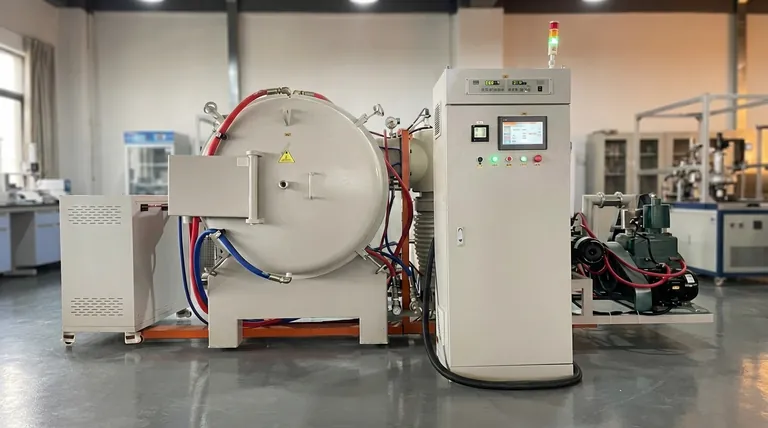
At its core, the heat treatment process consists of three distinct, sequential stages designed to manipulate a metal's internal structure. The universally recognized sequence is heating the material to a specific temperature, soaking it at that temperature for a set duration, and finally, cooling it back to room temperature at a controlled rate.
The entire purpose of this three-stage sequence—heating, soaking, and cooling—is to deliberately alter the microscopic crystal structure of a metal to achieve specific, predictable mechanical properties like hardness, toughness, or ductility.
The Three Foundational Stages of Heat Treatment
Each stage in the heat treatment process serves a unique and critical function. The success of the final outcome depends on precise control over the variables in each of the three phases.
Stage 1: Heating - Setting the Stage for Change
The process begins by uniformly heating the metal or alloy. The primary goal is to bring the material's internal structure to a specific transformation temperature.
For many common steels, this is known as the austenitizing temperature, where the crystal structure changes into a phase called austenite, which is capable of dissolving carbon. The rate of heating is also a critical factor, as heating too quickly can cause thermal stress and cracking, especially in complex shapes.
Stage 2: Soaking - Ensuring Complete Transformation
Once the target temperature is reached, the material is held there for a predetermined period. This stage is known as soaking.
The purpose of soaking is to ensure that the desired structural transformation occurs uniformly throughout the entire volume of the part, from the surface to the core. Soaking time depends heavily on the alloy type, the cross-sectional thickness of the component, and the initial condition of the material.
Stage 3: Cooling - Locking in the Final Properties
The final and often most critical stage is cooling. The rate at which the material is cooled from the soaking temperature directly determines the final microstructure and, consequently, its mechanical properties.
This controlled cooling "locks in" a specific crystal structure. The method and speed of cooling are chosen deliberately to produce the desired balance of hardness, strength, and ductility.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Cooling
The cooling stage is not a one-size-fits-all process. The choice of cooling method involves significant trade-offs that dictate the metal's final performance characteristics.
Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
Quenching involves cooling the material very rapidly by immersing it in a medium like water, oil, or a polymer solution.
This rapid cooling traps the transformed structure (e.g., creating martensite in steel), resulting in extremely high hardness and strength. However, the major trade-off is a significant increase in brittleness and high internal stresses, which can make the part susceptible to cracking.
Slower Cooling (Normalizing or Annealing)
Slower cooling methods, such as allowing the part to cool in still air (normalizing) or cooling it very slowly inside a furnace (annealing), produce different results.
These methods result in softer, more ductile microstructures. The benefit is significantly reduced internal stress and increased toughness, but the trade-off is lower hardness and tensile strength compared to a quenched part.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your desired outcome determines how you manage the variables within this three-stage process, particularly the cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness and wear resistance: You will need a very rapid cooling rate, achieved through quenching.
- If your primary focus is a balance of good strength and toughness: A more moderate cooling rate, such as cooling in air (normalizing), is the appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing ductility and machinability: You will require a very slow, controlled cooling rate, typically achieved through furnace cooling (annealing).
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about understanding how to manipulate this fundamental sequence to produce a material perfectly suited for its intended application.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Raise to a specific temperature | Achieve uniform structural transformation |
| 2. Soaking | Hold at temperature | Ensure complete, uniform change throughout the part |
| 3. Cooling | Cool at a controlled rate | Lock in the final microstructure and properties |
Ready to achieve precise material properties in your lab? The right equipment is crucial for controlling each stage of the heat treatment sequence. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and quenching systems that deliver the exact heating, soaking, and cooling rates you need for consistent, repeatable results. Whether your goal is maximum hardness, improved toughness, or enhanced ductility, our solutions are designed for your success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific heat treatment requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- How long does it take to do a heat treatment? A Full Day for a 100% Bed Bug Kill Rate
- Does hardening increase tensile strength? Boost Material Strength for Demanding Applications
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing



















