablative reactor operating at 450-600°C is an example of a fast pyrolysis system.
Slow Pyrolysis (Carbonization)
Slow pyrolysis, also known as carbonization, uses low heating rates and very long residence times (hours or even days).
This slow "cooking" process is designed to maximize the yield of the solid product, bio-char. The slow decomposition allows carbon atoms to rearrange into stable, solid structures.
Gasification (An Adjacent Process)
While distinct from pyrolysis, gasification operates on a similar principle but at much higher temperatures.
The extreme heat and longer residence times are designed to break down almost all the material, including the char and oil, into syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High Energy Demand
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. It requires a significant and consistent heat supply to reach and maintain the necessary operating temperatures, which can impact its overall energy balance and economic viability.
Bio-oil Quality Issues
While bio-oil can be used as a fuel, it is not a direct replacement for petroleum. As the references note, its high oxygen content makes it corrosive, thermally unstable, and immiscible with fossil fuels. It often requires significant upgrading to be used as a transport fuel.
Feedstock Dependency
The exact composition and yield of the products are highly dependent on the specific organic material being processed. The results from wood biomass will be very different from those from waste plastic or tires.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of pyrolysis you choose depends entirely on the product you want to create.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (bio-oil): You need a fast pyrolysis system with high heating rates and short residence times.
- If your primary focus is maximizing solid carbon (bio-char): You need a slow pyrolysis system with low heating rates and long residence times.
- If your primary focus is generating combustible gas (syngas): You need to operate at very high temperatures, which shifts the process toward gasification.
By understanding these principles, you can select the right thermochemical process to transform a specific waste stream into a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Heating Rate | Residence Time | Primary Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Low | Hours to Days | Bio-char (Solid) |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Very High | < 2 Seconds | Bio-oil (Liquid) |
| Gasification | Very High | Longer | Syngas (Gas) |
Ready to transform your biomass or waste streams into valuable products?
The right pyrolysis equipment is critical to achieving your target yields of bio-char, bio-oil, or syngas. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and scalable systems for thermochemical processes. Our experts will help you select the perfect solution to optimize your process efficiency and output.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















